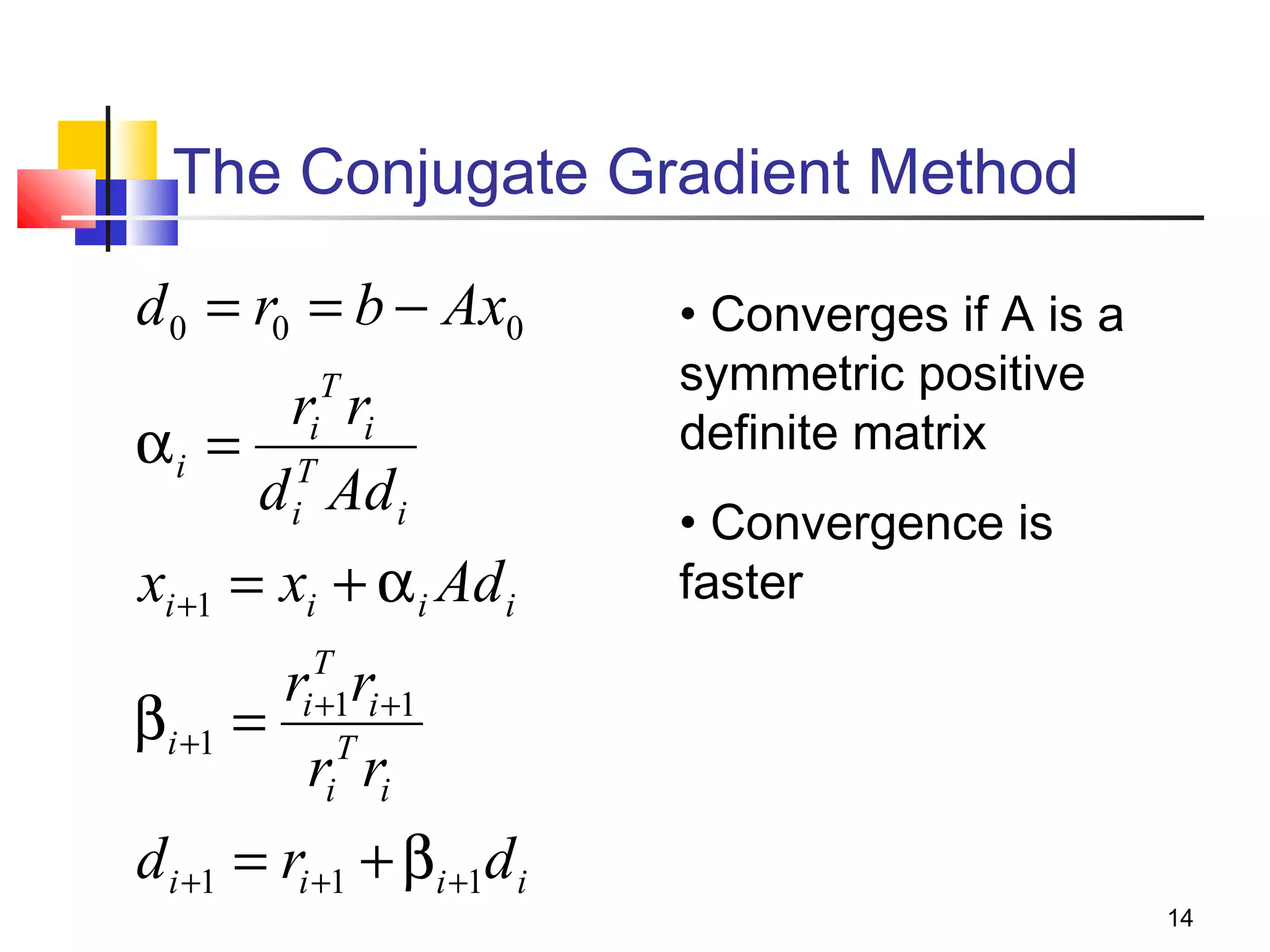
