This document provides an overview of stem cell research, including:
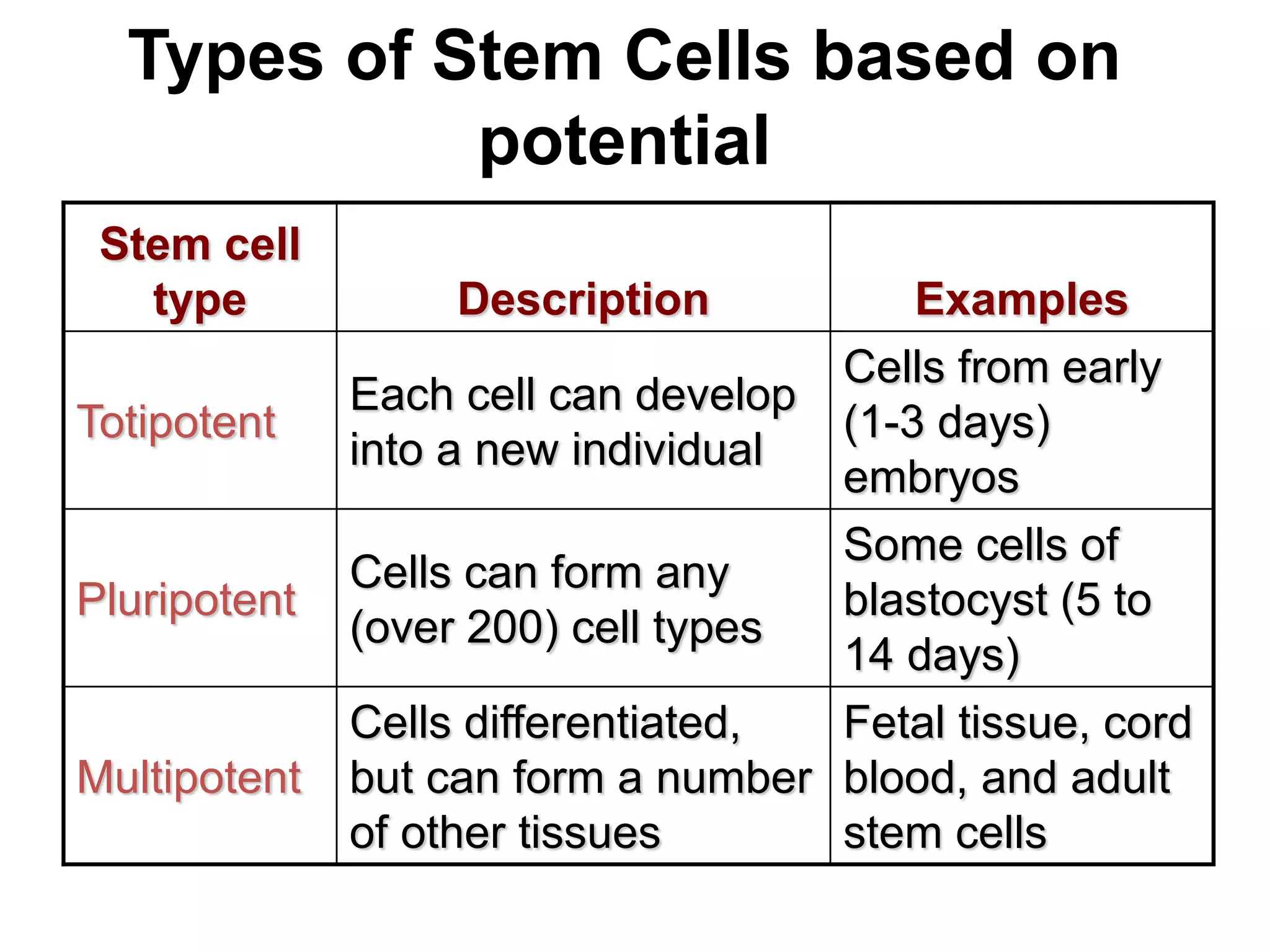
