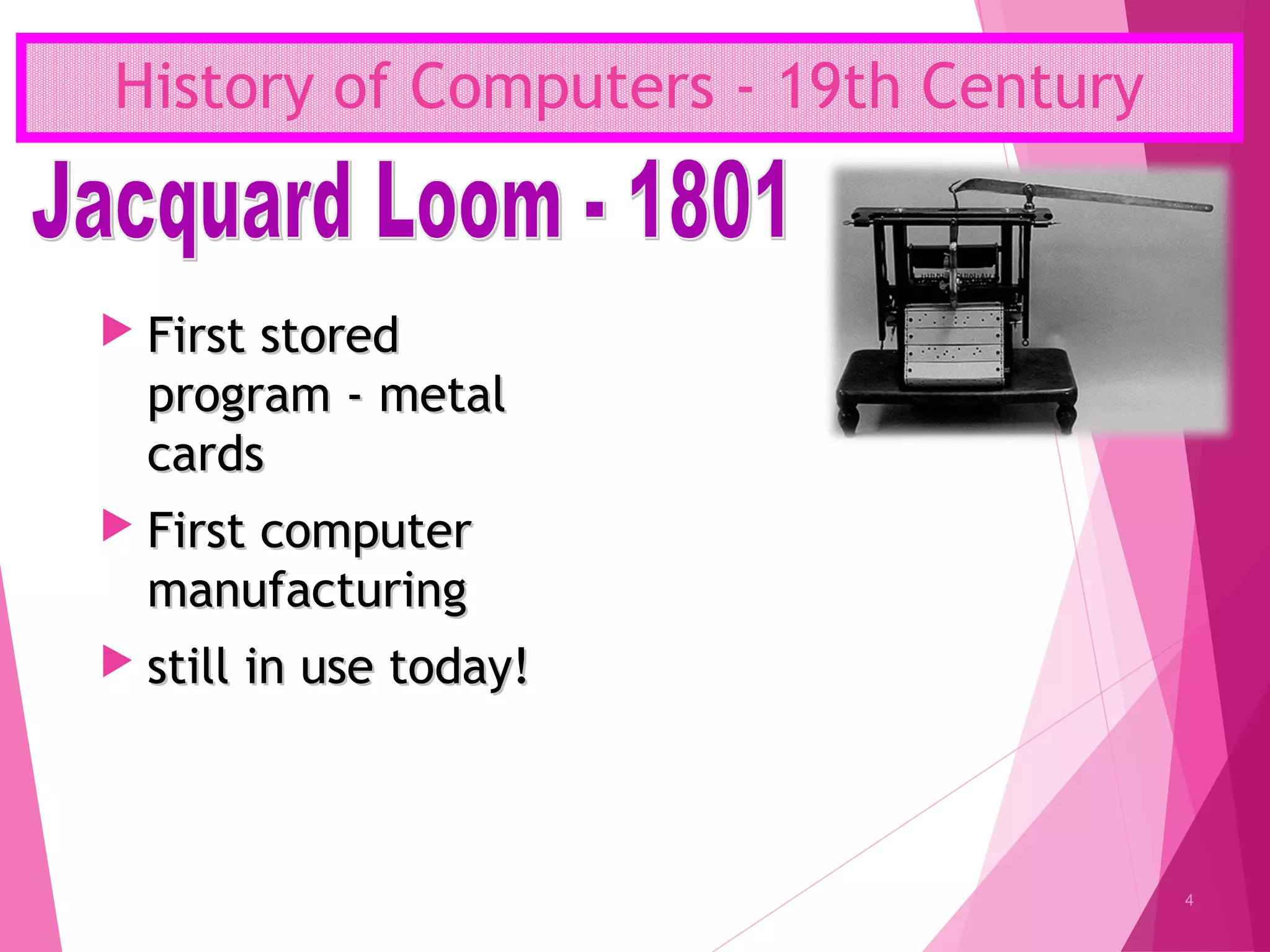
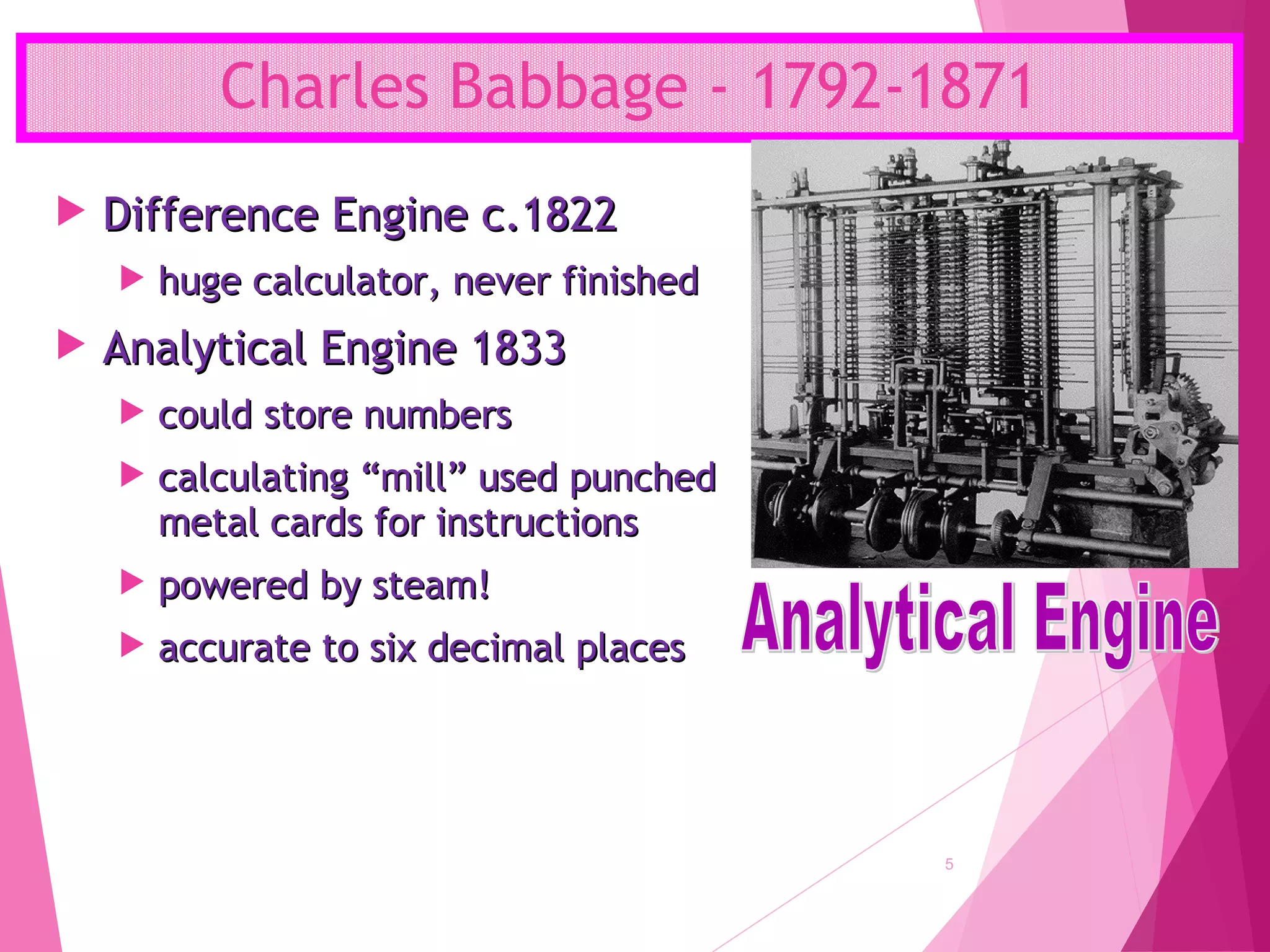
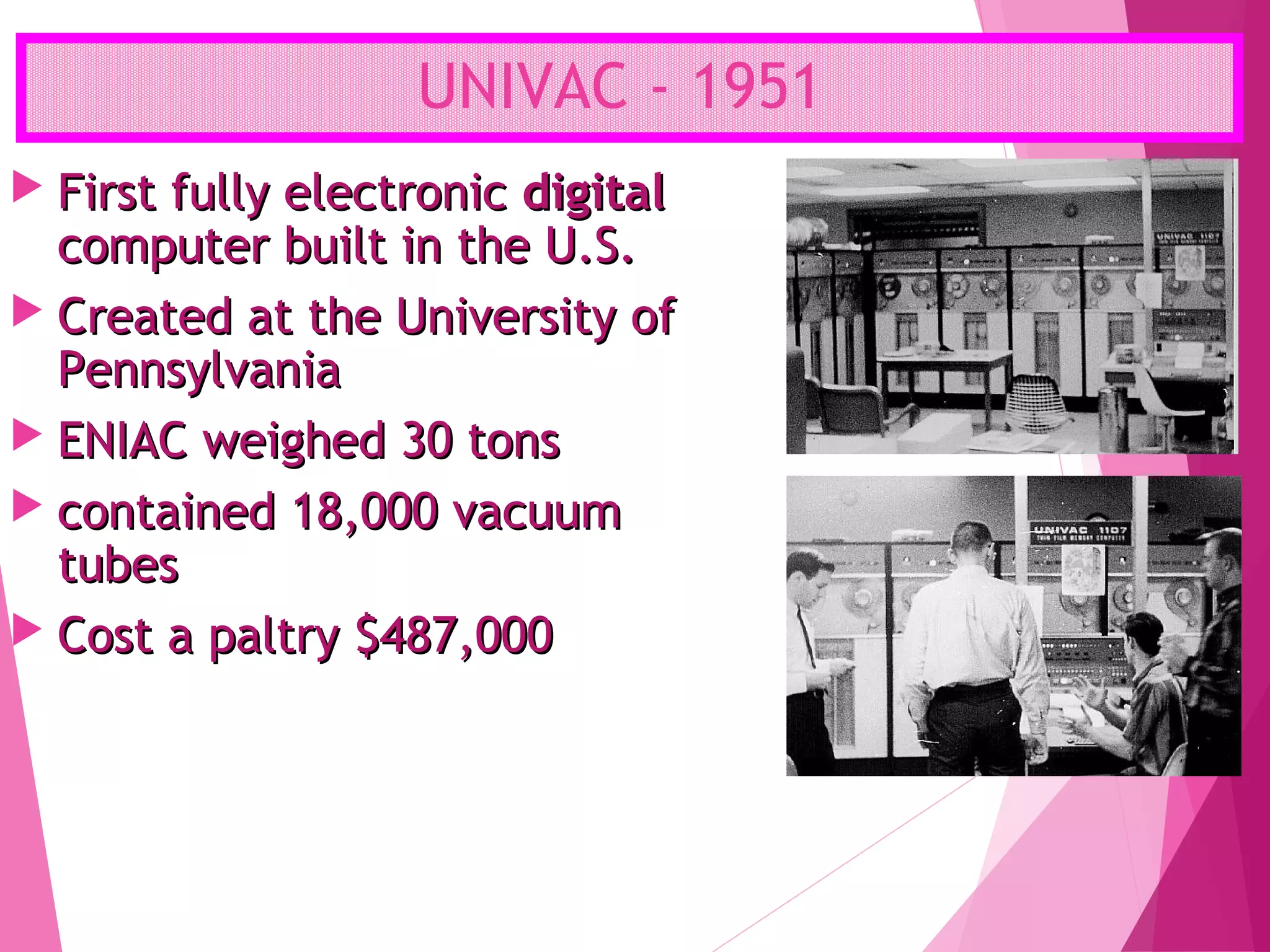