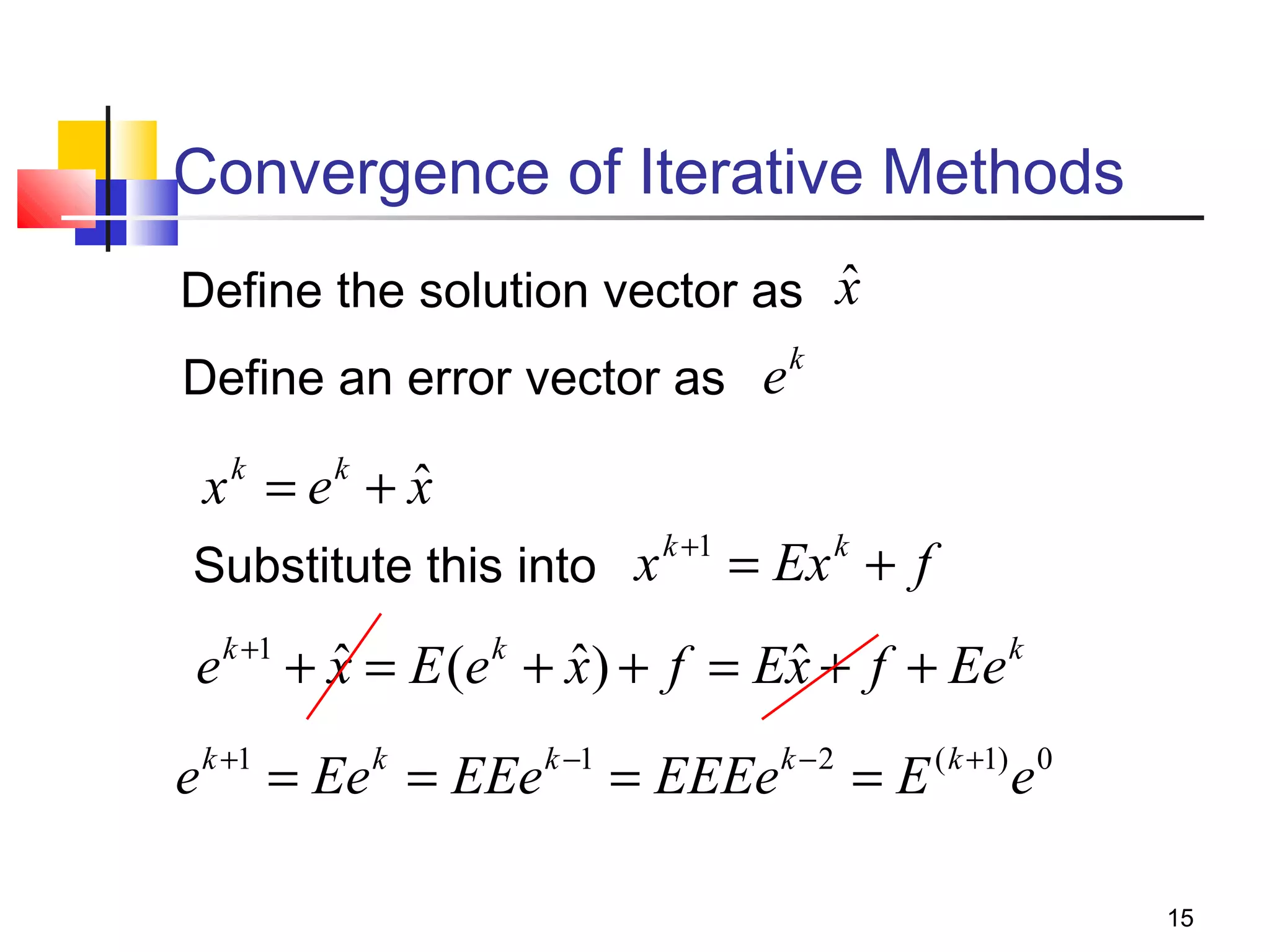
