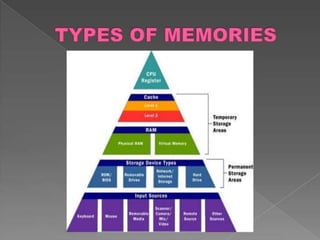
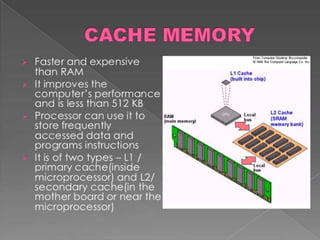
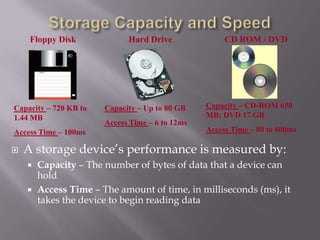
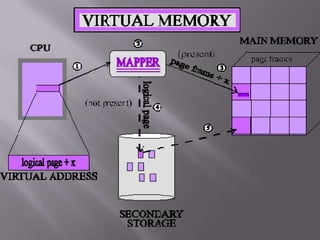
This document provides an overview of different storage types and devices in computer systems, including hard drives, floppy disks, and optical storage like CD/DVD. It categorizes storage by their operations, access methods, technologies, and hierarchies, explaining concepts such as online, near-online, and offline storage. Additionally, it discusses the performance metrics of storage devices, including capacity and access times.