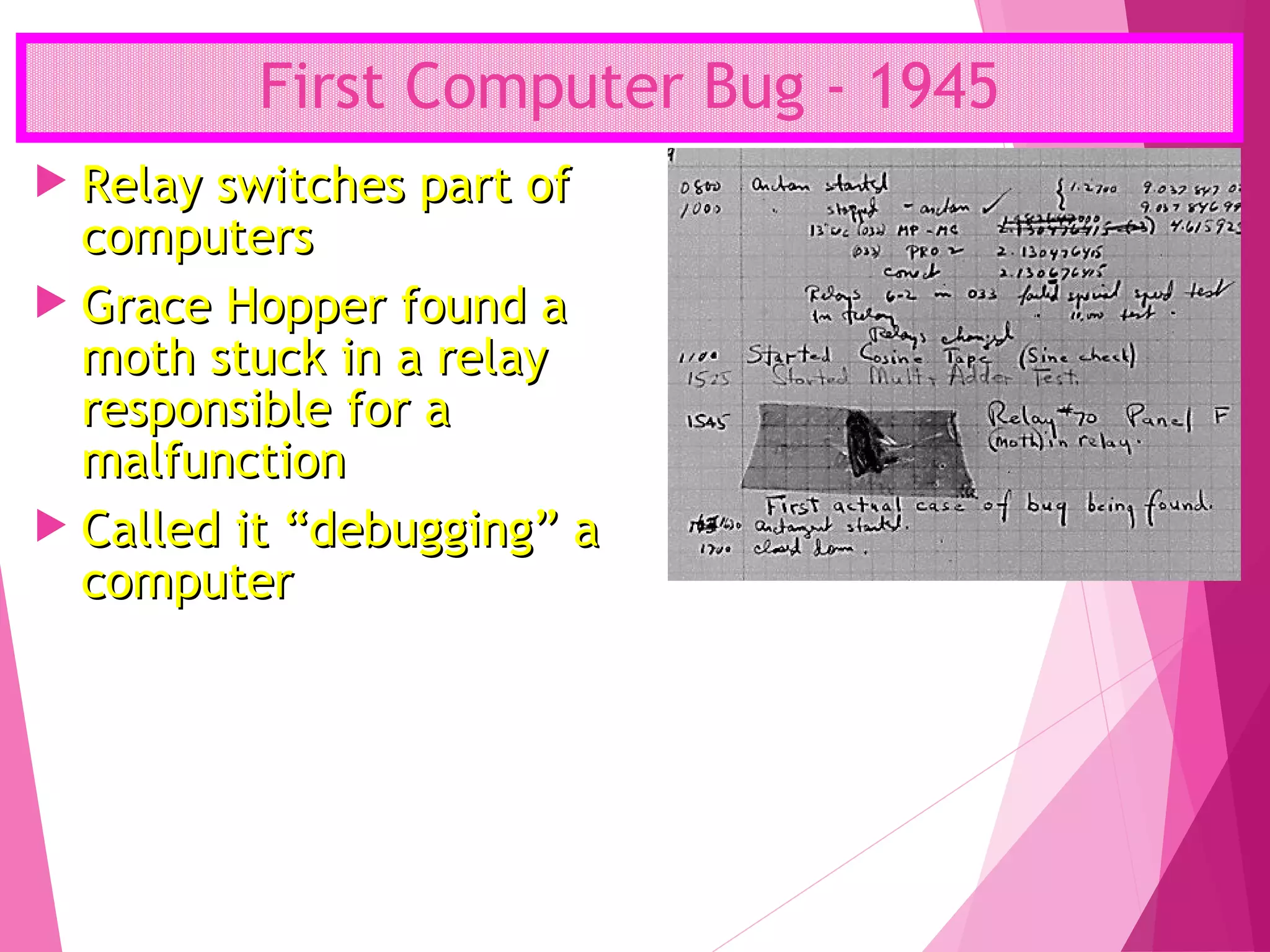
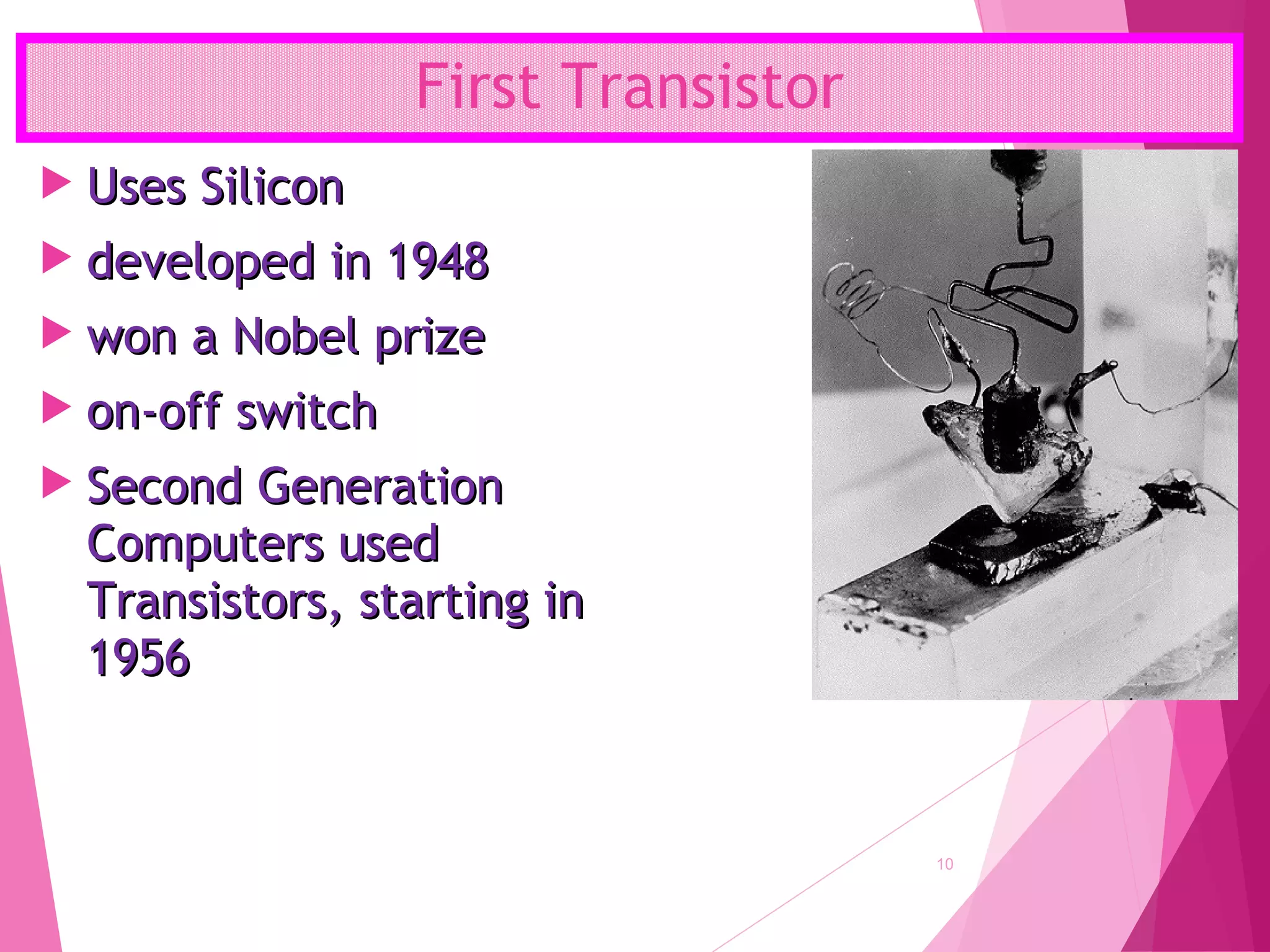
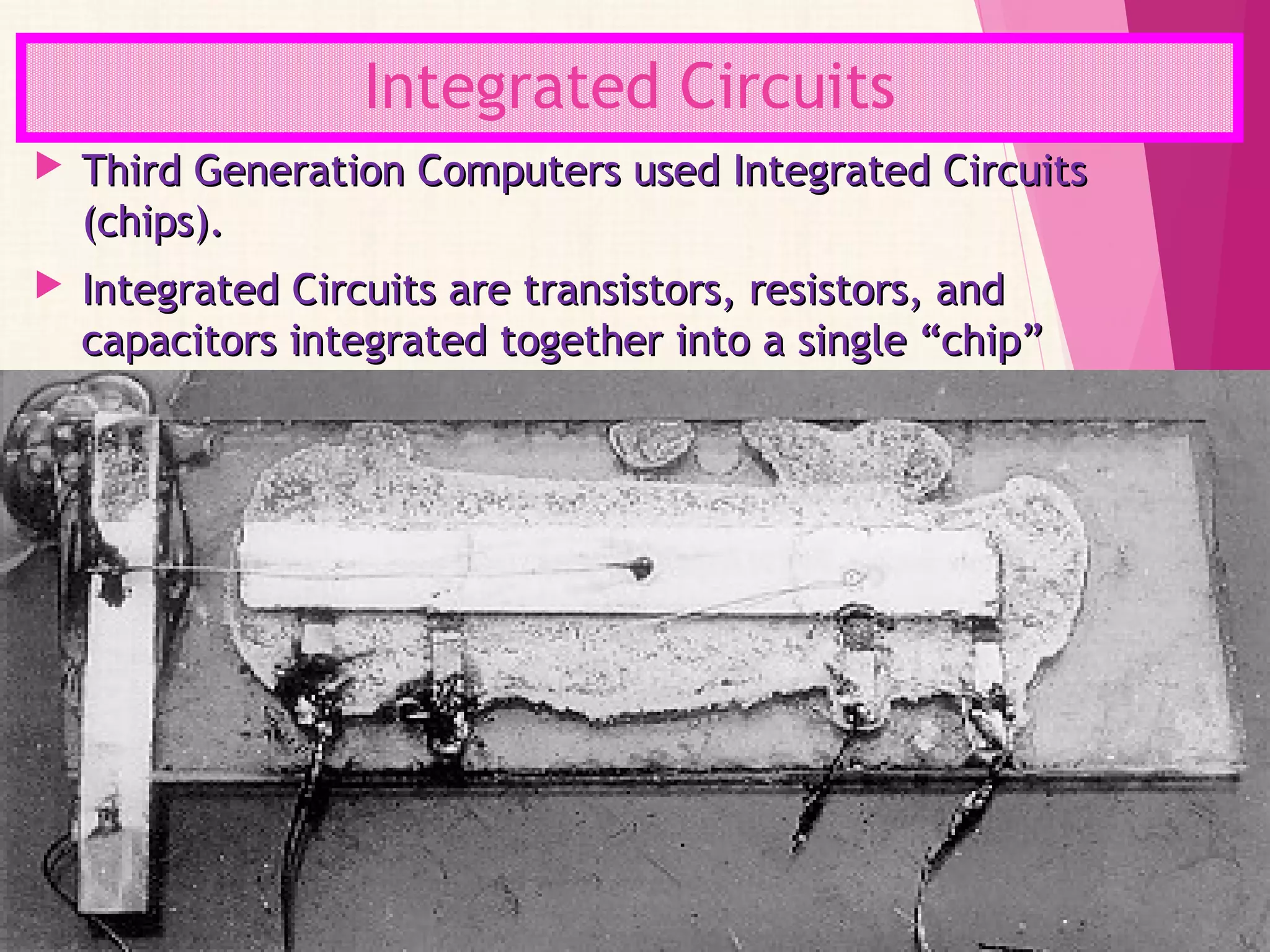