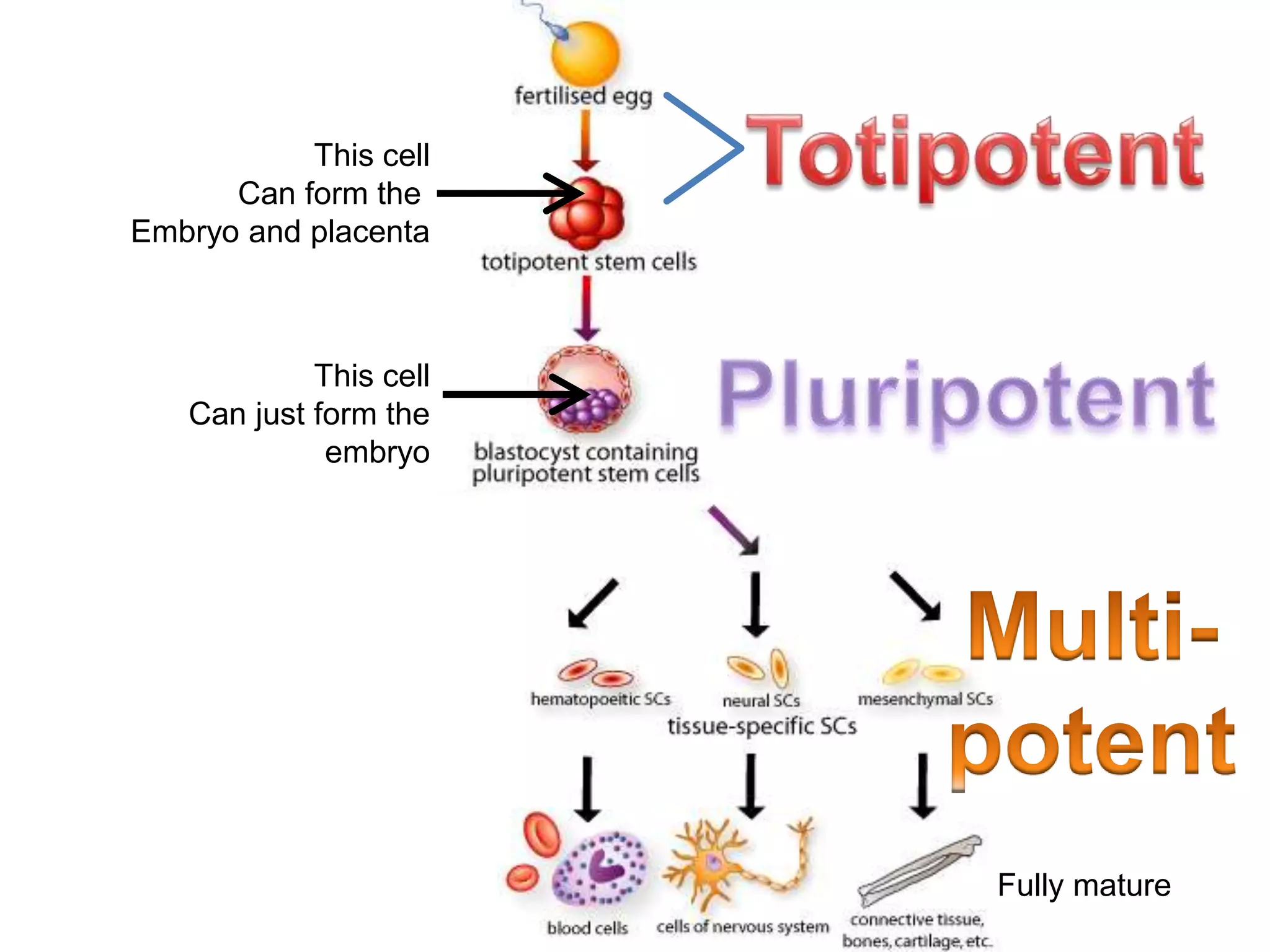
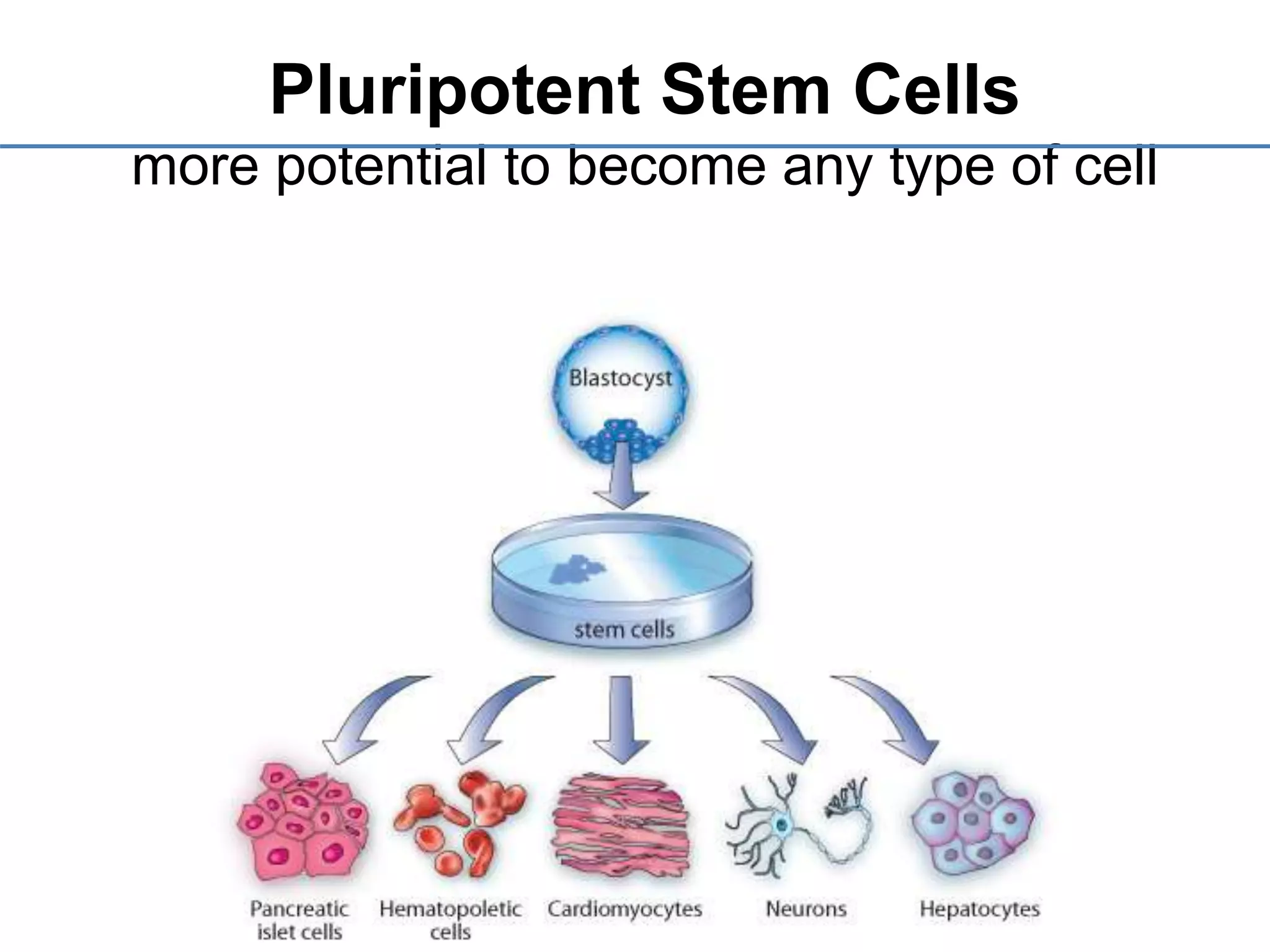
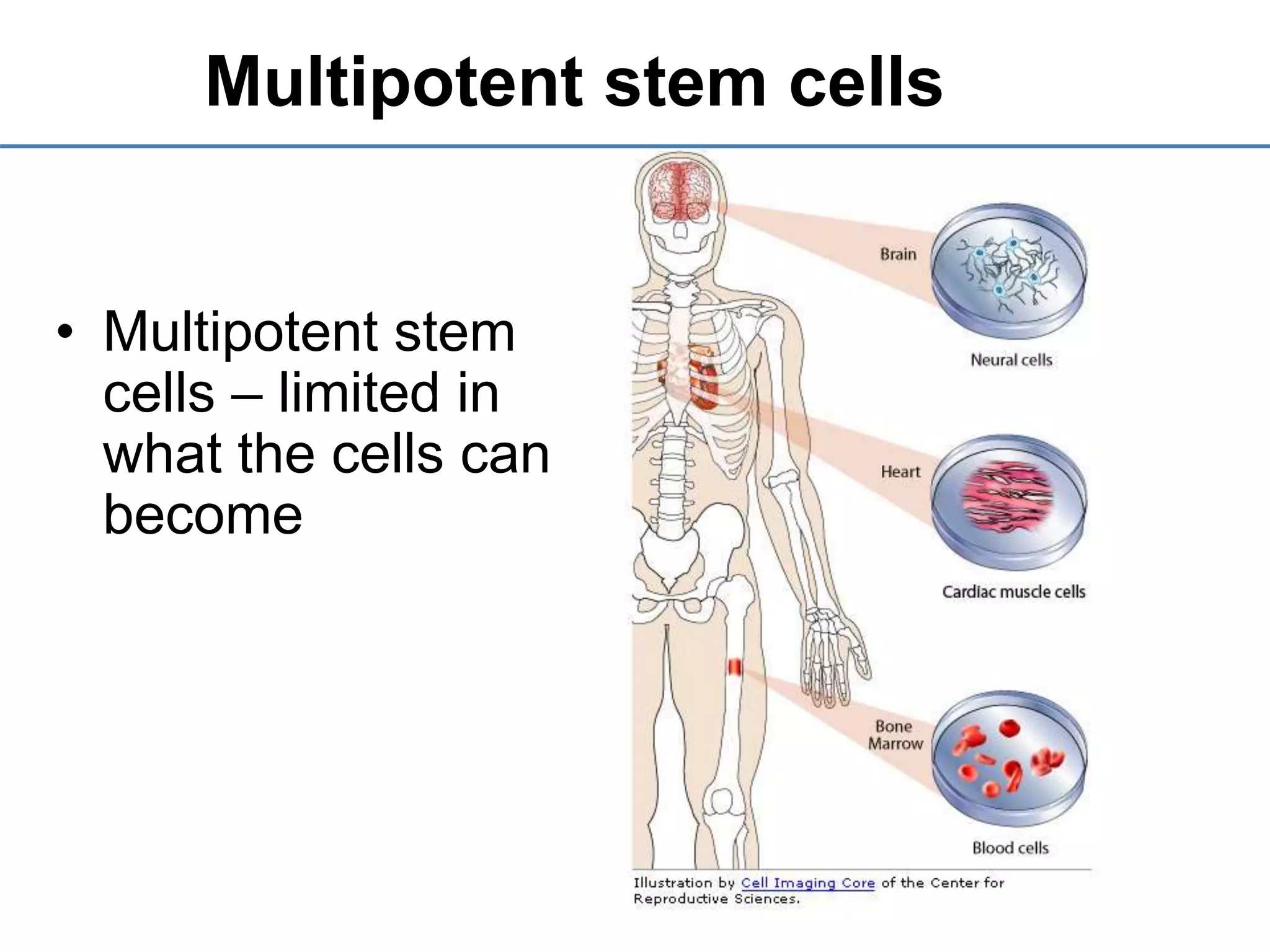
1) It defines stem