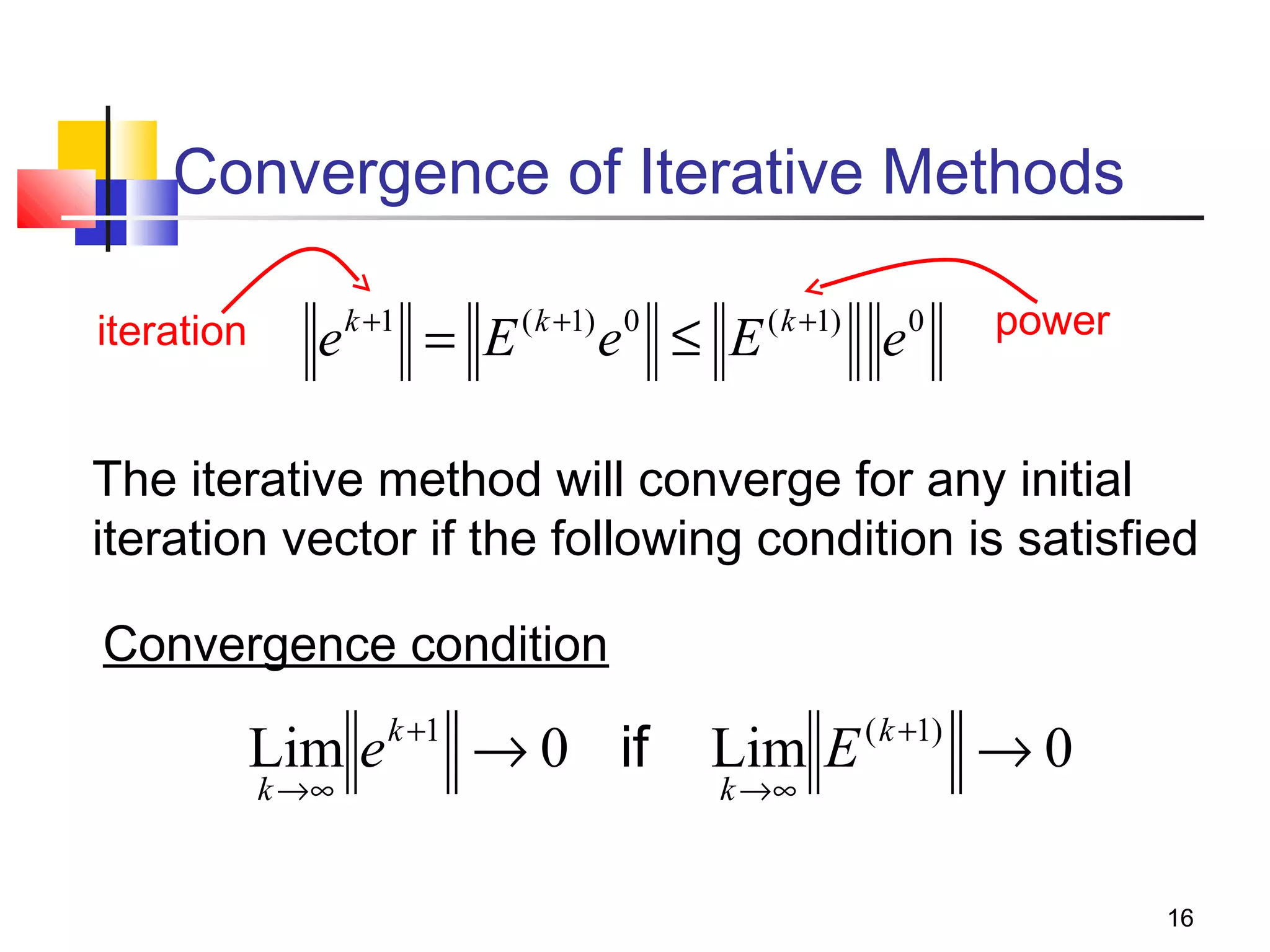
