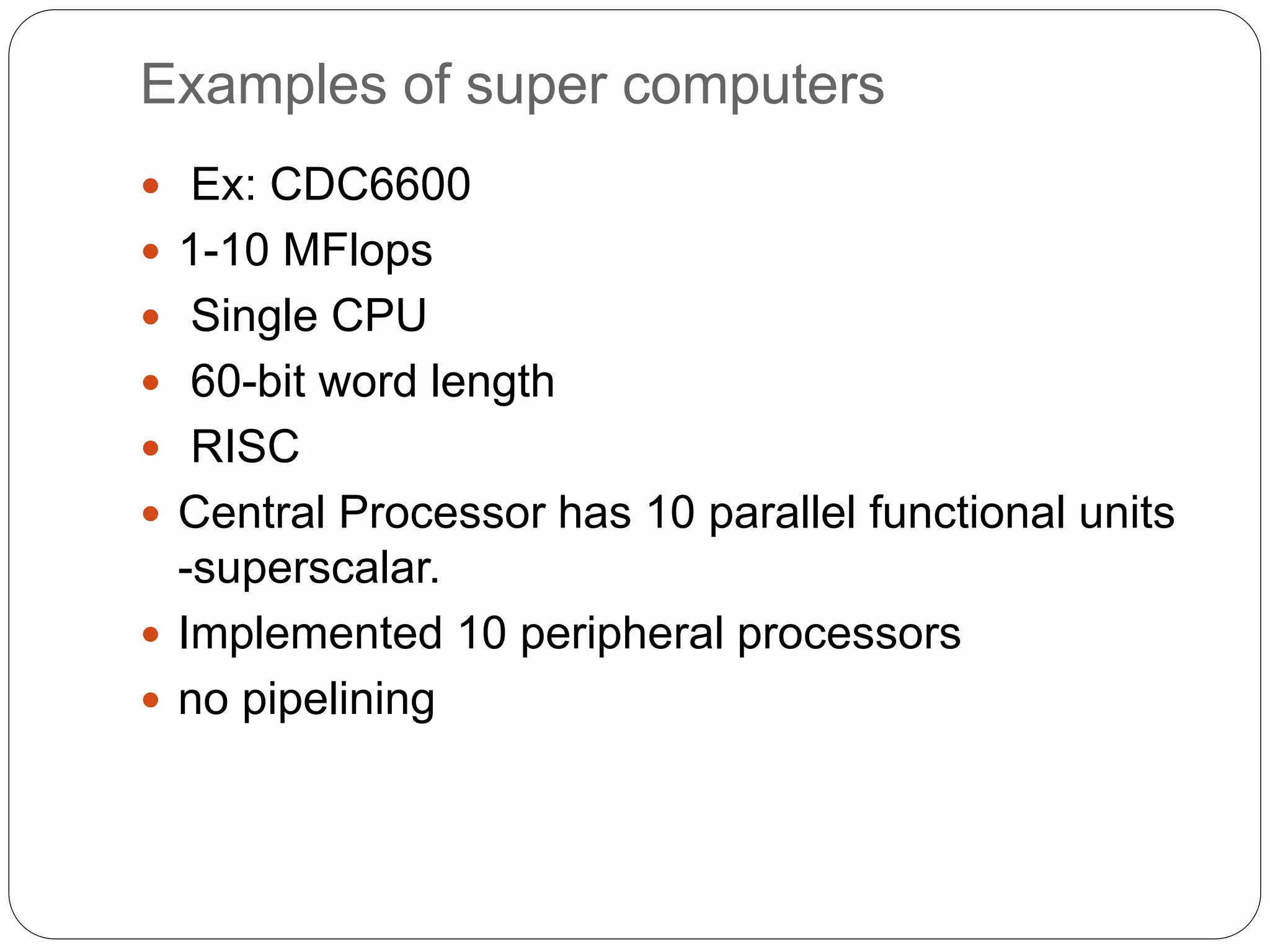
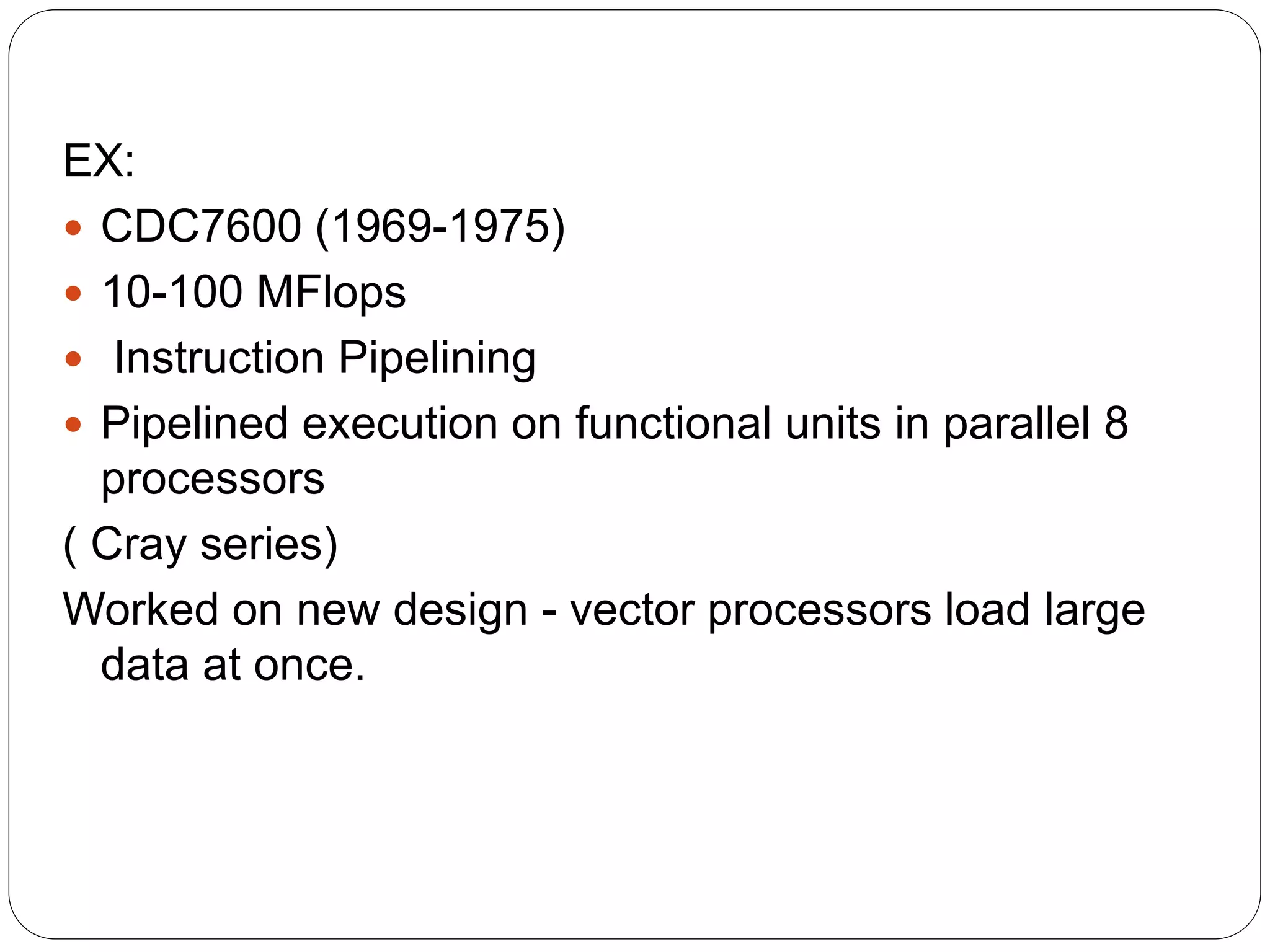
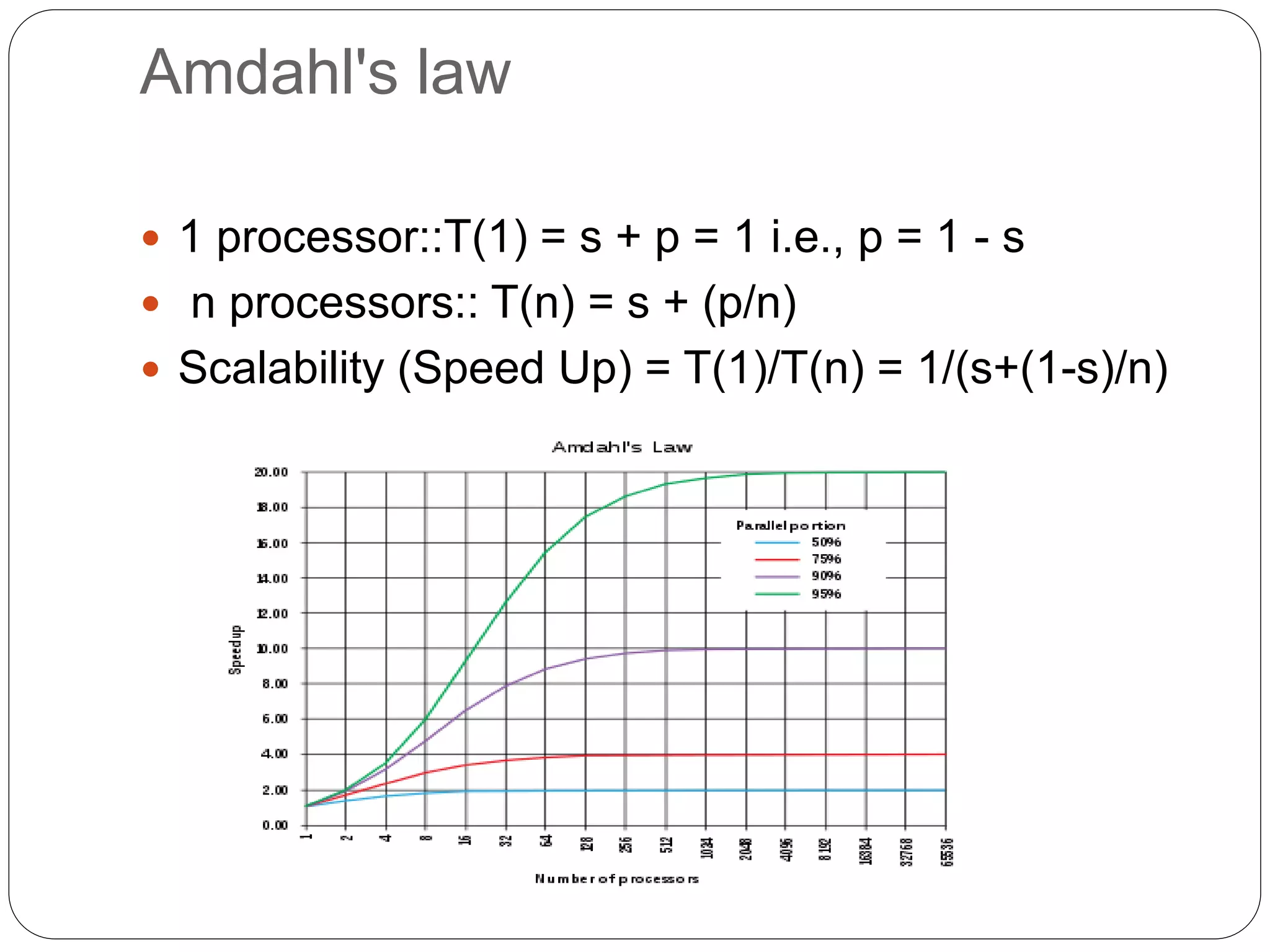