cells, outlines the history of stem cell research, and describes the different types of stem cells based on their potential.
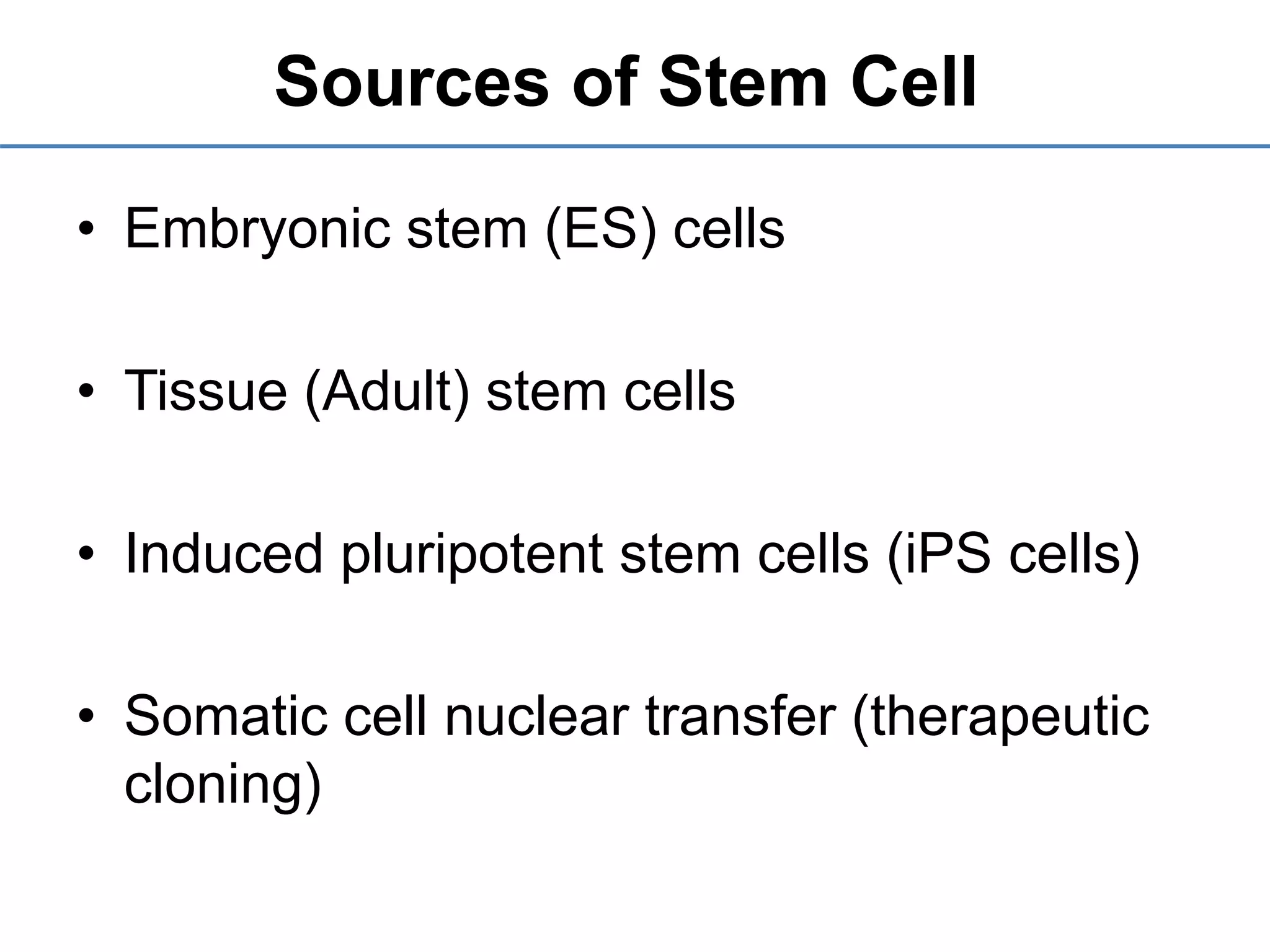
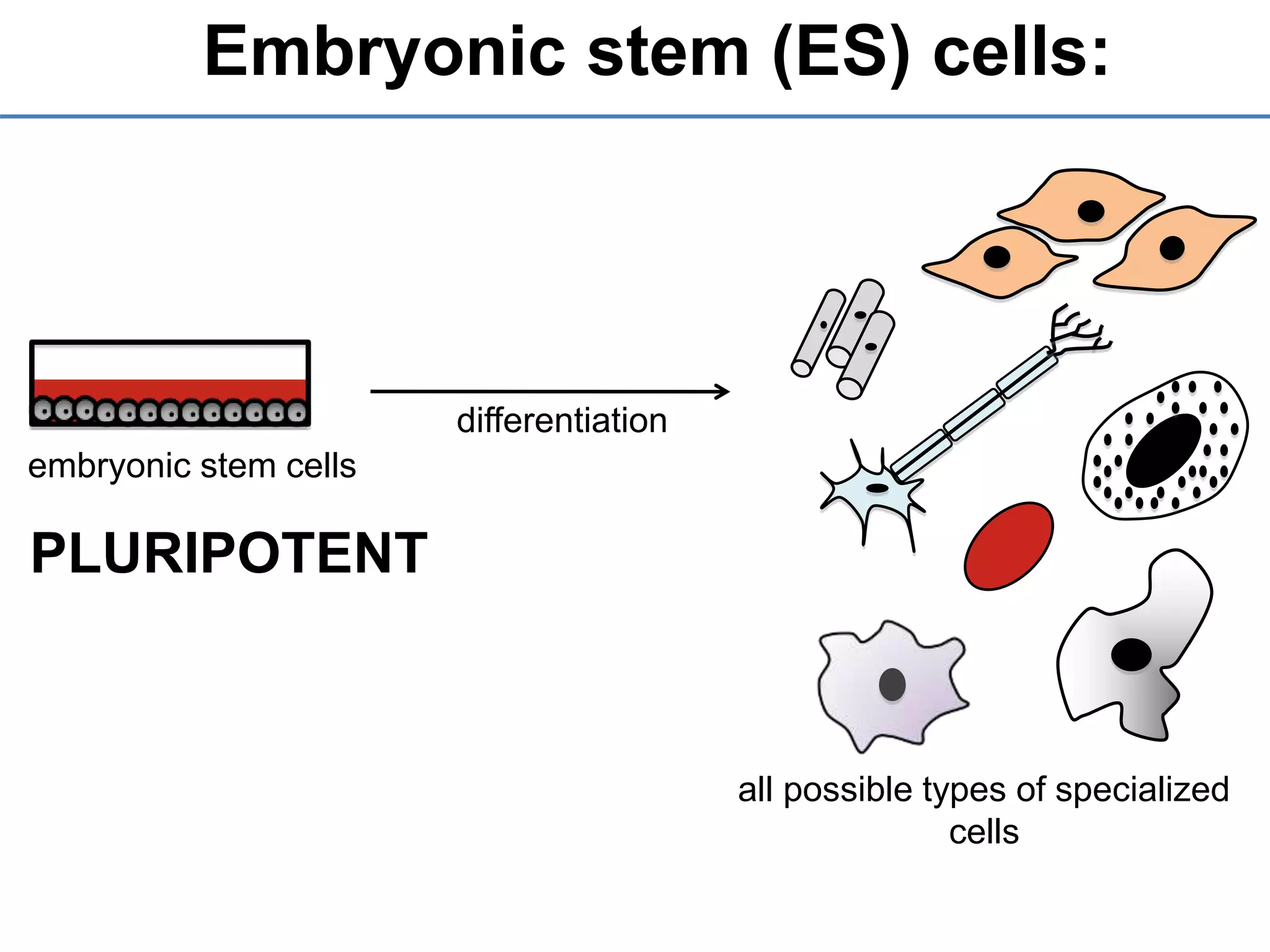
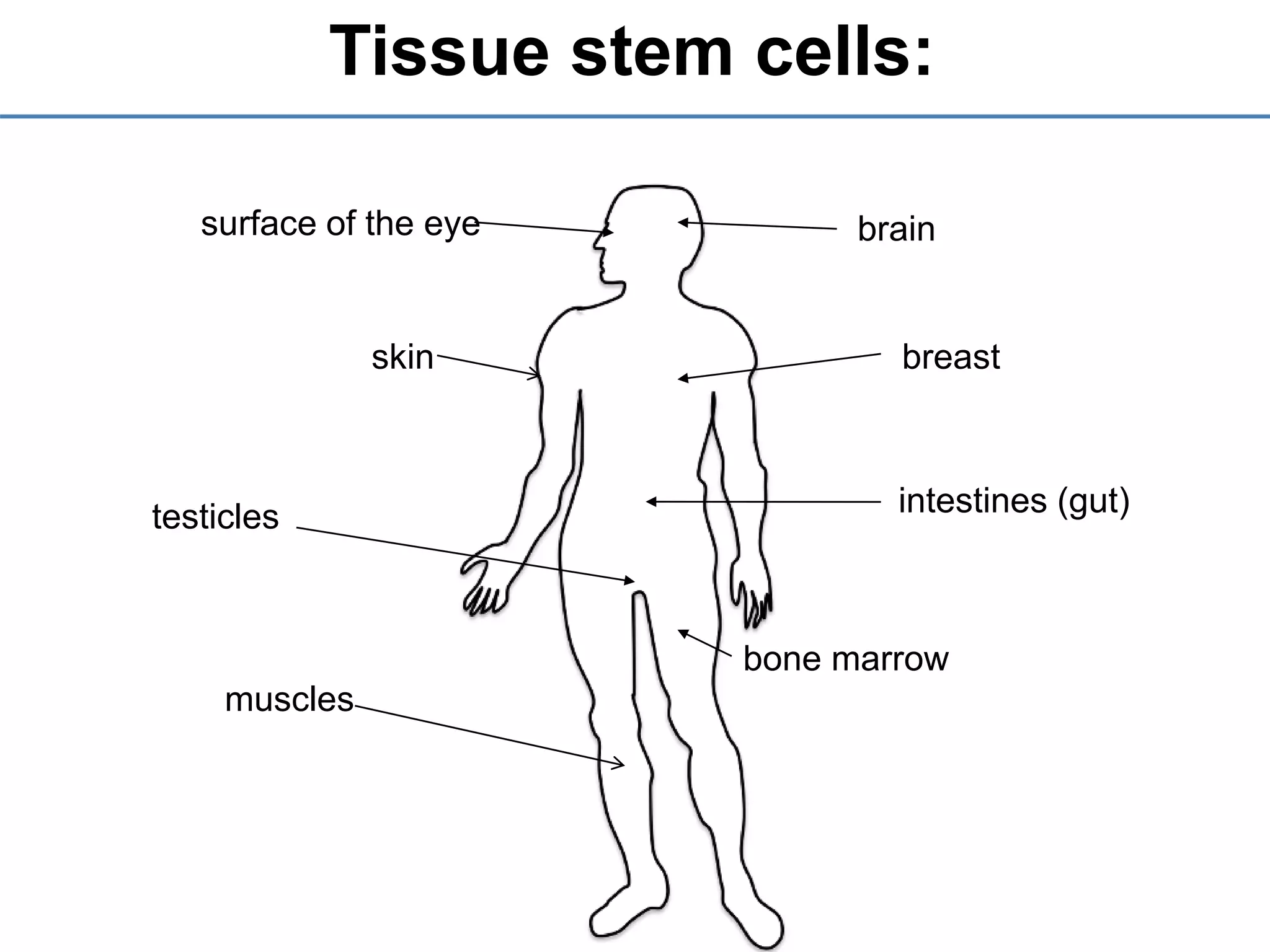