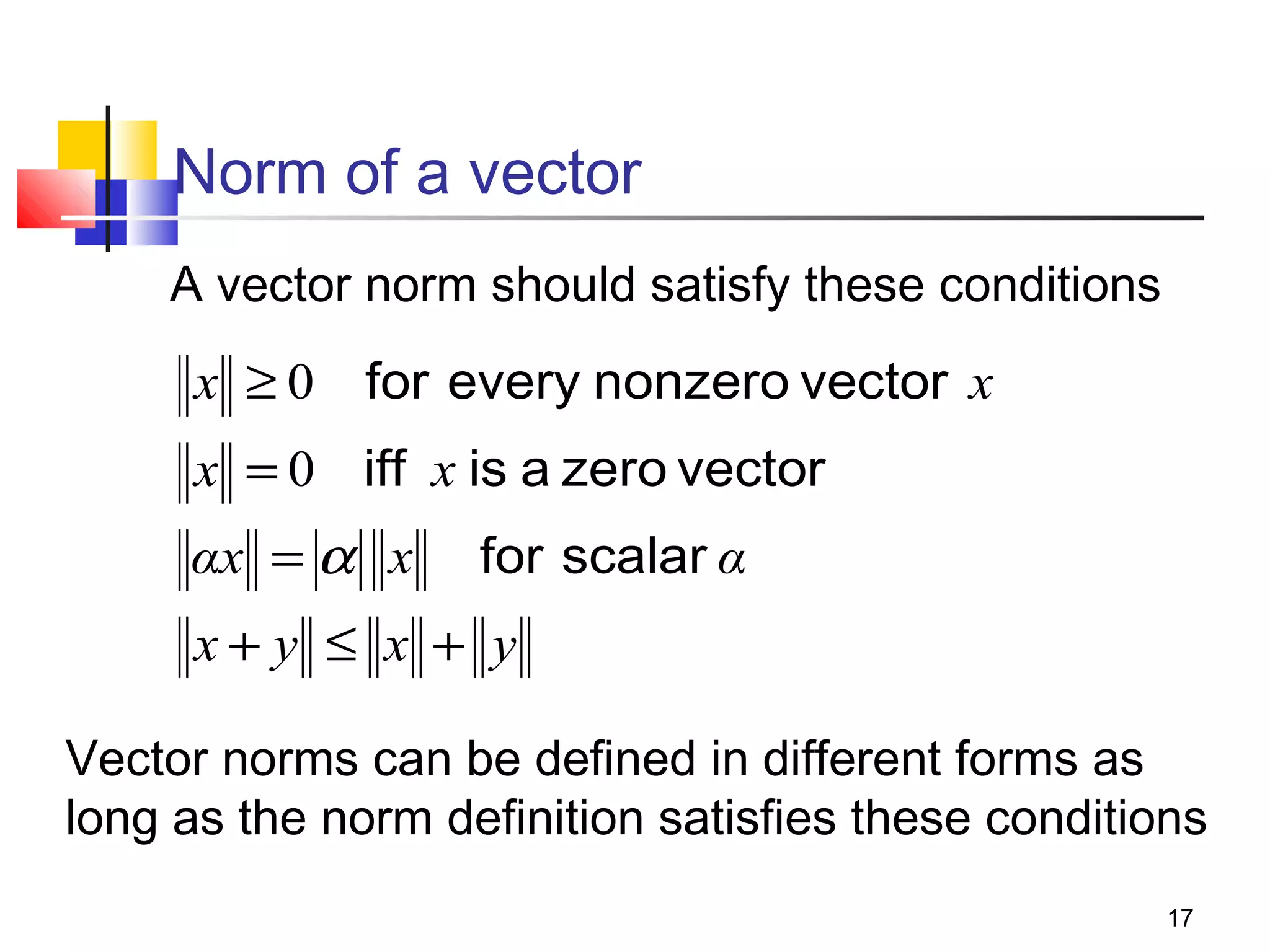
