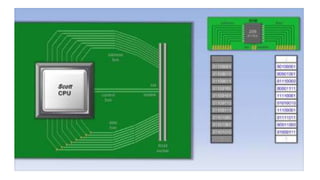
RAM allows stored data to be accessed directly in any random order. There are two main types: static RAM and dynamic RAM. Static RAM keeps data without refreshing but is more expensive, while dynamic RAM needs refreshing but is cheaper. RAM is a temporary memory that does not store data permanently once power is turned off. Future RAM technologies aim to provide smaller, faster, and cheaper memory chips compared to today's options like DDR3 RAM.