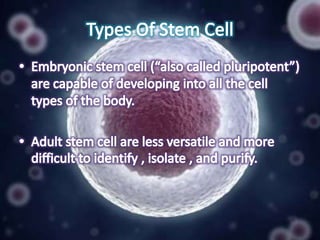
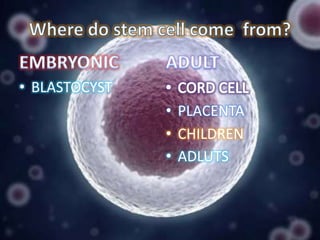
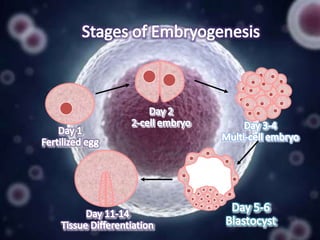
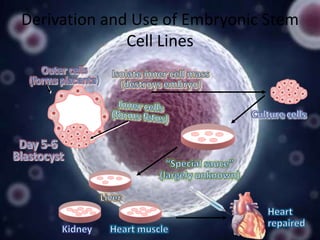
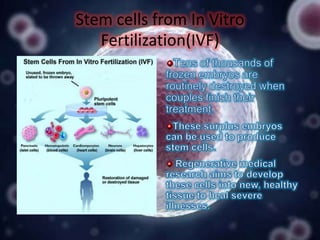
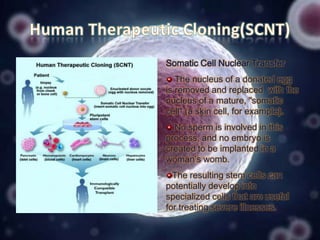
Stem cell research has progressed significantly since the 1960s when scientists first isolated stem cells. In 1998, James Thomson derived the first human embryonic stem cell lines from the inner cell mass of human embryos. There are two main sources of embryonic stem cells: in vitro fertilization embryos and somatic cell nuclear transfer. Embryonic stem cell research holds promise for developing treatments for diseases like Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and cancer. However, it also faces ethical debates because it involves the destruction of embryos. Both advantages and disadvantages of this research must be considered regarding its future.