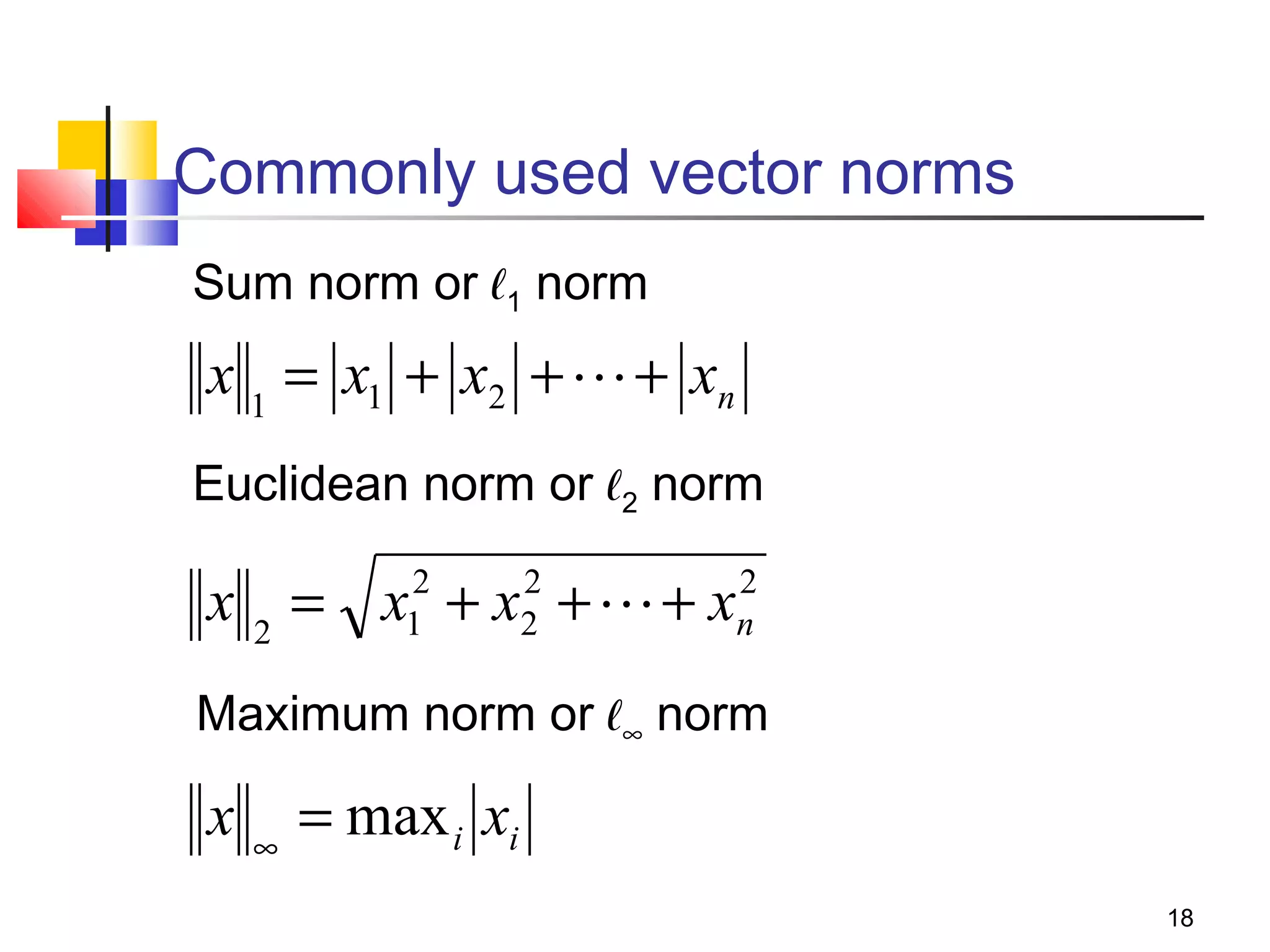
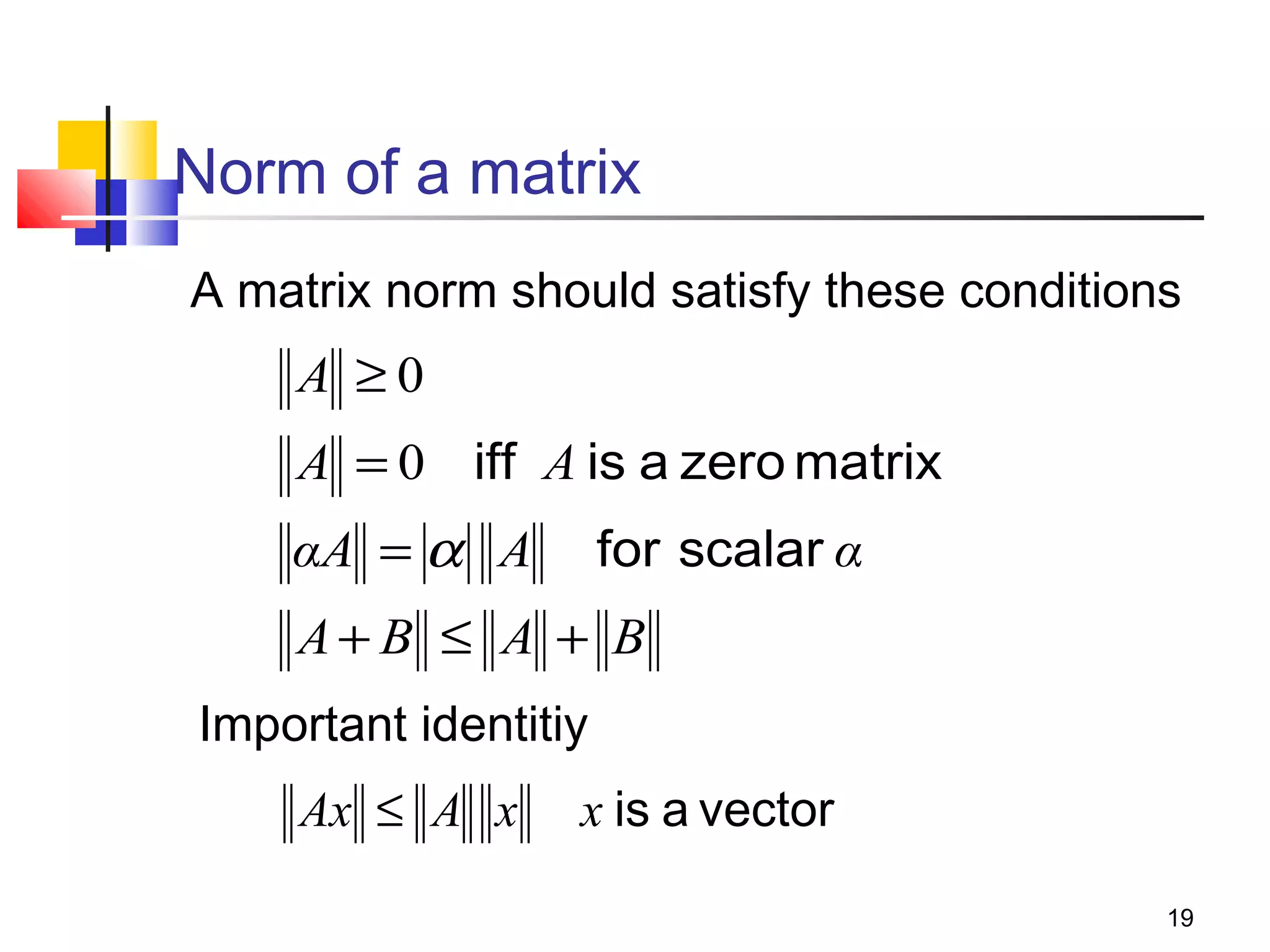
