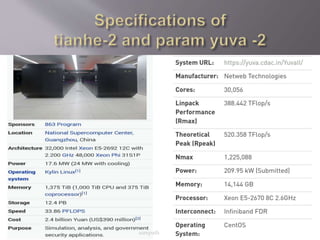
The document provides an overview of supercomputers, highlighting their capabilities to perform complex calculations and process trillions of operations per second, typically using Linux or Unix operating systems. It discusses the measurement of speed in flops, various types of supercomputers, their applications in fields like climate forecasting and scientific simulations, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Notably, it mentions the world's fastest supercomputer, Tianhe-2, and India's fastest, Param Yuva-II.