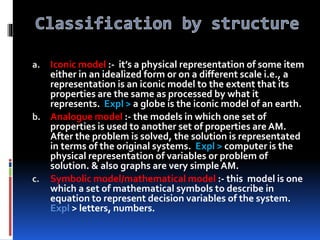
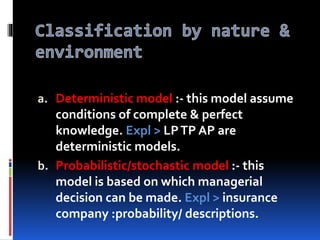
Operations research is a scientific approach to problem solving and decision making that is useful for managing organizations. It has its origins in World War II and is now widely used in business and industry. Some key areas where operations research models are applied include forecasting, production scheduling, inventory control, and transportation. Models are an essential part of operations research and can take various forms like physical, mathematical, or conceptual representations of real-world problems. Models are classified in different ways such as by their structure, purpose, solution method, or whether they consider deterministic or probabilistic systems. Operations research techniques help solve complex business problems through mathematical analysis and support improved organizational performance.