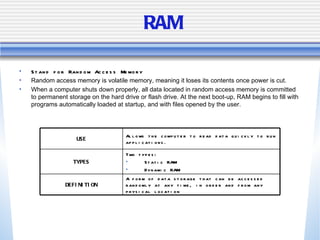
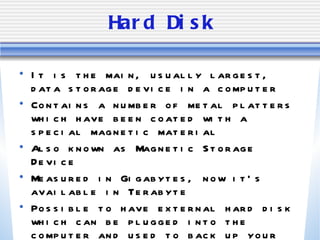
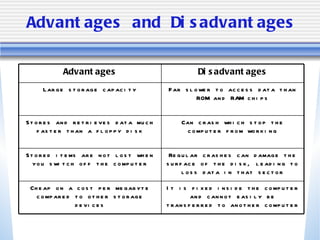
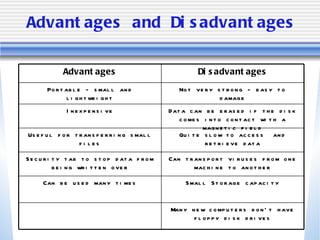
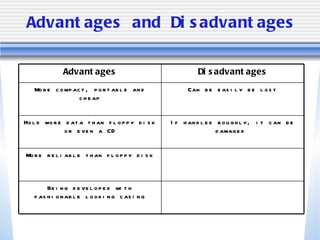
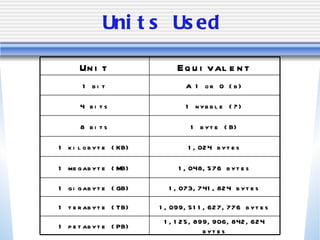
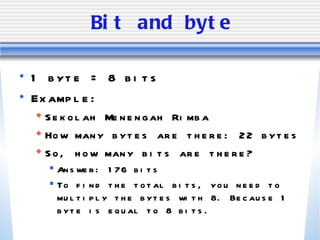
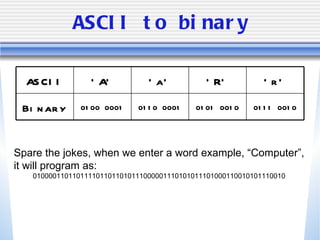
The document discusses various computer storage devices and their characteristics. It describes primary storage RAM and secondary storage devices like hard disk drives. It explains what RAM and ROM are, their differences, and provides examples of different types of storage media like CD-ROMs, DVDs, hard disks, floppy disks, flash memory, and how many bytes and bits are used to store data.