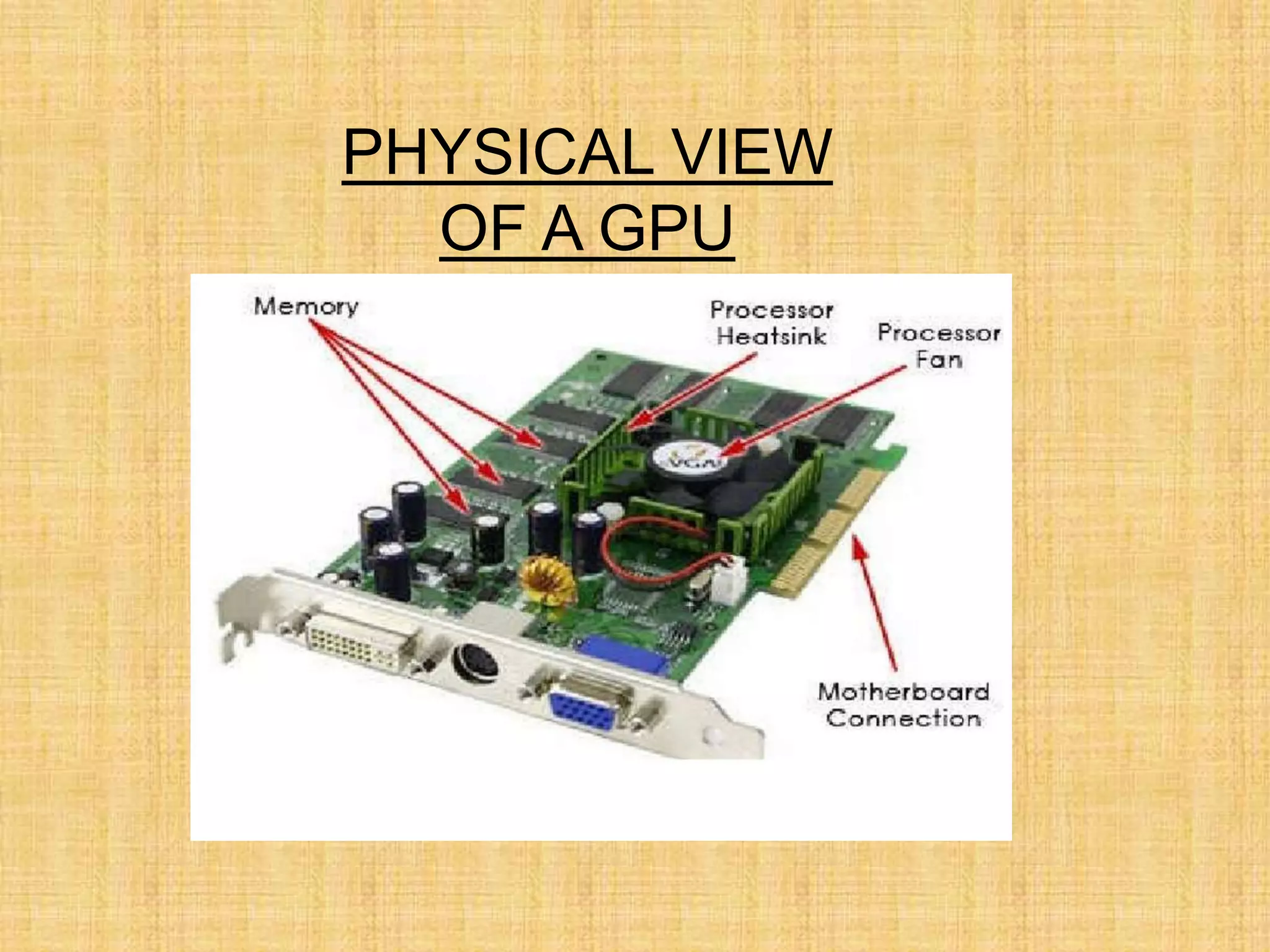
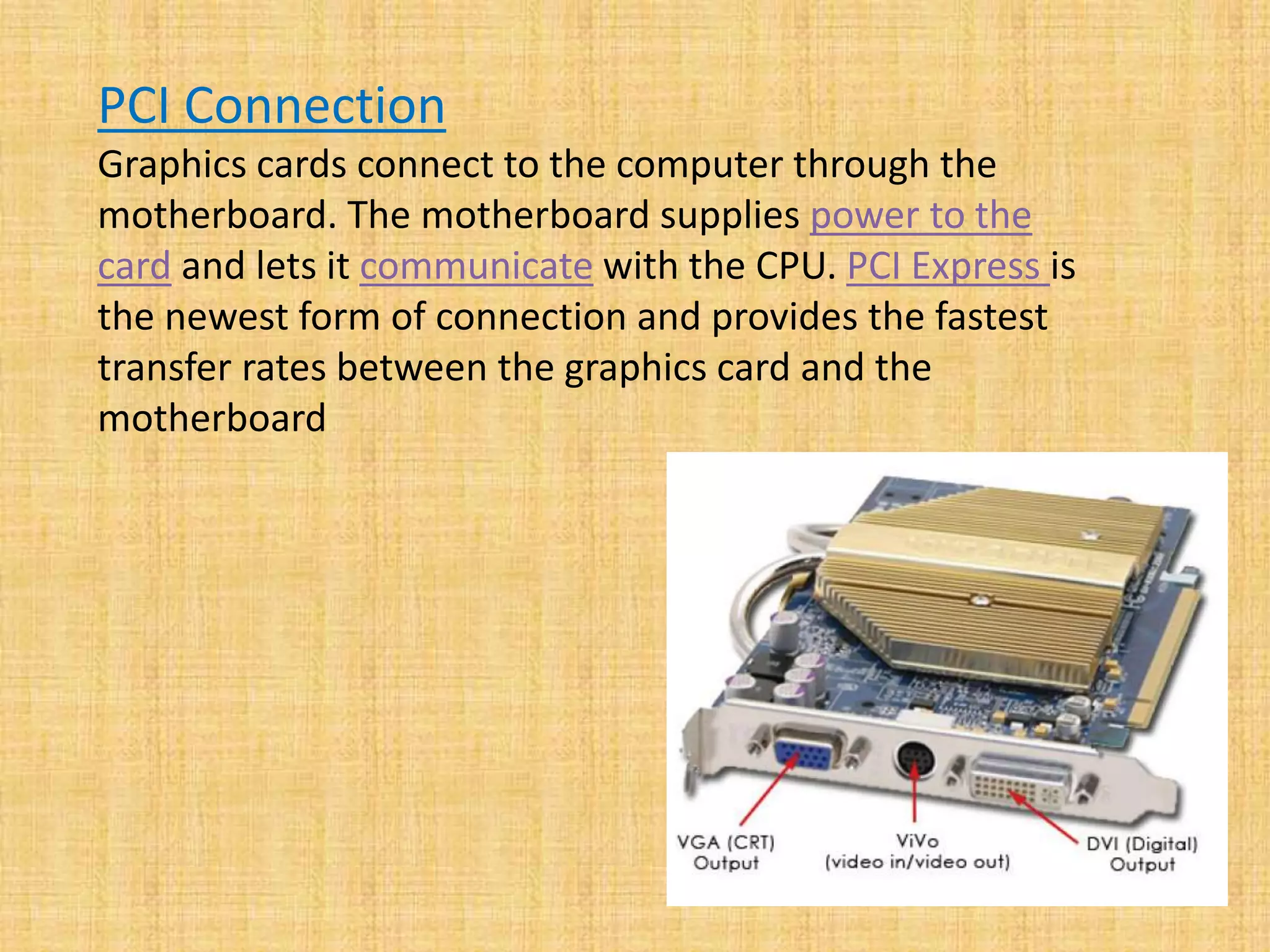
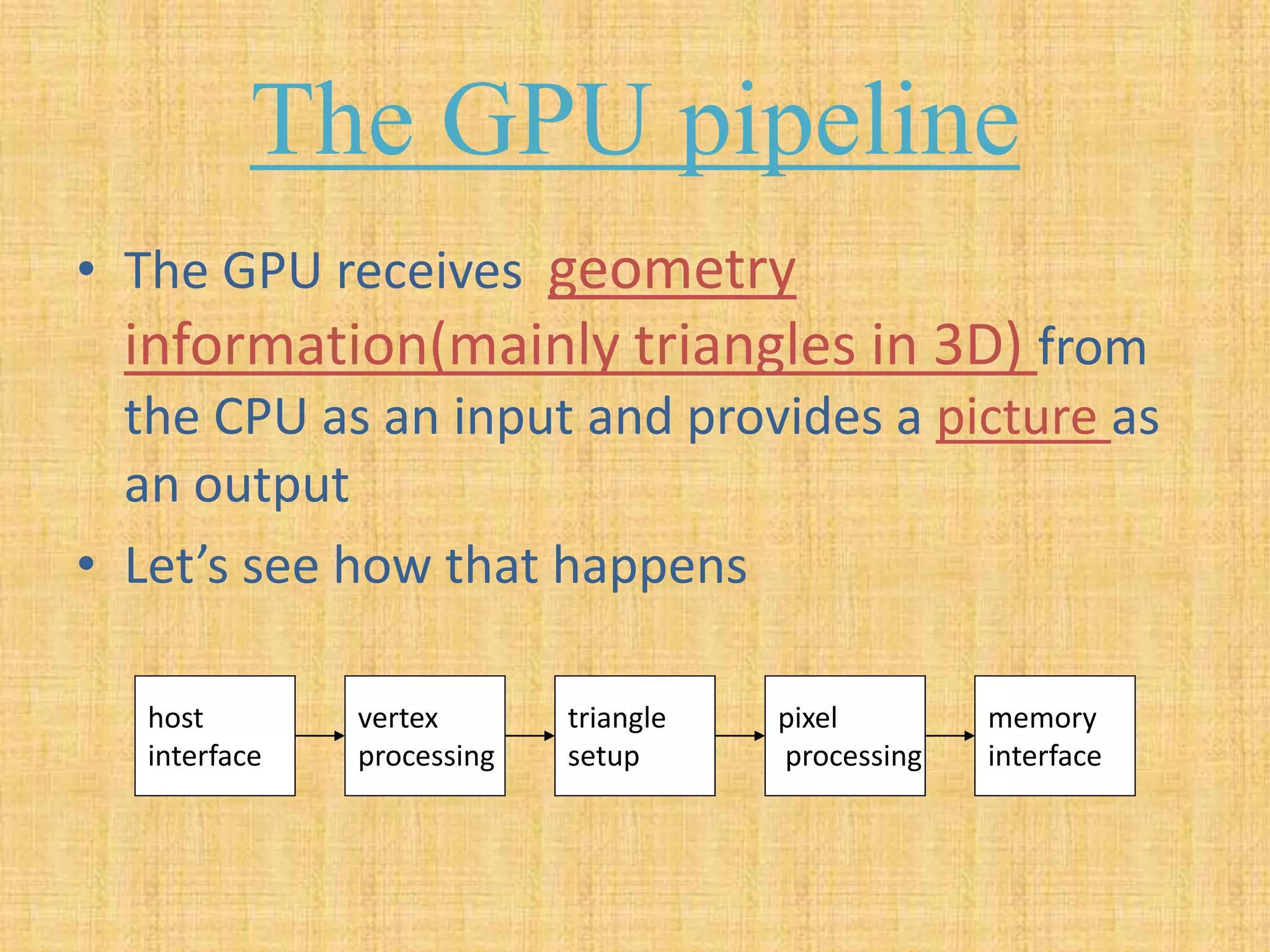
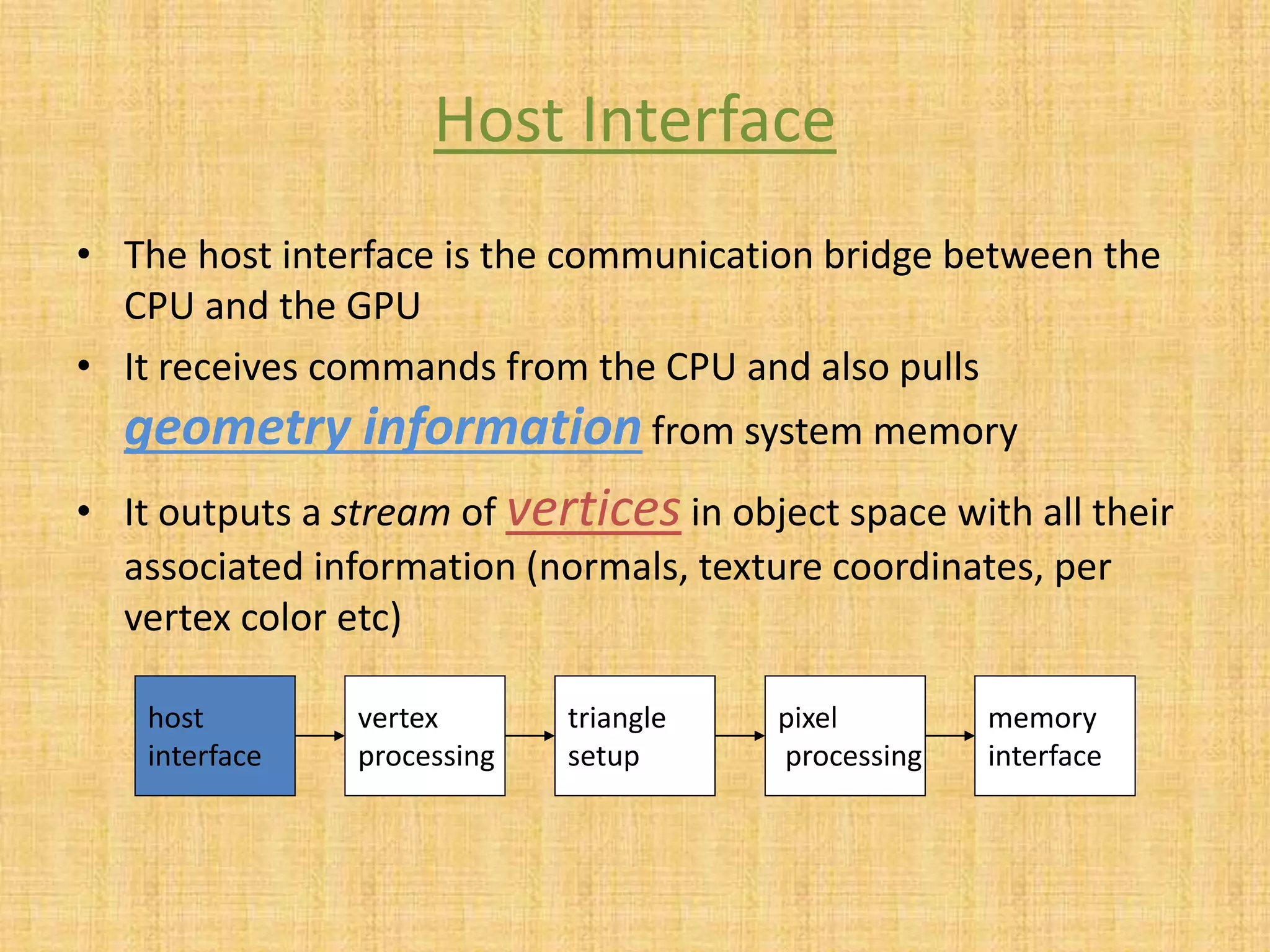