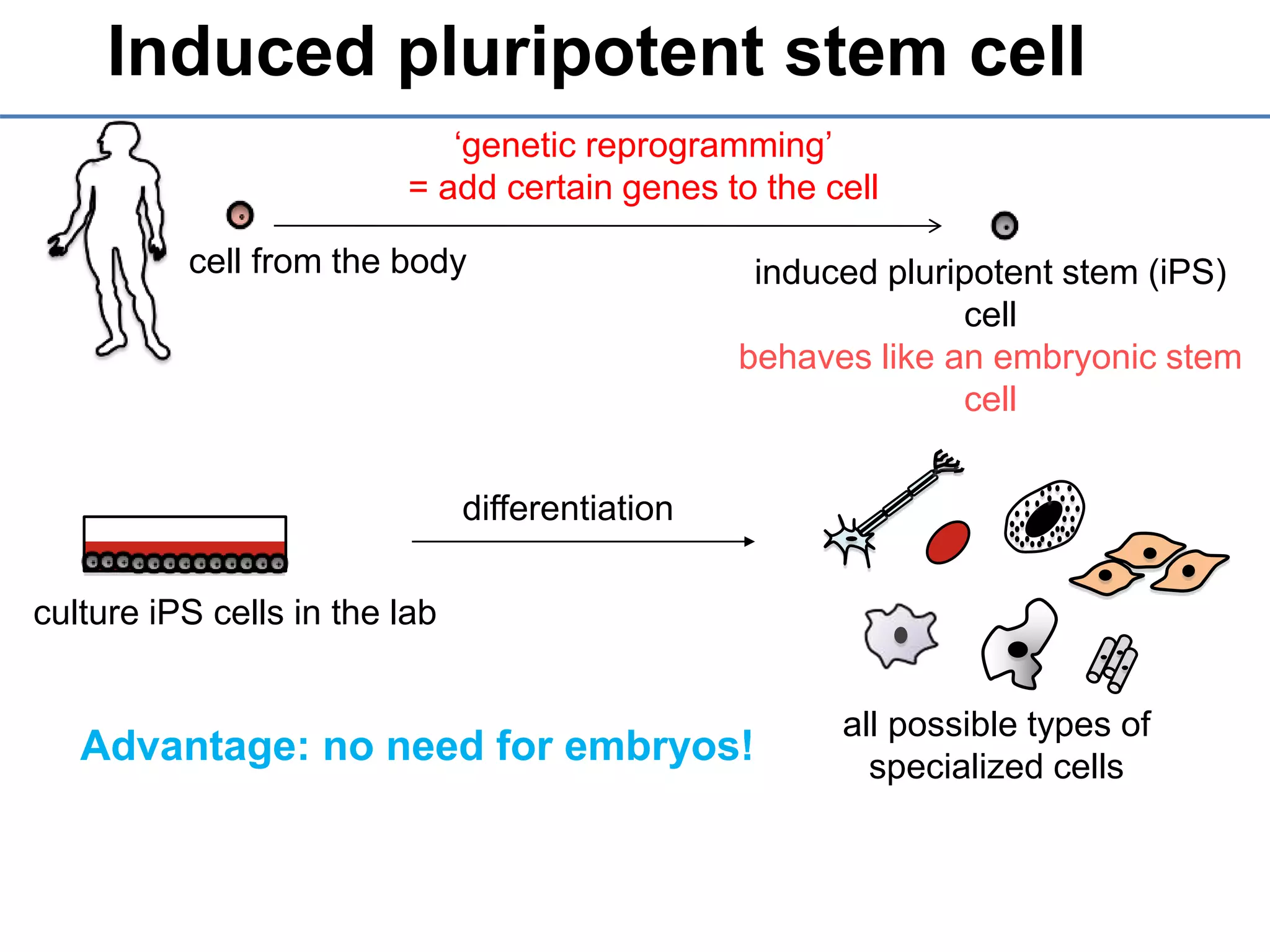
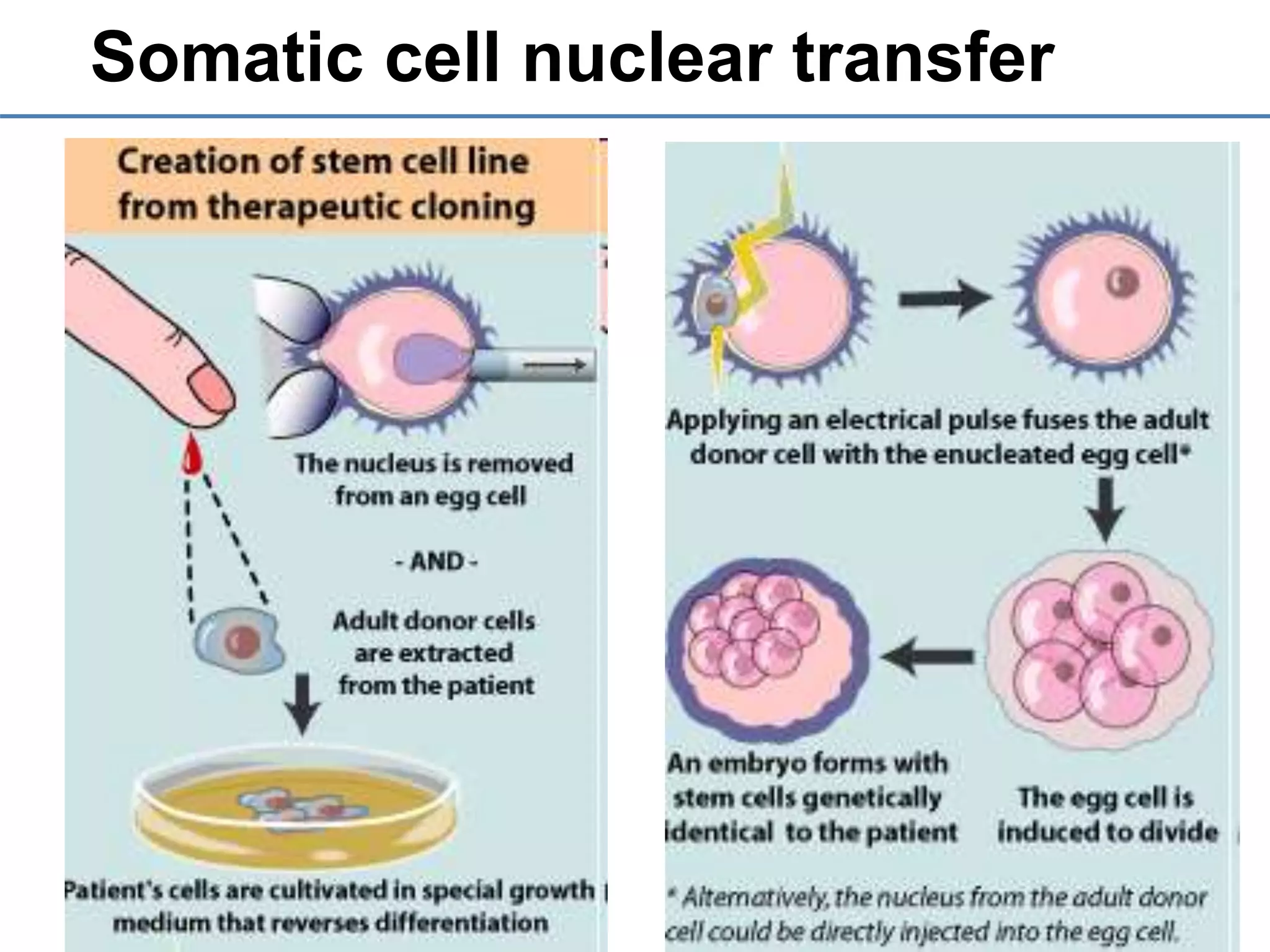
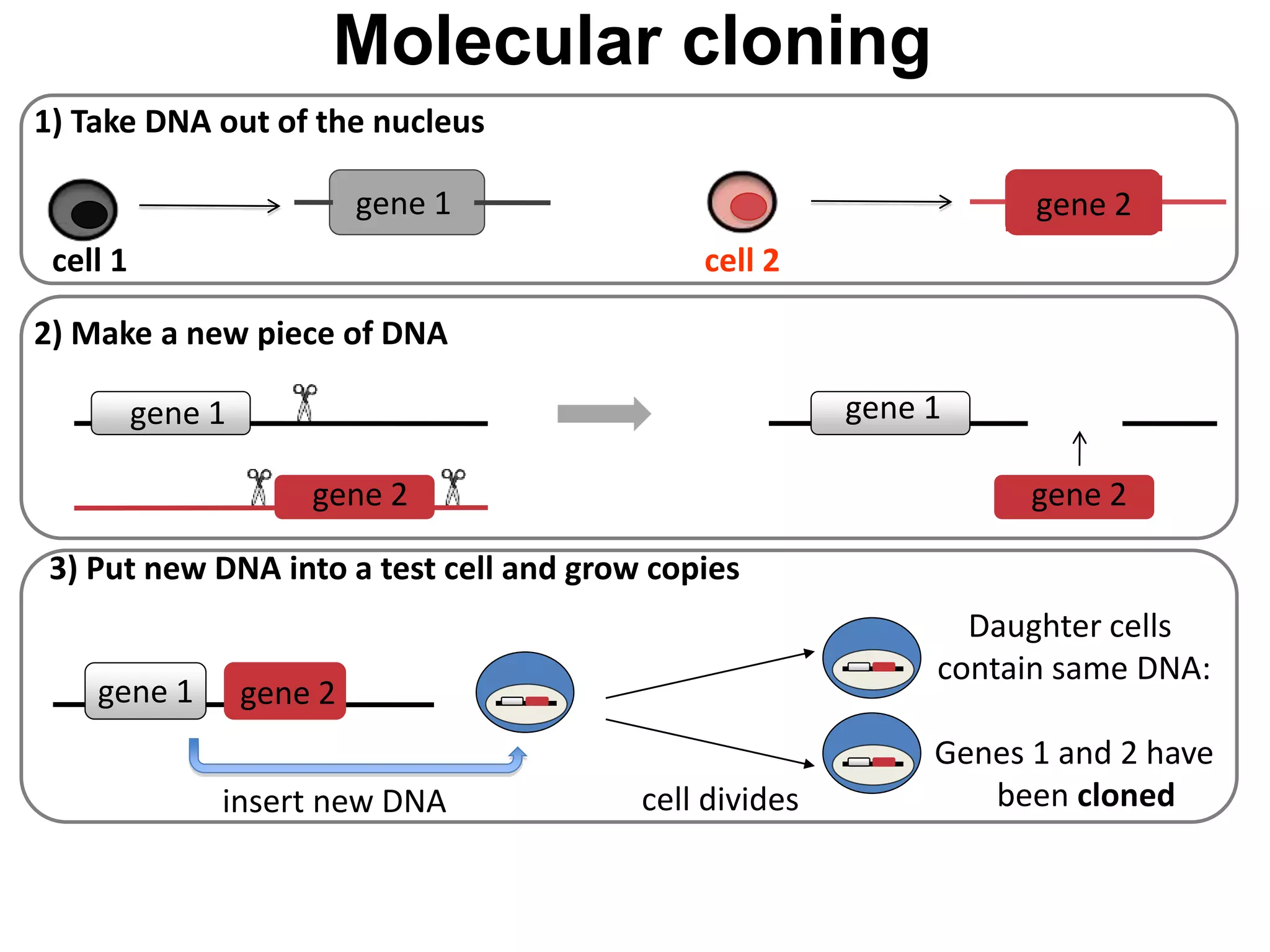
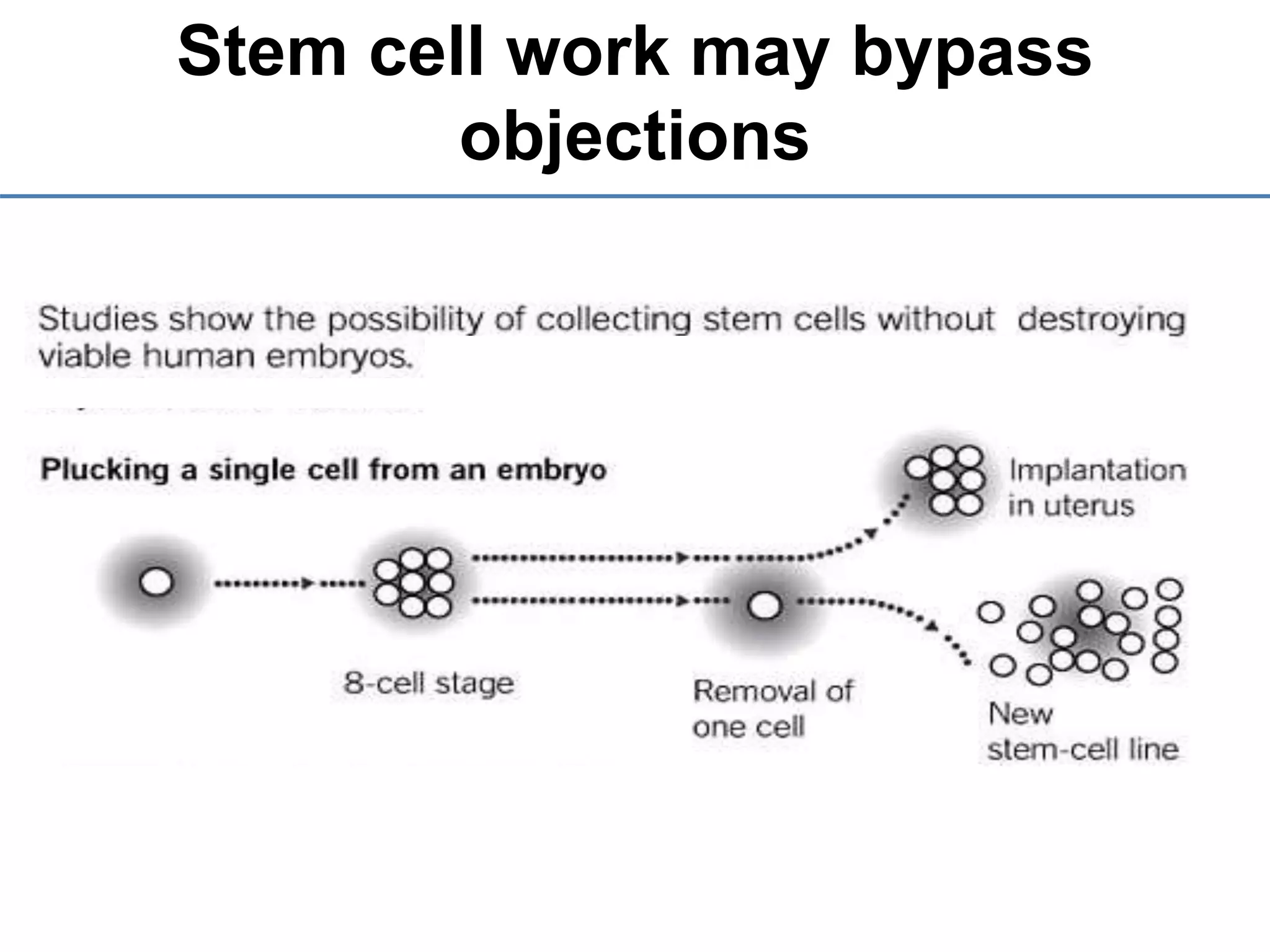
