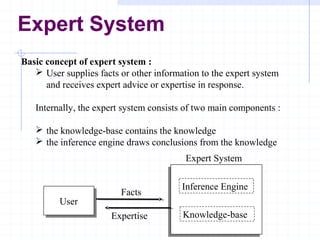
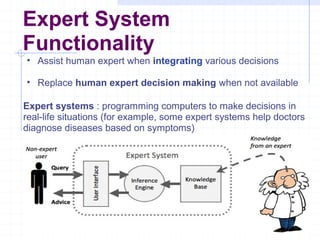
The document discusses expert systems, which are intelligent computer programs that use knowledge and inference procedures to solve problems that require significant human expertise. It describes how expert systems consist of a knowledge base containing knowledge and an inference engine that draws conclusions. It provides examples of applications like medical diagnosis and mining site selection. It outlines the key components of an expert system and discusses their benefits in replacing human experts as well as limitations like limited domains and high development costs.