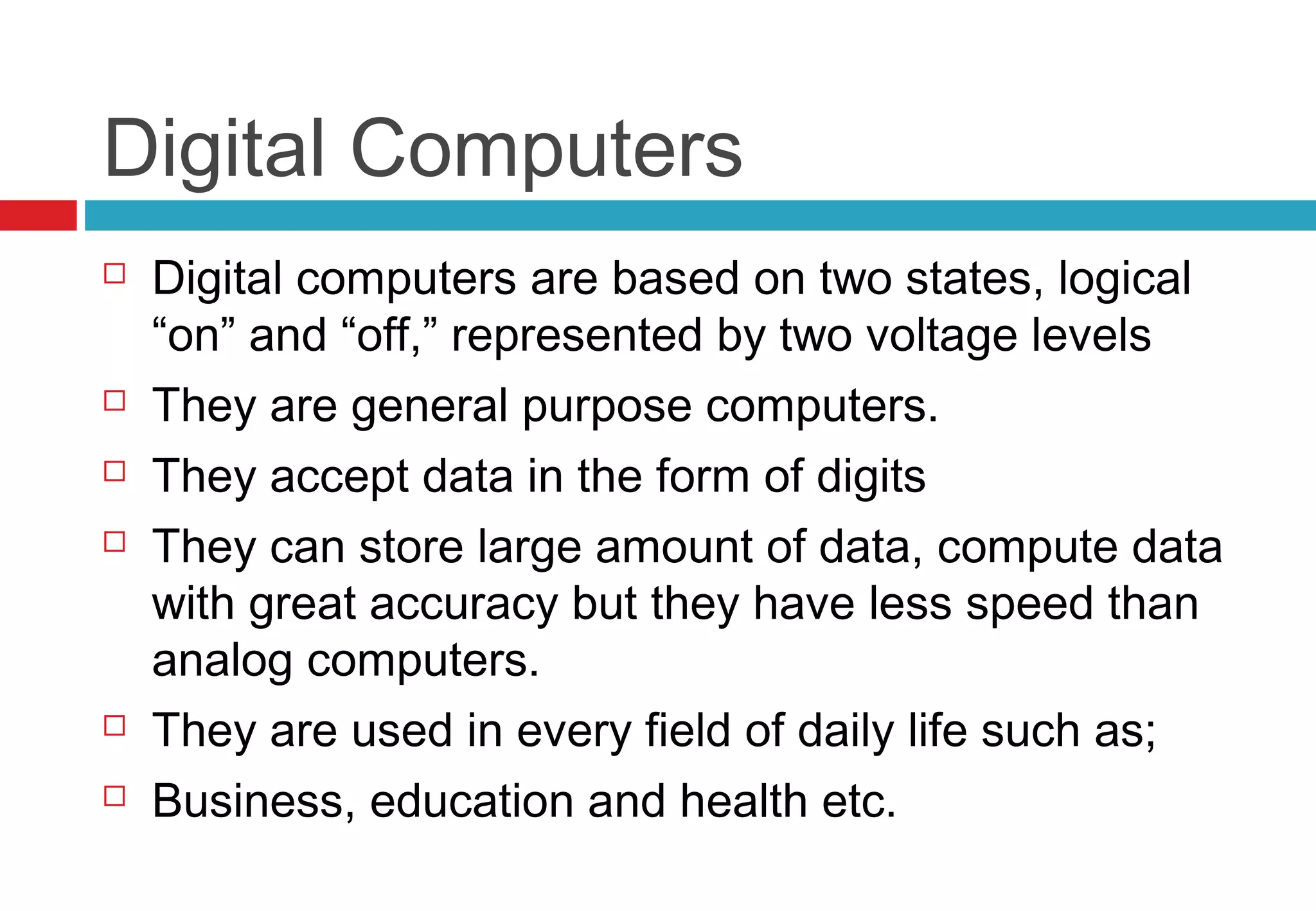
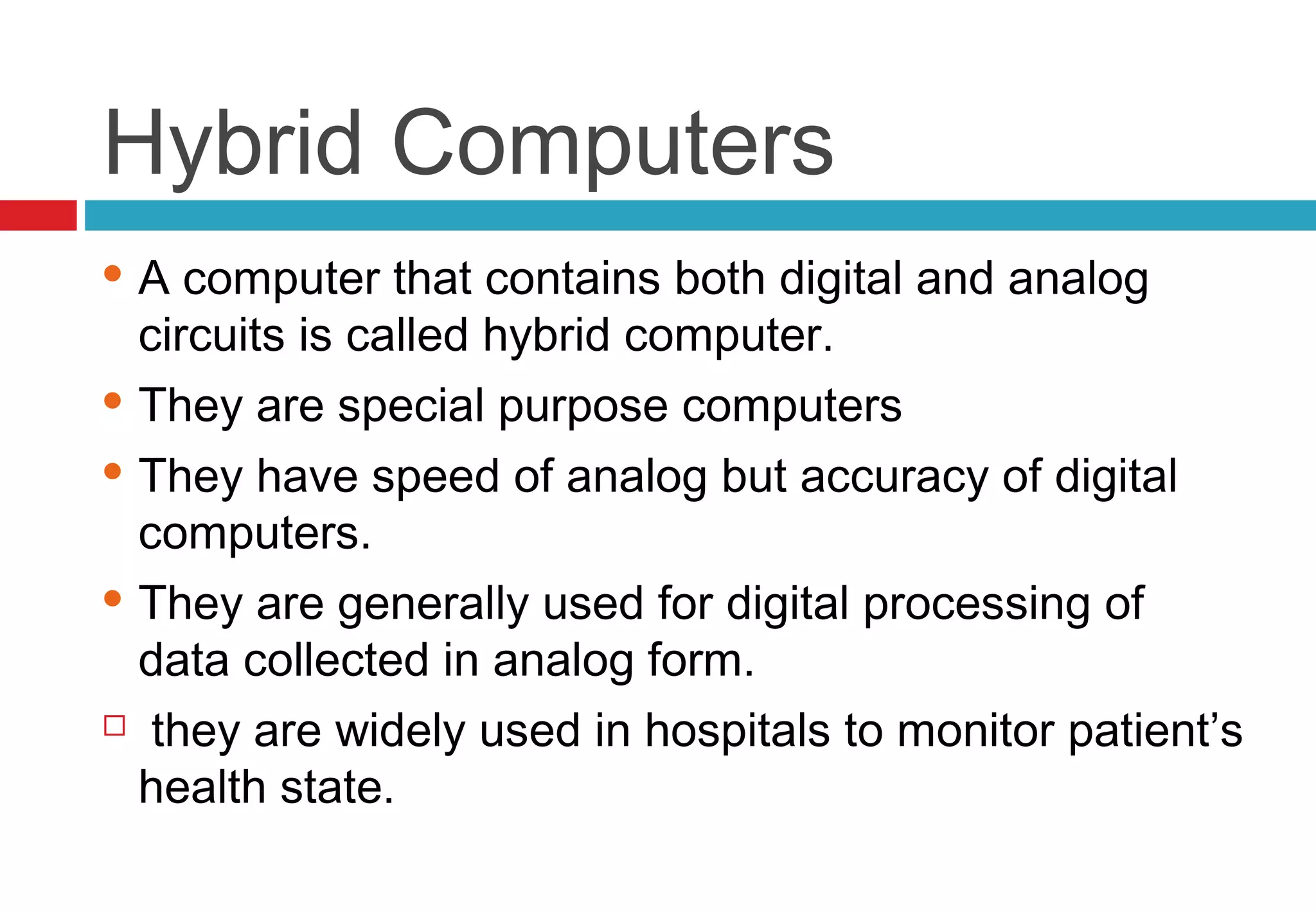
The document discusses the classification of computers into three main categories: by type (analog, digital, and hybrid), by purpose (special and general purpose), and by capacity or size (supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, and microcomputers). Analog computers measure continuously varying data and are high-speed but less accurate, while digital computers are accurate and store data in digits. Hybrid computers combine features of both, and various computer types serve different applications across industries.