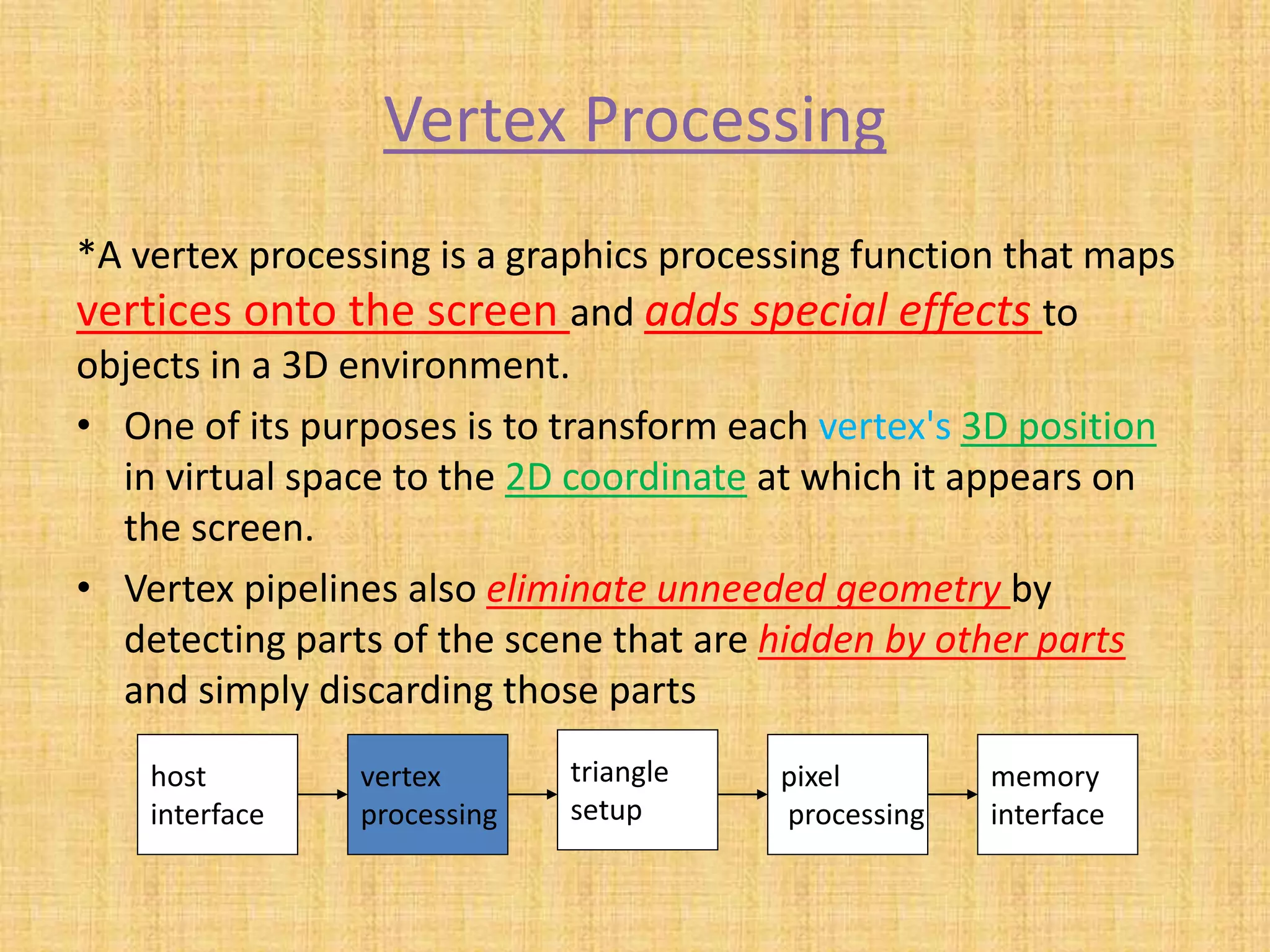
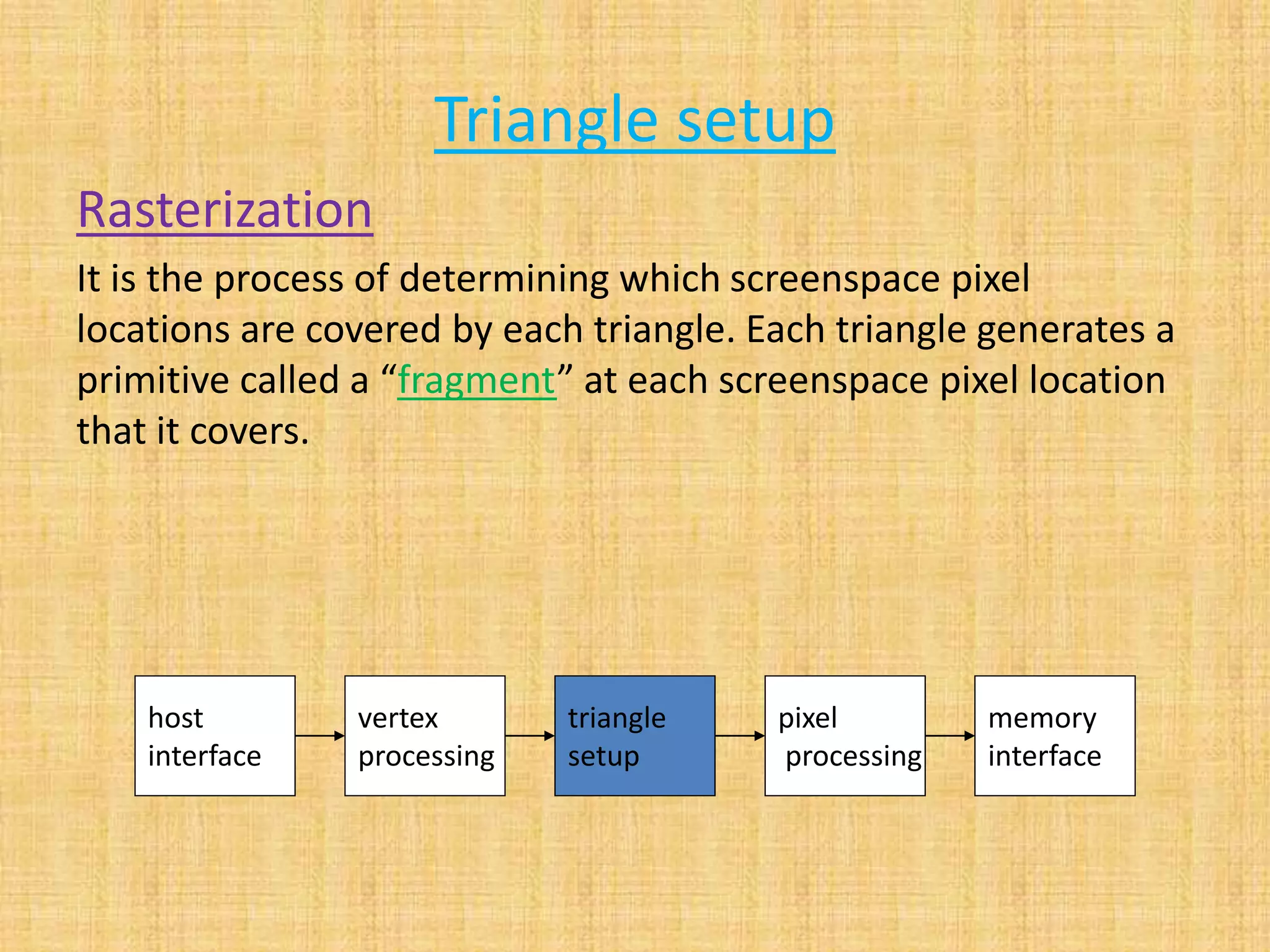
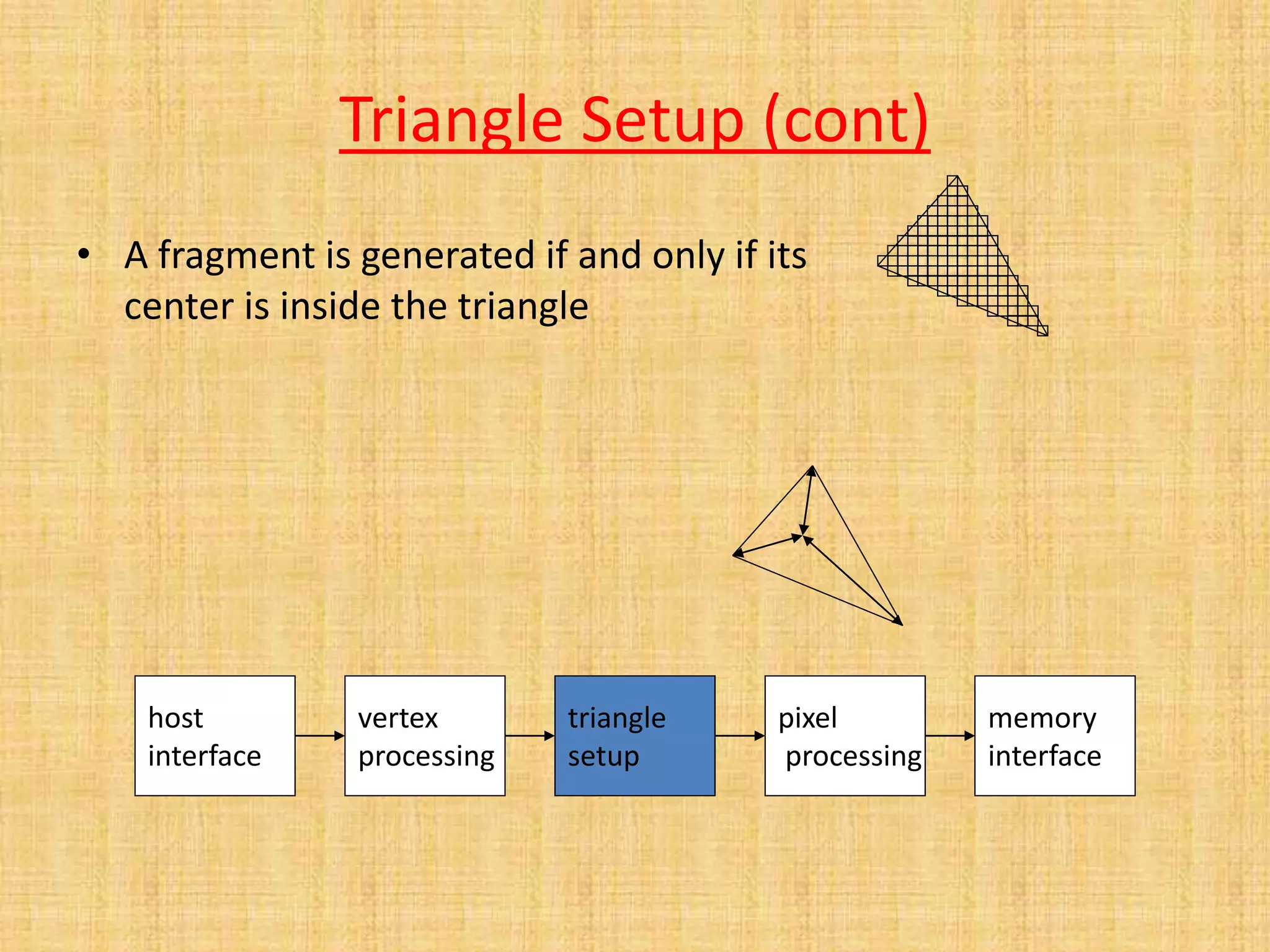
