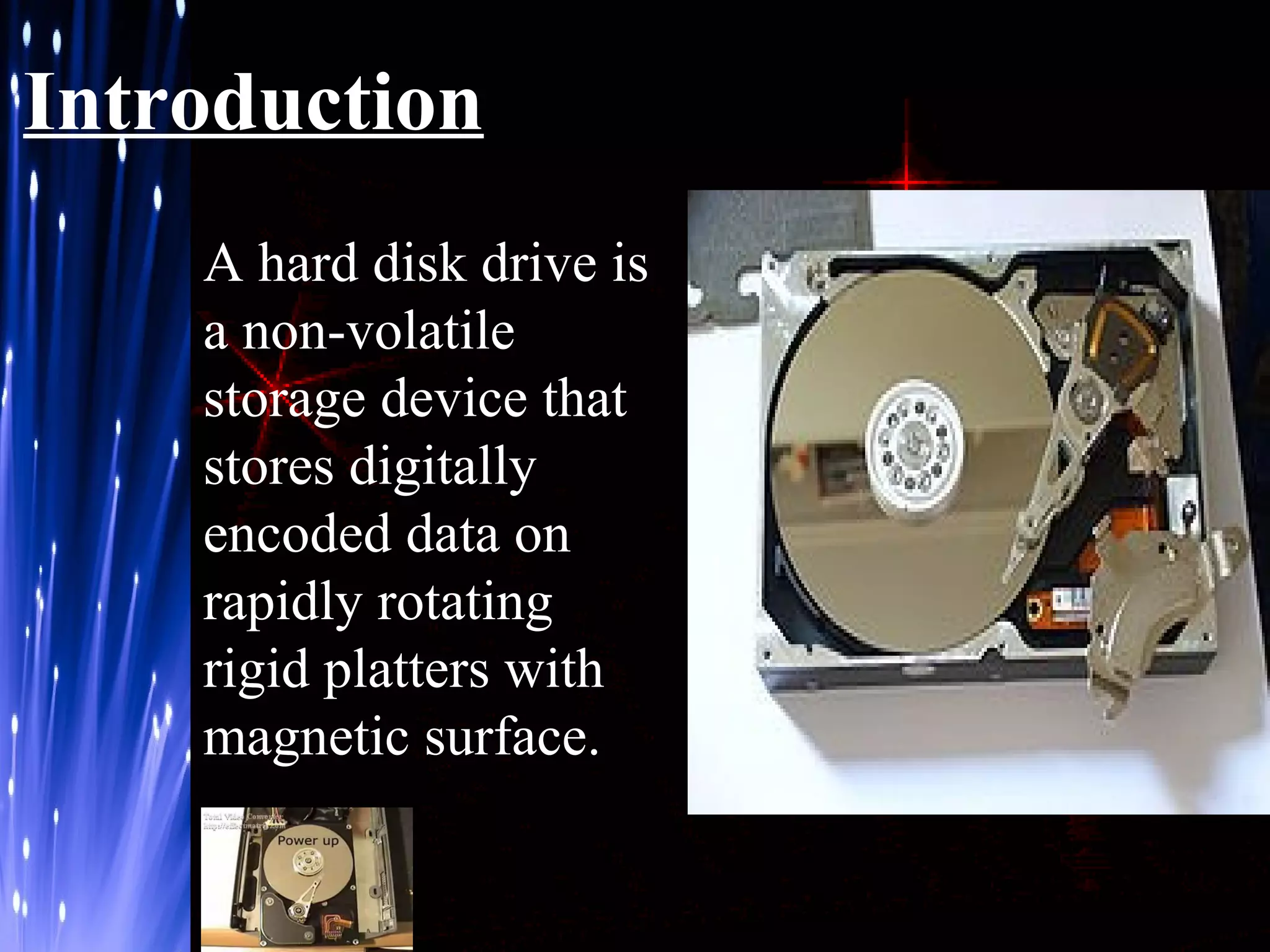
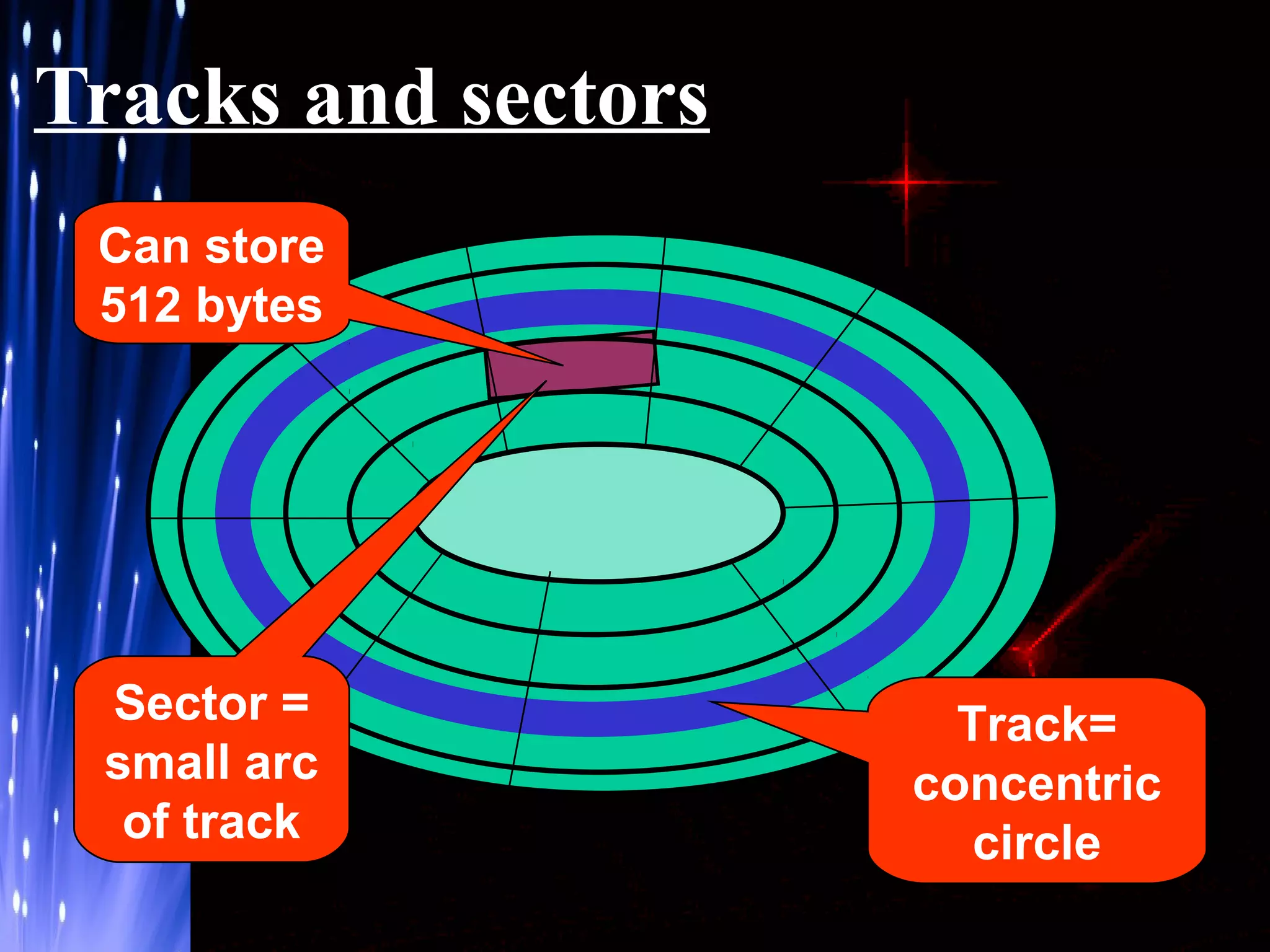
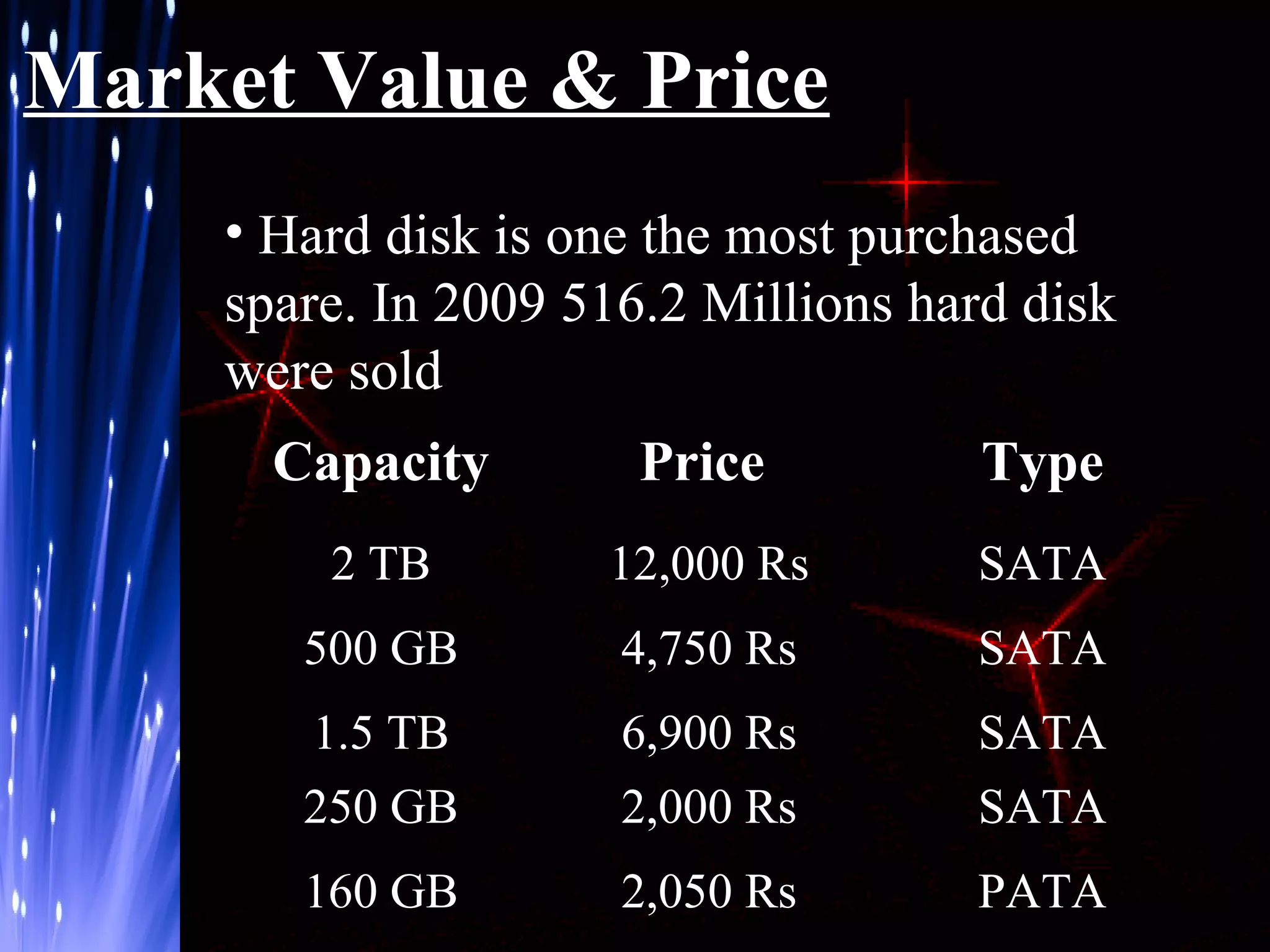
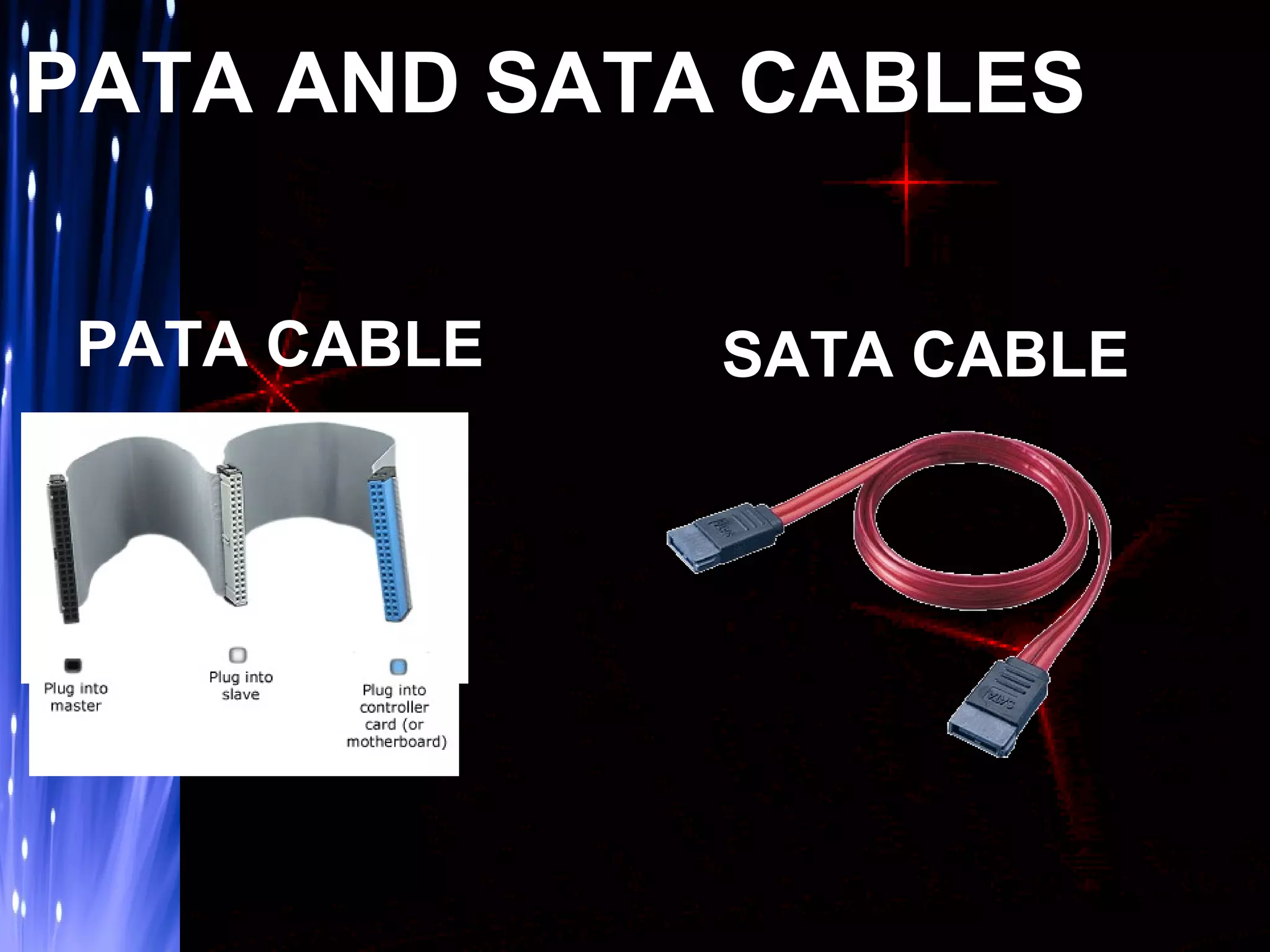
