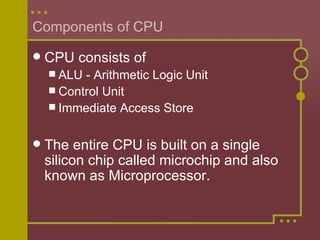
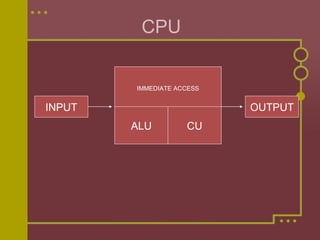
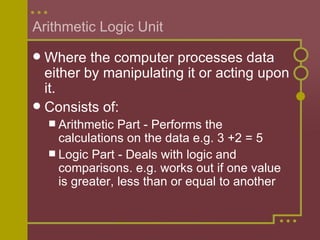
The CPU is the brain of the computer. It manages startup processes, controls data flow and input/output operations, loads programs and data into memory, and manages file operations. The CPU consists of an ALU for processing data, a control unit for monitoring operations and controlling data flow, and immediate access storage for temporary data and programs. The entire CPU is built on a single microchip called the microprocessor.