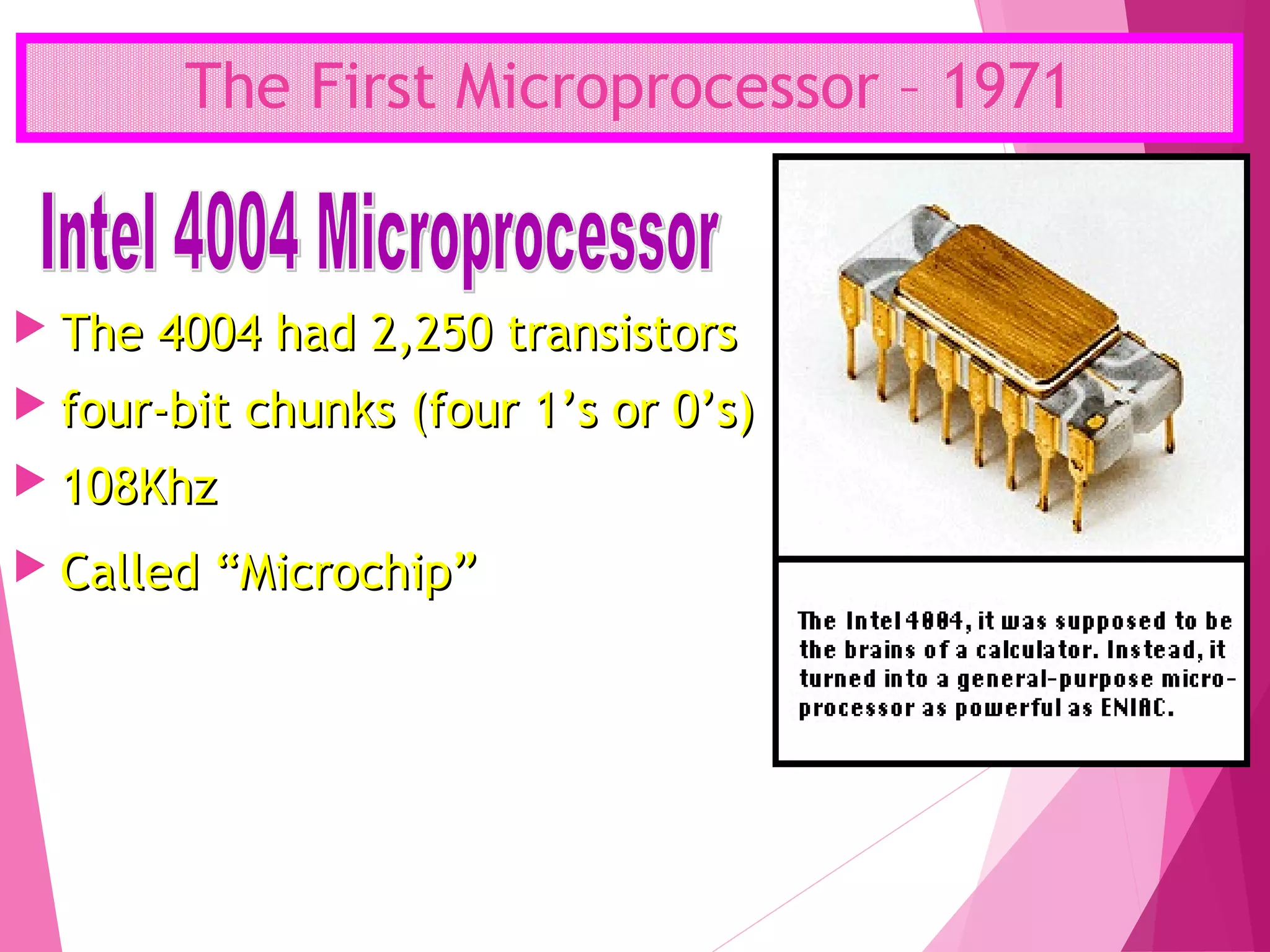
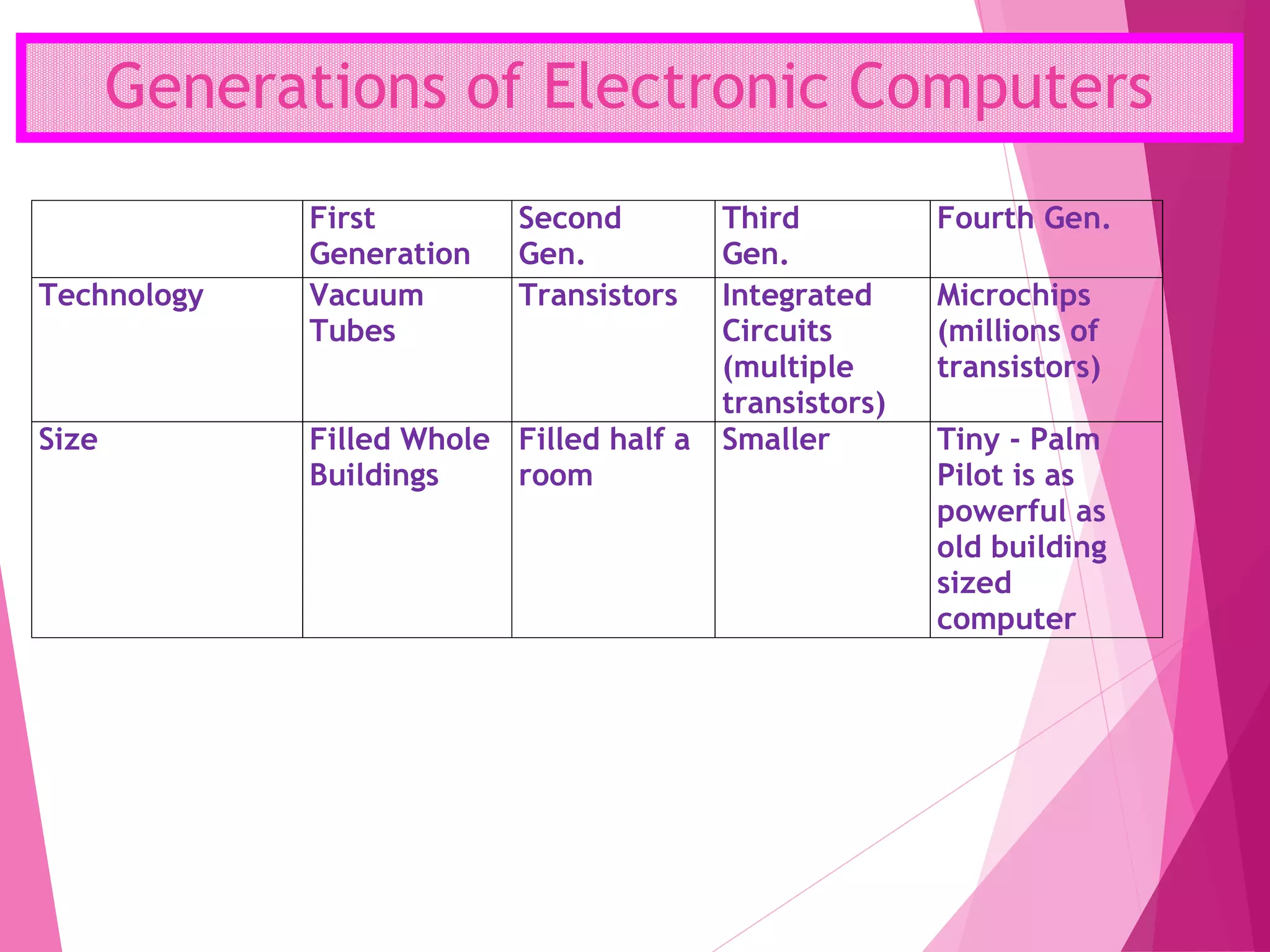
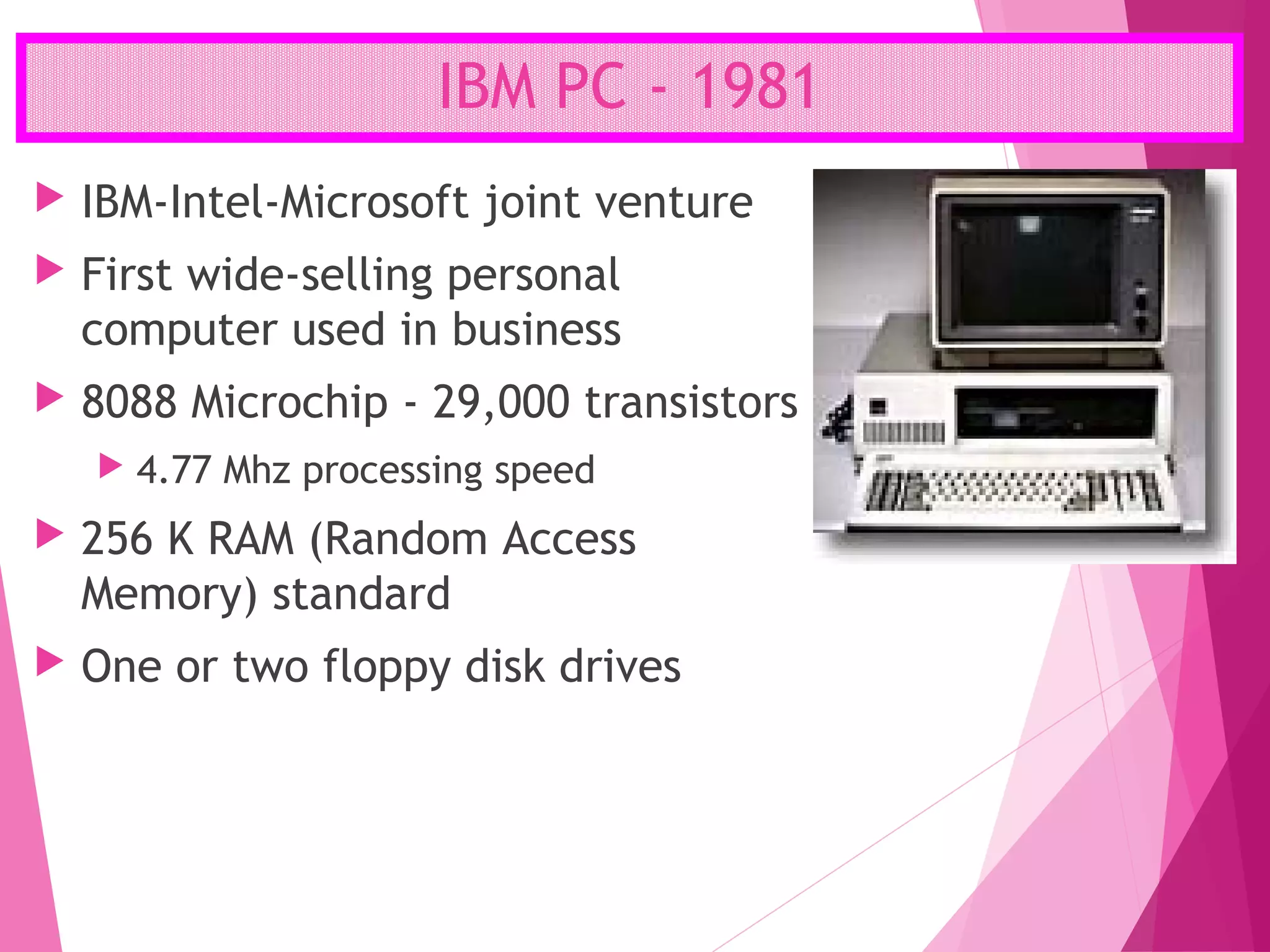
The document summarizes the history of computers over 5 generations from the 17th century to present day. It describes the progression from early mechanical calculators and computers using punched cards, to modern computers that are now tiny microchips containing millions of transistors. Key developments included Charles Babbage's analytical engine, the first stored program computer, the invention of the vacuum tube and transistor, integrated circuits, microprocessors, and the creation of personal computers by companies like IBM and Apple. Current and future computers are exploring artificial intelligence and fifth generation technologies.