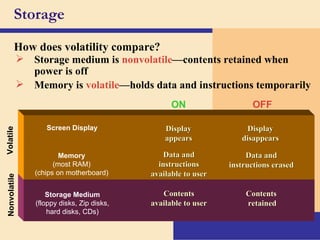
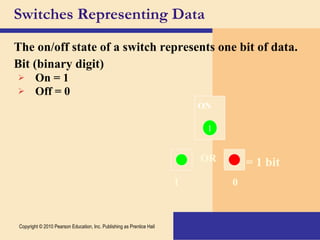
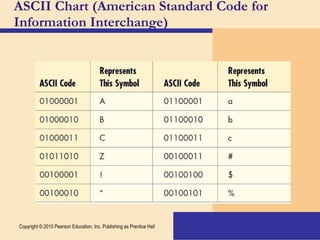
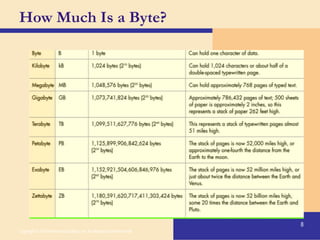
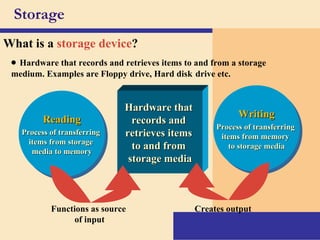
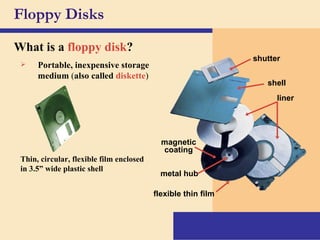
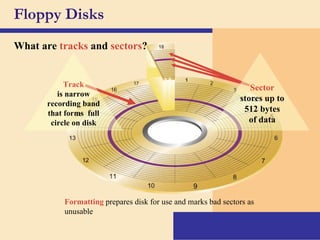
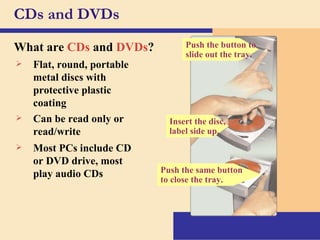
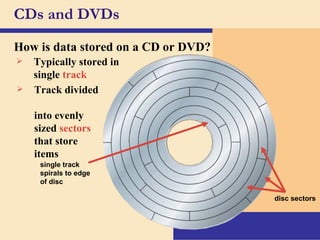
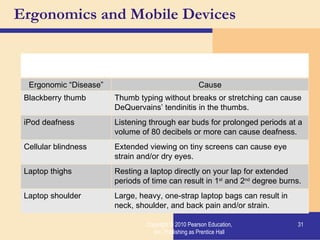
Storage devices such as floppy disks, hard disks, CDs, DVDs, and tape are used to store digital data outside of the computer's main memory. Floppy disks store data on flexible magnetic disks inside a protective case. Hard disks store larger amounts of data than floppy disks on rigid magnetic platters inside a sealed case. CDs and DVDs store large amounts of fixed data and programs on compact discs that can only be read from. Tape is used for backup storage and can store large amounts of data sequentially. Proper ergonomics are important when using computers and mobile devices to prevent injury.