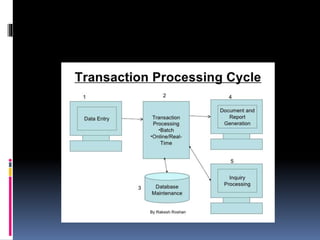
A transaction processing system (TPS) collects, stores, modifies, and retrieves data about business transactions. It must pass the ACID test, ensuring atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability of transactions. There are two types - batch processing, where data is collected and processed periodically, and real-time processing, where data is processed immediately. The transaction processing cycle involves data entry, processing transactions, maintaining databases, generating documents and reports, and allowing for inquiries. The overall purpose is to keep records of the organization, process transactions that affect those records, and produce reports.