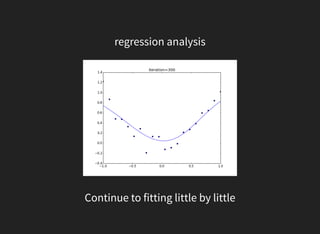
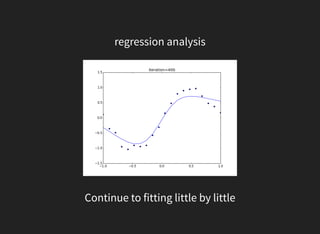
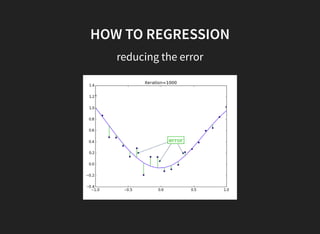
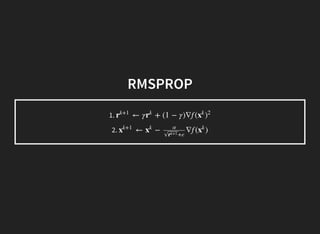
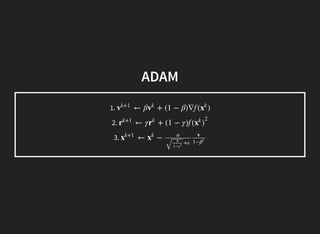
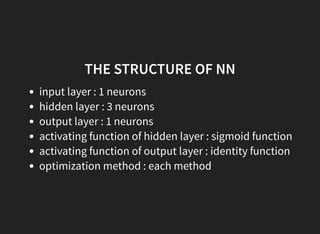
This document discusses gradient descent optimization methods. It begins by explaining where gradient methods are used, such as in regression and machine learning problems. It then introduces several gradient descent algorithms - steepest descent, momentum, Nesterov's accelerated gradient, and others. It provides explanations of how each algorithm works. The document ends by performing benchmarks comparing the algorithms on MNIST data and a regression problem, finding that quasi-Newton and Adam methods tend to work best. In summary, it outlines common gradient descent optimization algorithms and compares their performance on sample problems.