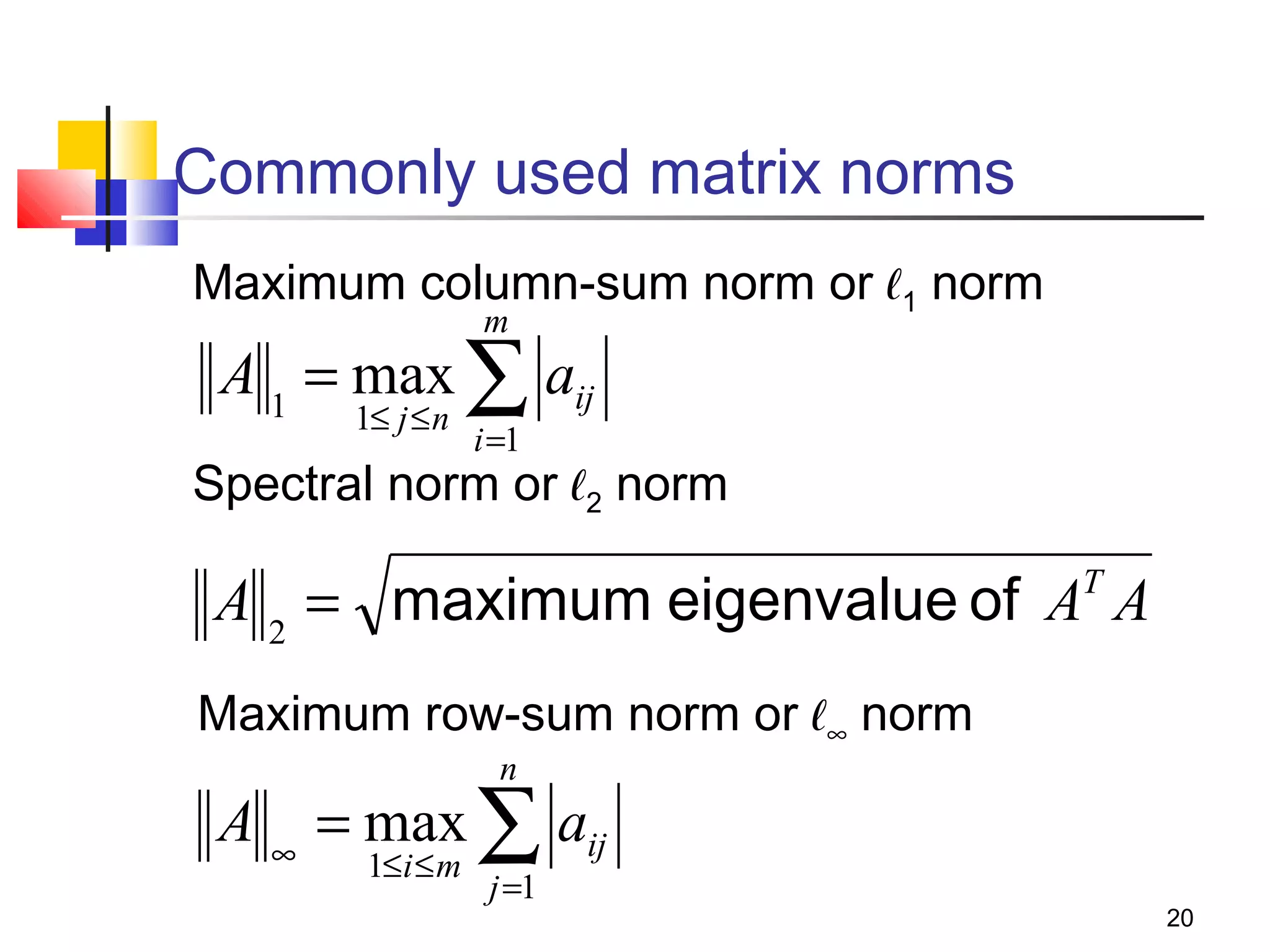