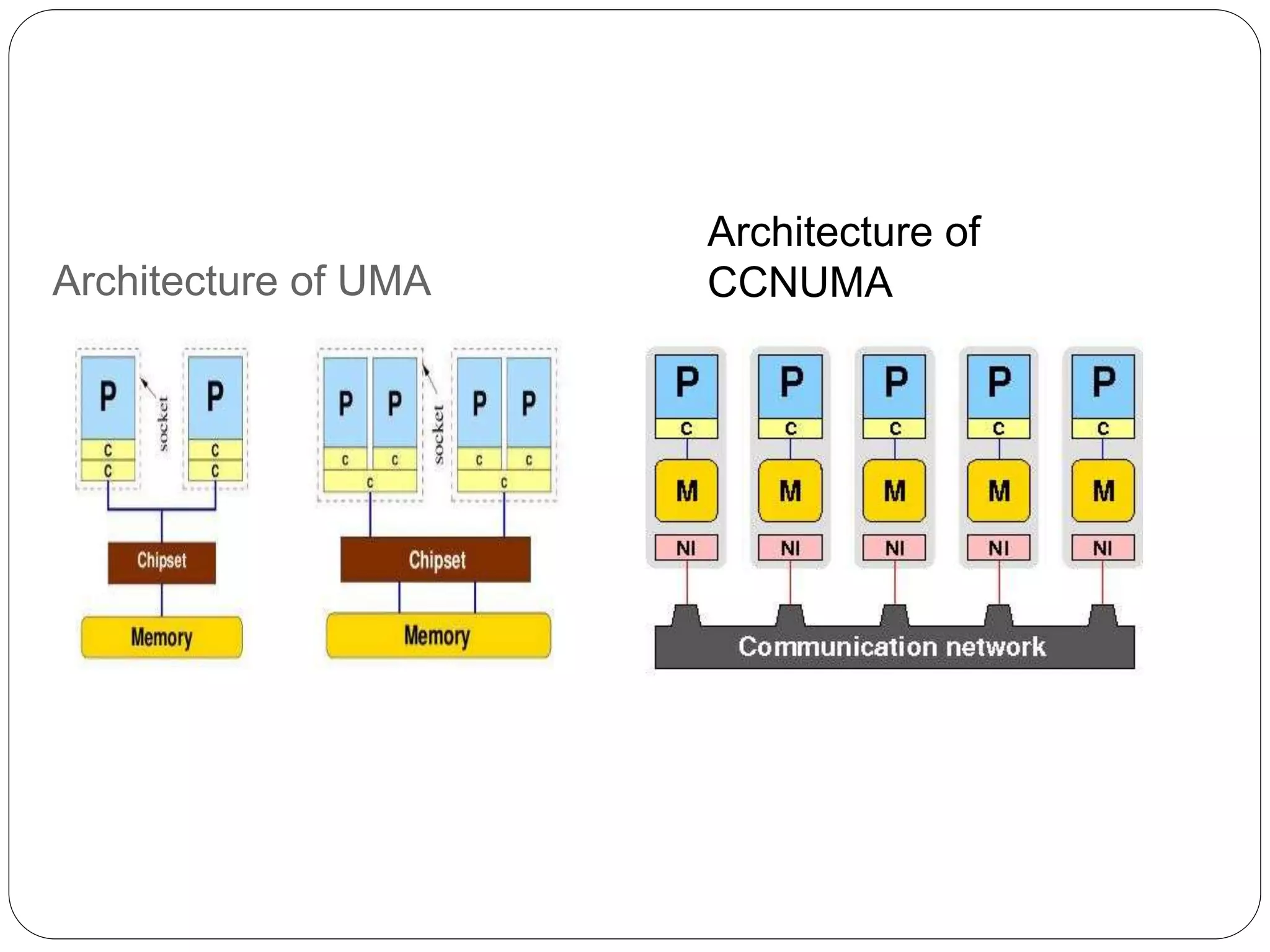
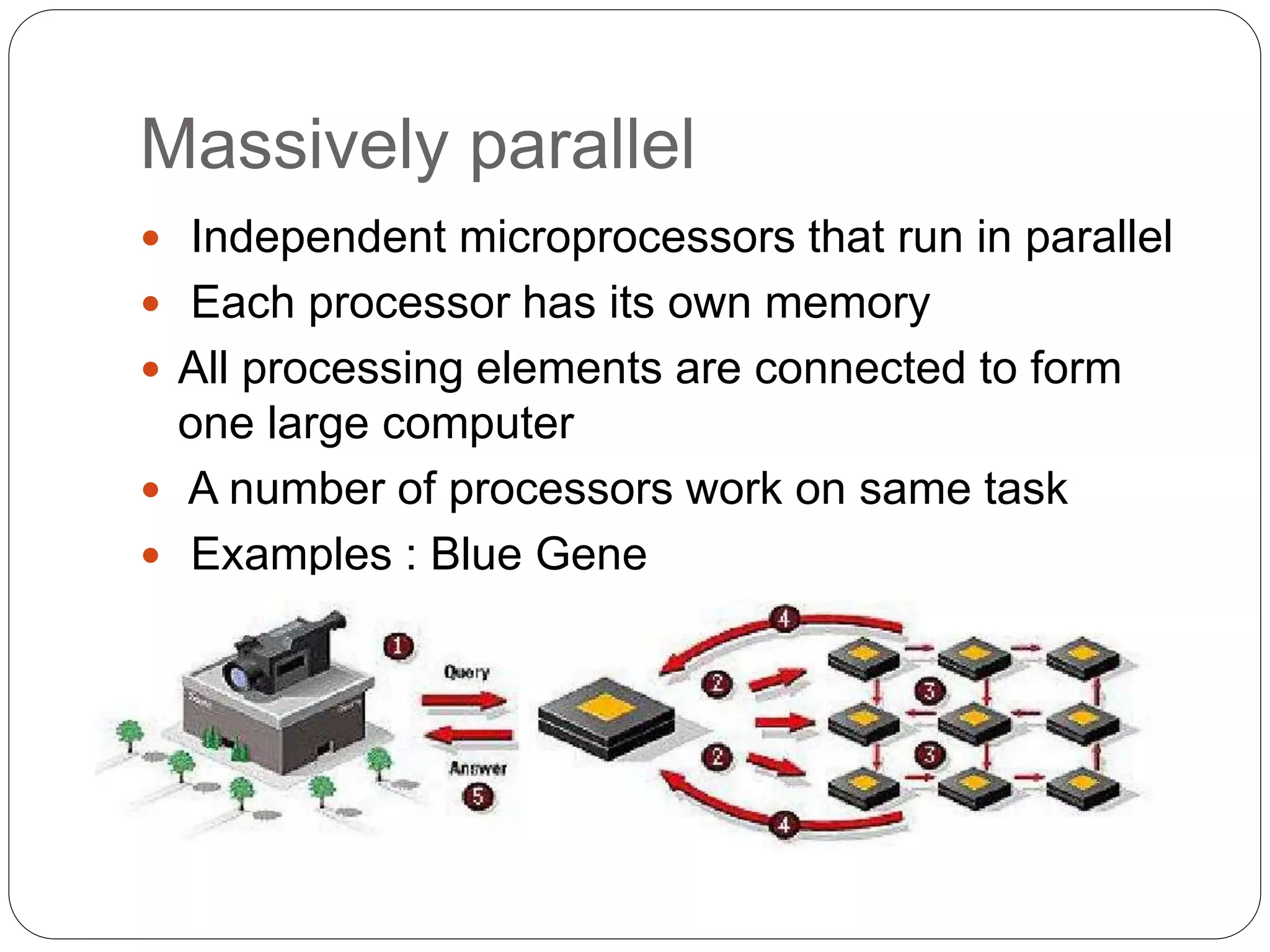
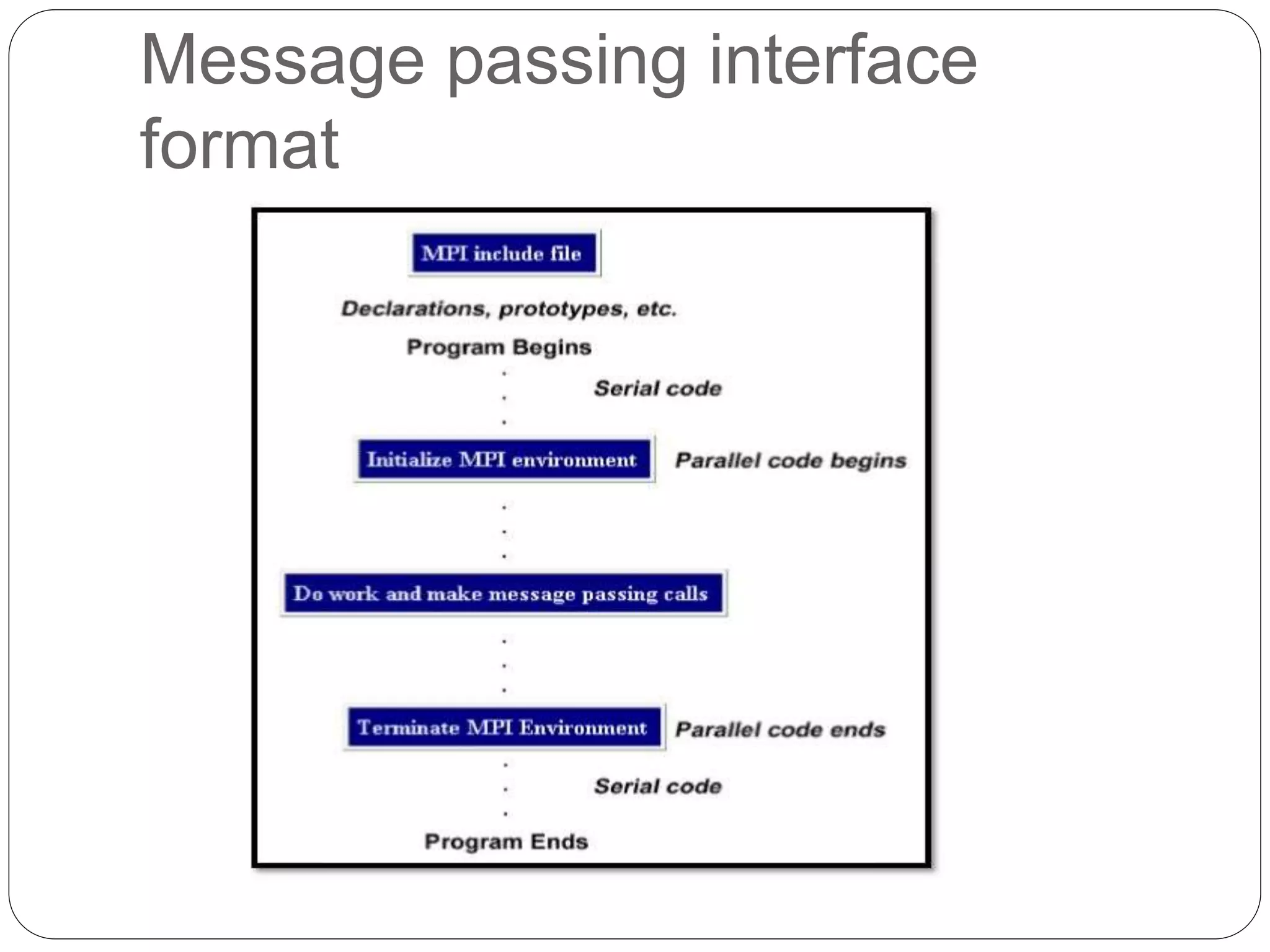