2) It discusses the sources of stem cells, including embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells, and therapeutic cloning.
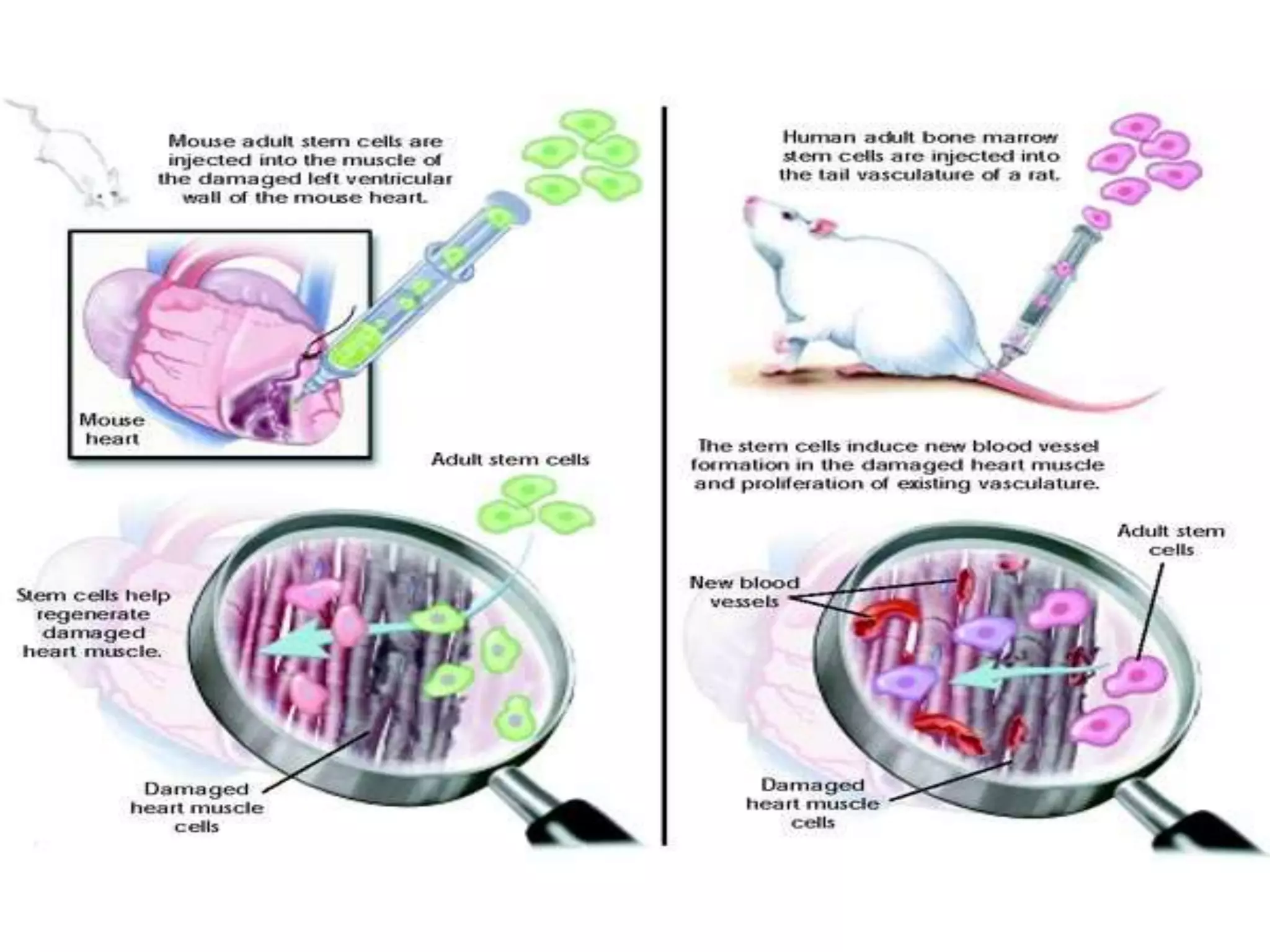
3) It outlines the steps involved in stem cell therapy and provides examples of health problems that may be treated by stem cells, such as Parkinson's disease, heart disease, and diabetes.