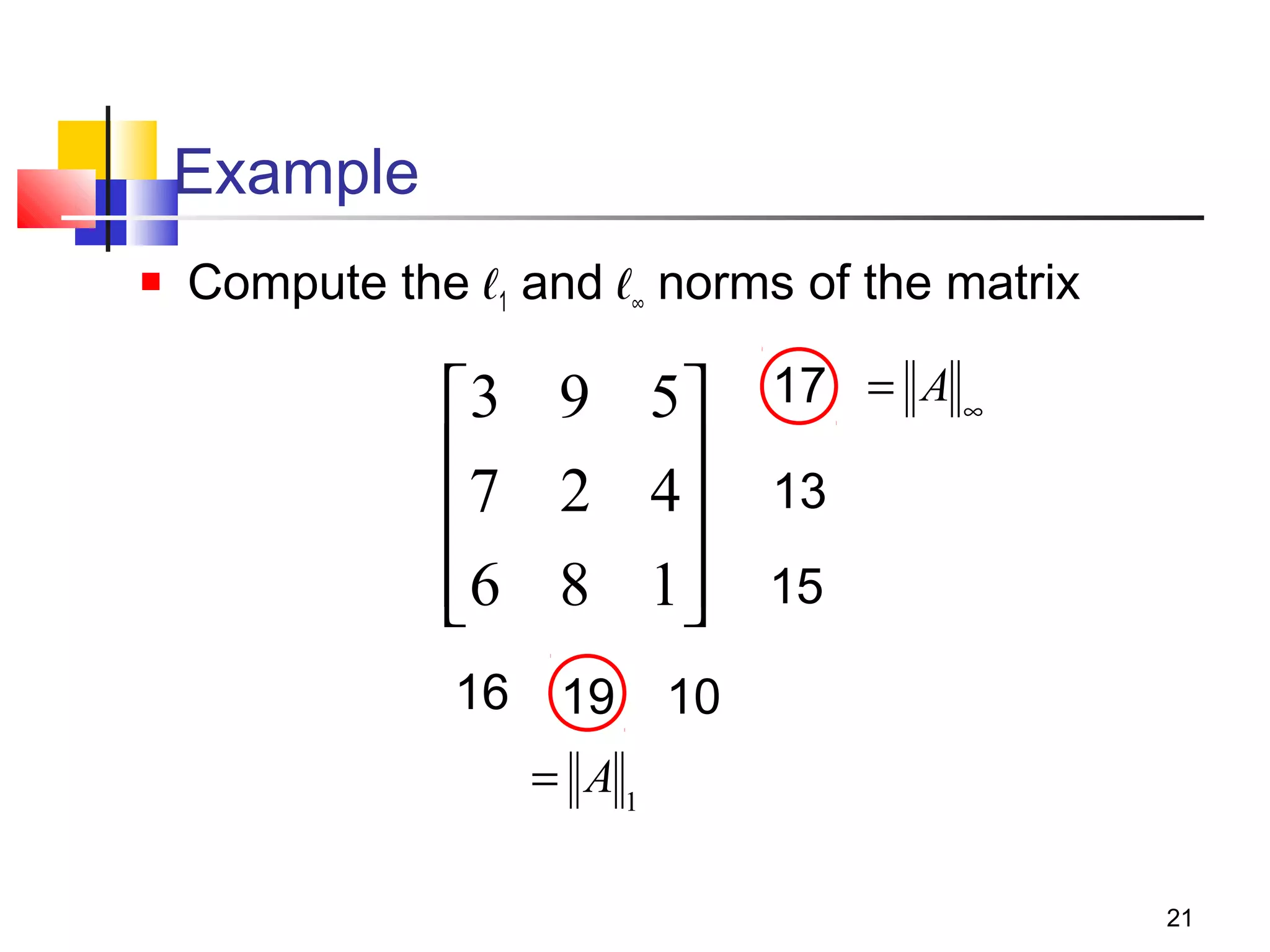
