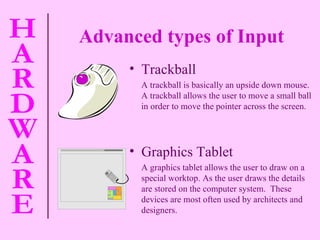
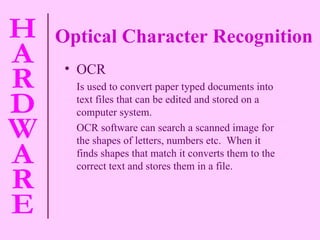
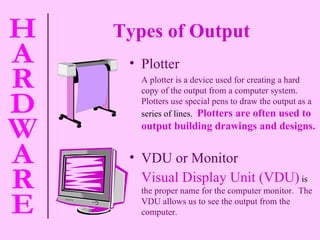
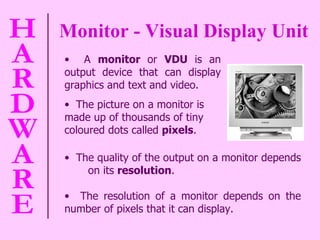
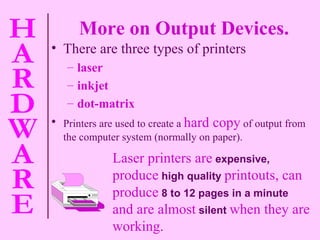
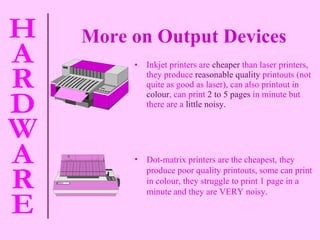
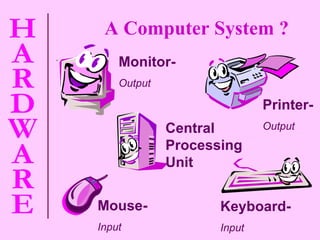
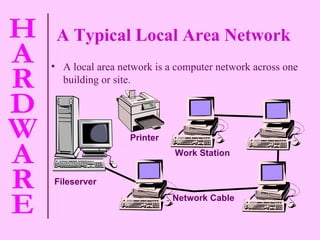
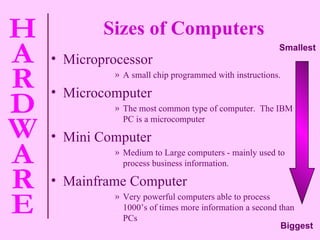
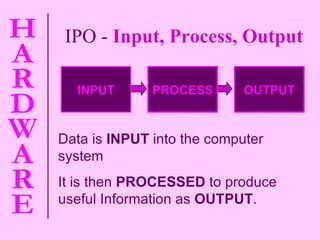
The document provides information about computer hardware and components. It defines hardware as the physical parts of a computer system that can be touched, such as monitors, processors, and printers. It also explains that software refers to programs and data used with the computer. The document then covers various computer components in more detail, including the central processing unit, memory, storage devices, input devices, and output devices.



![Computer - Block Diagram The Computer System consists of four parts. Input, Processor [CPU], Output, Backing Storage Backing Storage Devices Input Devices Central Processing Unit (CPU) Output Devices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardware-101010040308-phpapp01/85/Hardware-11-320.jpg)
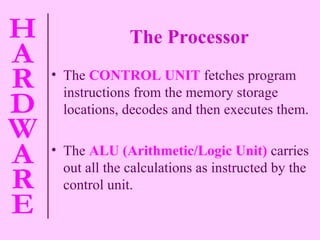
![The central processing unit (CPU) This is the part of the computer where the searching and sorting of data, calculating and decision-making goes on. The CPU contains the processor [ Control Unit and the Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) ] and the Main Memory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardware-101010040308-phpapp01/85/Hardware-12-320.jpg)



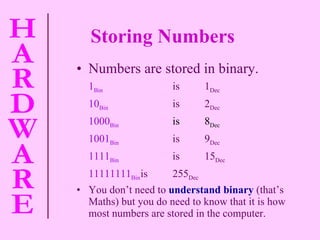
![Bits and Bytes [BINARY] Each 1 or 0 is called a BIT (short for Binary Digit). Eight bits are called a BYTE. 1024 bytes is a KILOBYTE (Kb for short) 1024 kilobytes is a MEGABYTE (Mb for short) 1024 megabytes is a GIGABYTE (Gb for short) These units are used to measure the size of storage or storage requirements e.g. the available memory, hard disk space, program size.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardware-101010040308-phpapp01/85/Hardware-17-320.jpg)
![Bits and Bytes [BINARY]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardware-101010040308-phpapp01/85/Hardware-18-320.jpg)