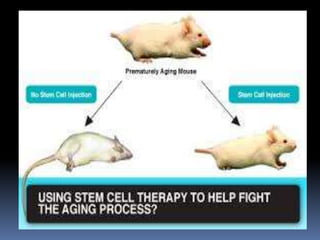
This document provides an overview of stem cells, including their definition, history, characteristics, types, potency, treatments, and research. It discusses embryonic stem cells, which are pluripotent cells derived from blastocysts, and adult stem cells found in tissues like bone marrow. The document also outlines the importance of stem cell research for developing new medical treatments, testing drugs, and studying development, while acknowledging the ethical controversies around embryonic stem cell derivation and challenges with stem cell therapies.