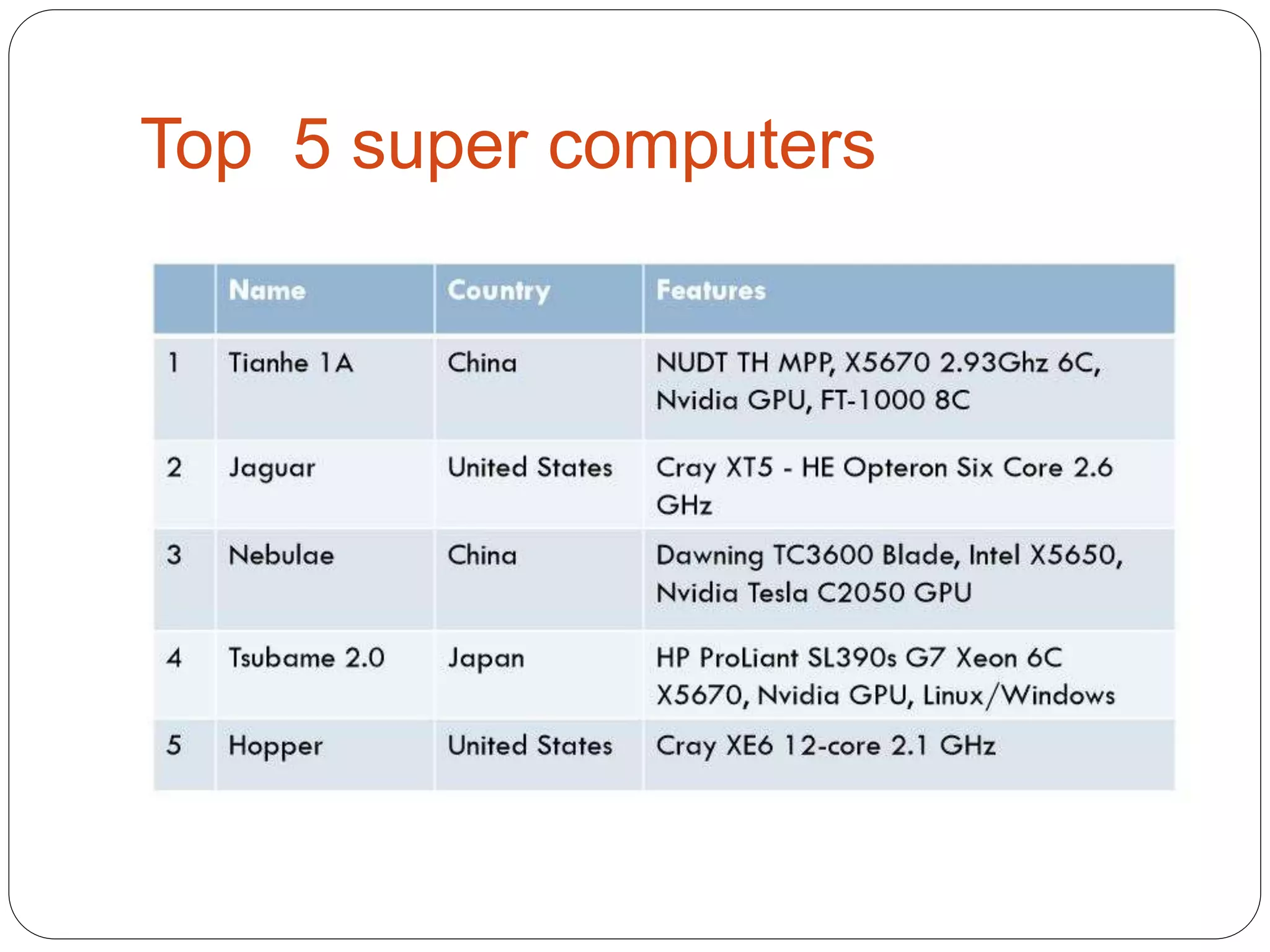
Supercomputers are computers with a high level of computational capacity compared to general purpose computers. They are used for highly calculation intensive tasks like weather forecasting, nuclear weapon simulations, and data analysis. The history of supercomputing dates back to the 1960s. Modern supercomputers use parallel processing techniques like distributed and shared memory architectures to achieve very high performance measured in floating-point operations per second. Common supercomputer architectures include UMA, ccNUMA, massively parallel processing, and clusters.