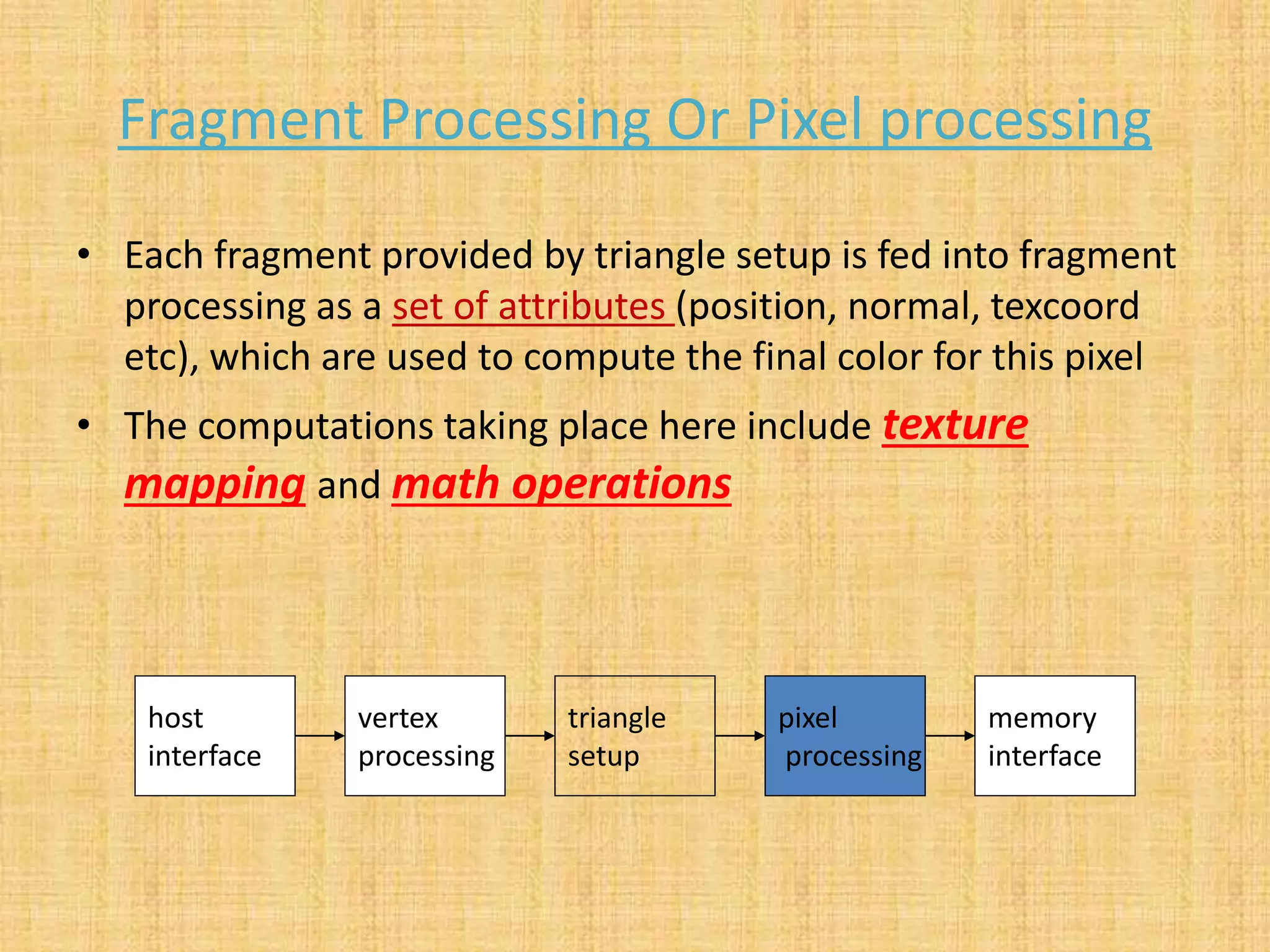
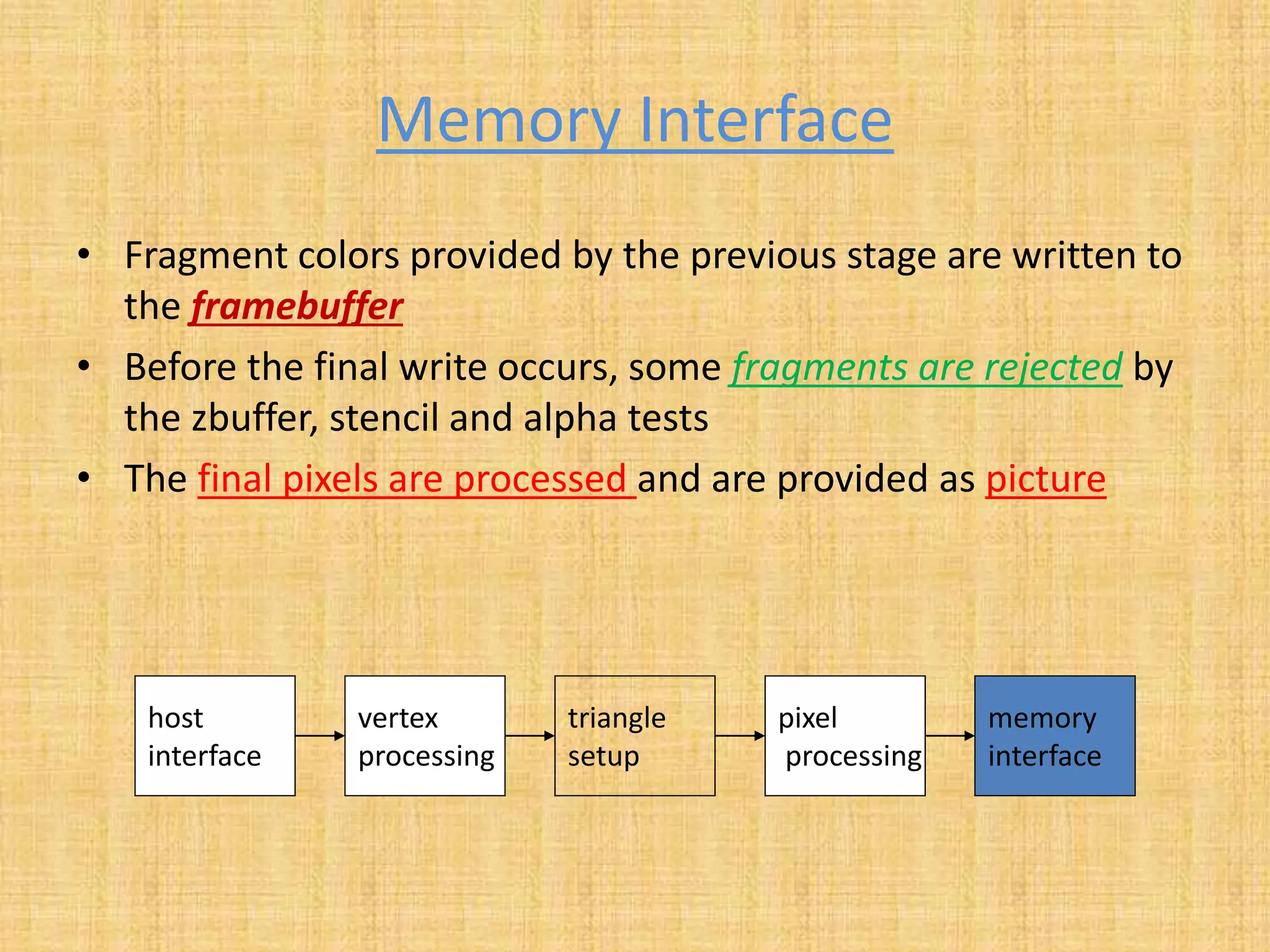
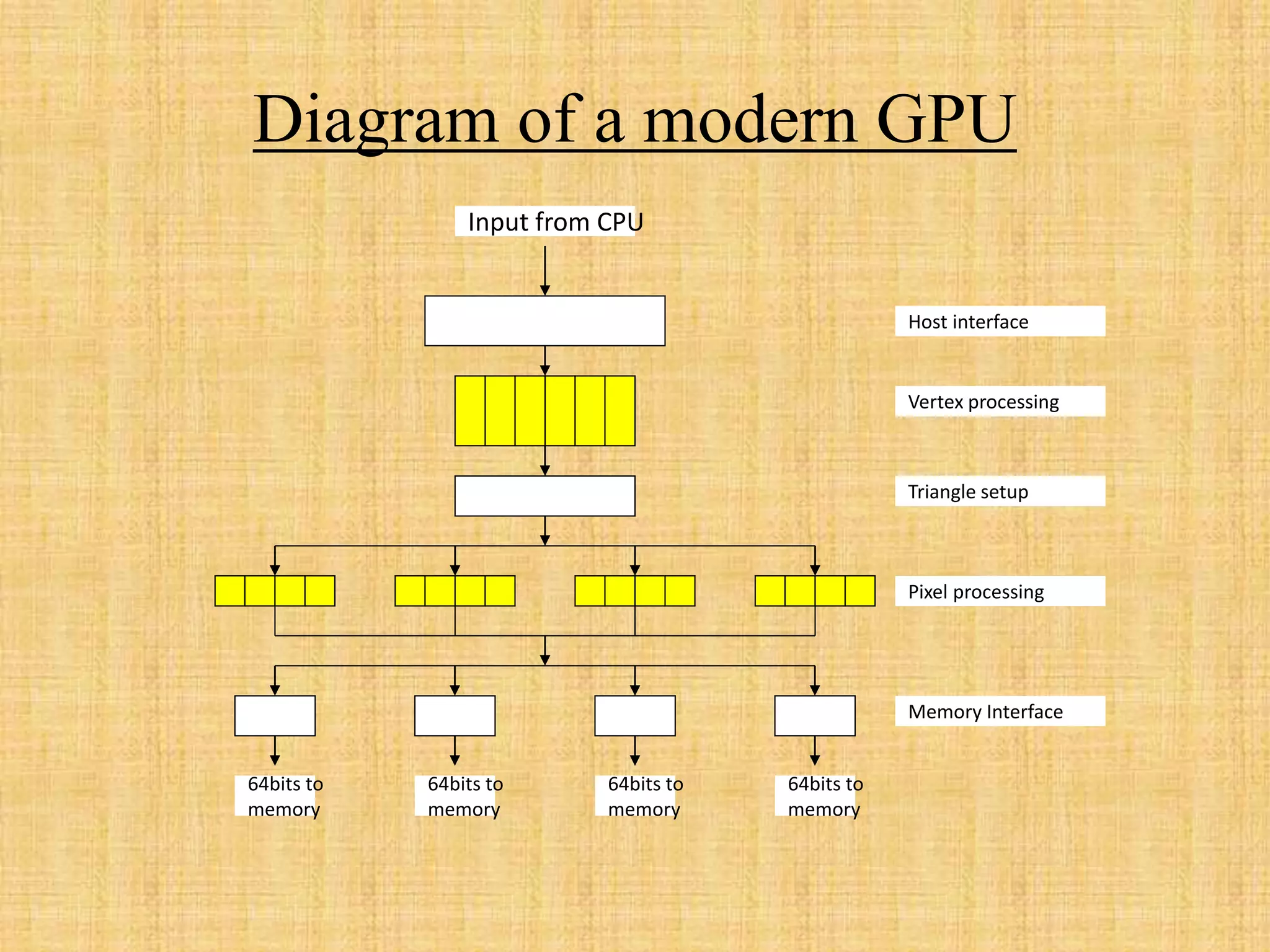
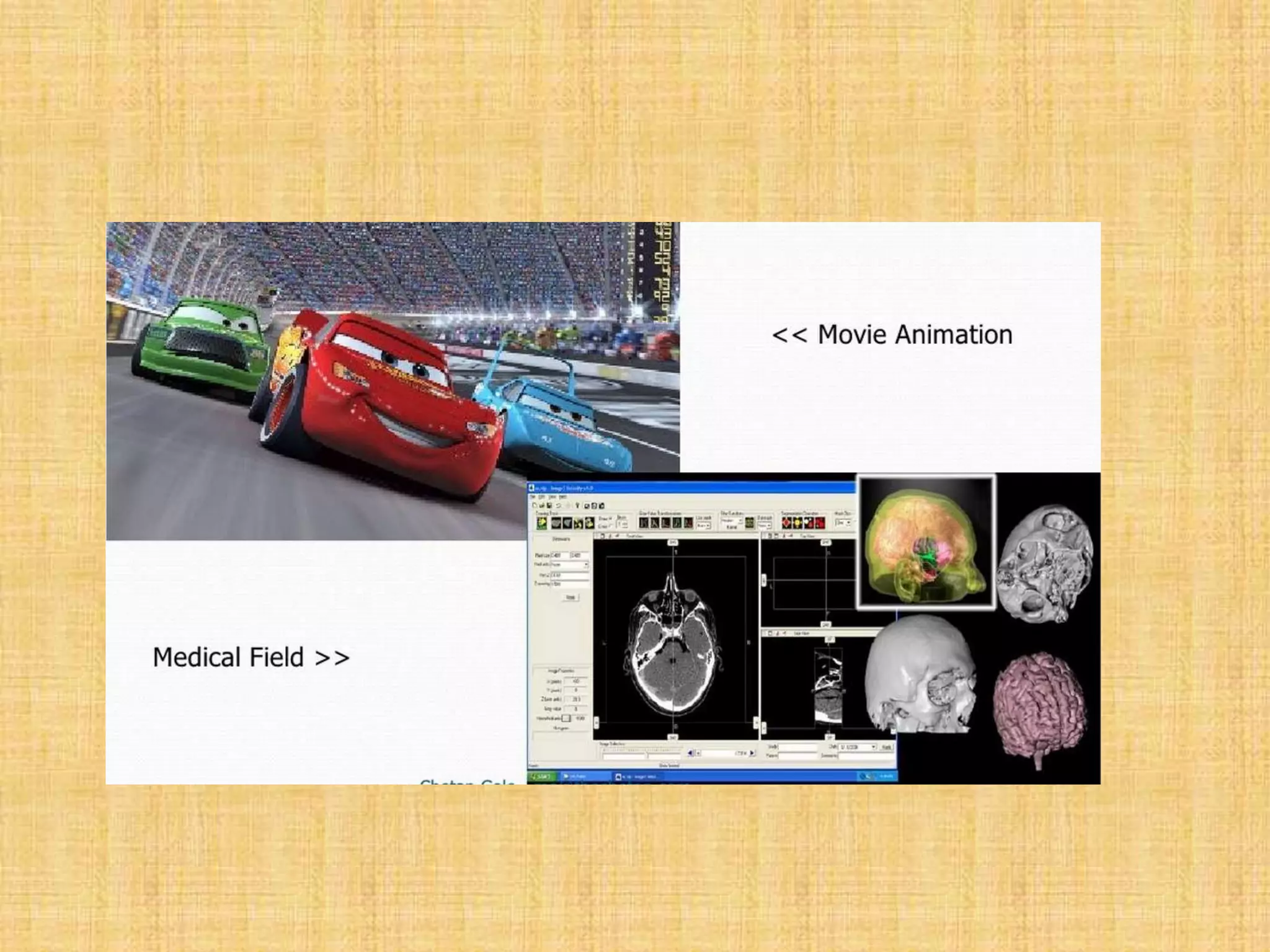
The document provides an overview of graphics processing units (GPUs). It defines a GPU as a processor optimized for graphics, video, and visual computing. GPUs have a highly parallel architecture with thousands of smaller cores designed to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, unlike CPUs which have fewer serial cores. The document compares CPU and GPU architectures, describes the physical components of a GPU including the motherboard, graphics processor, memory, and display connector. It provides details on GPU memory, pipelines, and manufacturers like NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel. The document concludes with information on latest GPU technologies such as CUDA, PhysX, 3D Vision, and examples of high-end consumer GPUs.