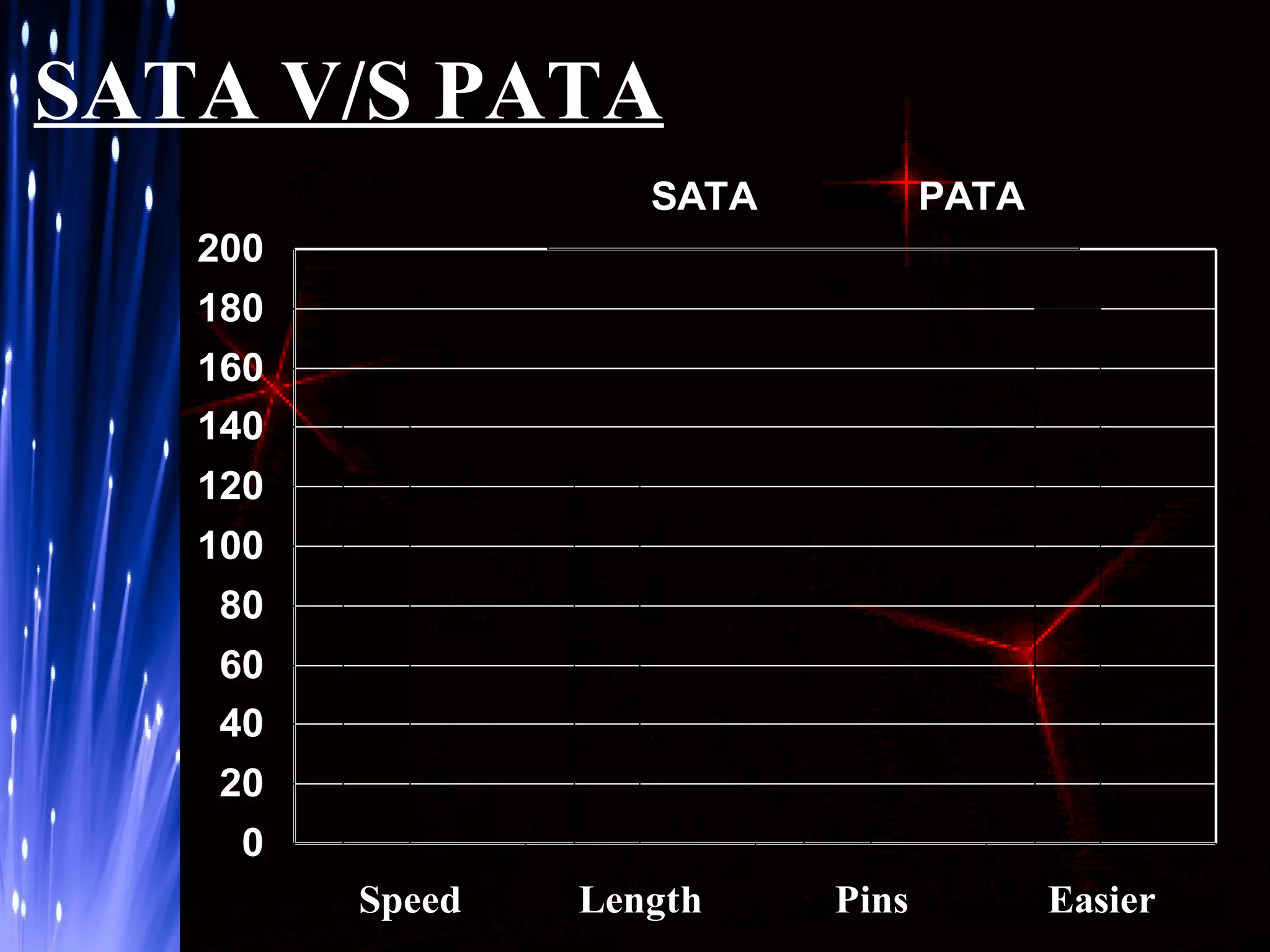
The document provides an overview of hard disk drives including their history, working, characteristics, types, organization of data, and manufacturers. Hard disk drives were first introduced in 1956 to store data for IBM computers and now come in two main types - PATA and SATA. They work by magnetizing ferromagnetic material to represent binary digits and reading the data back by detecting magnetization. Proper shutdown is needed before unplugging a computer to allow the hard disk head to safely separate from the disk platter.