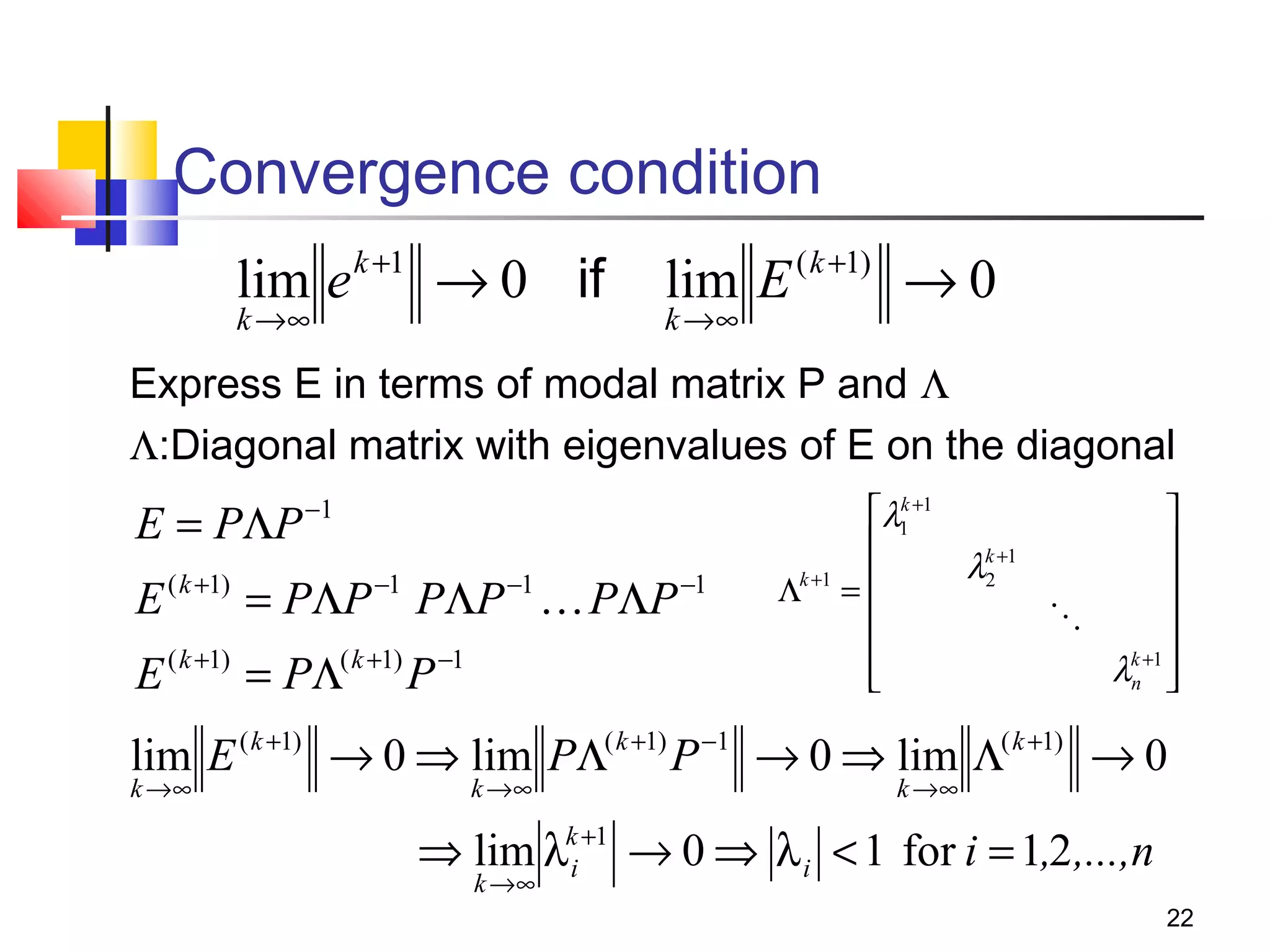
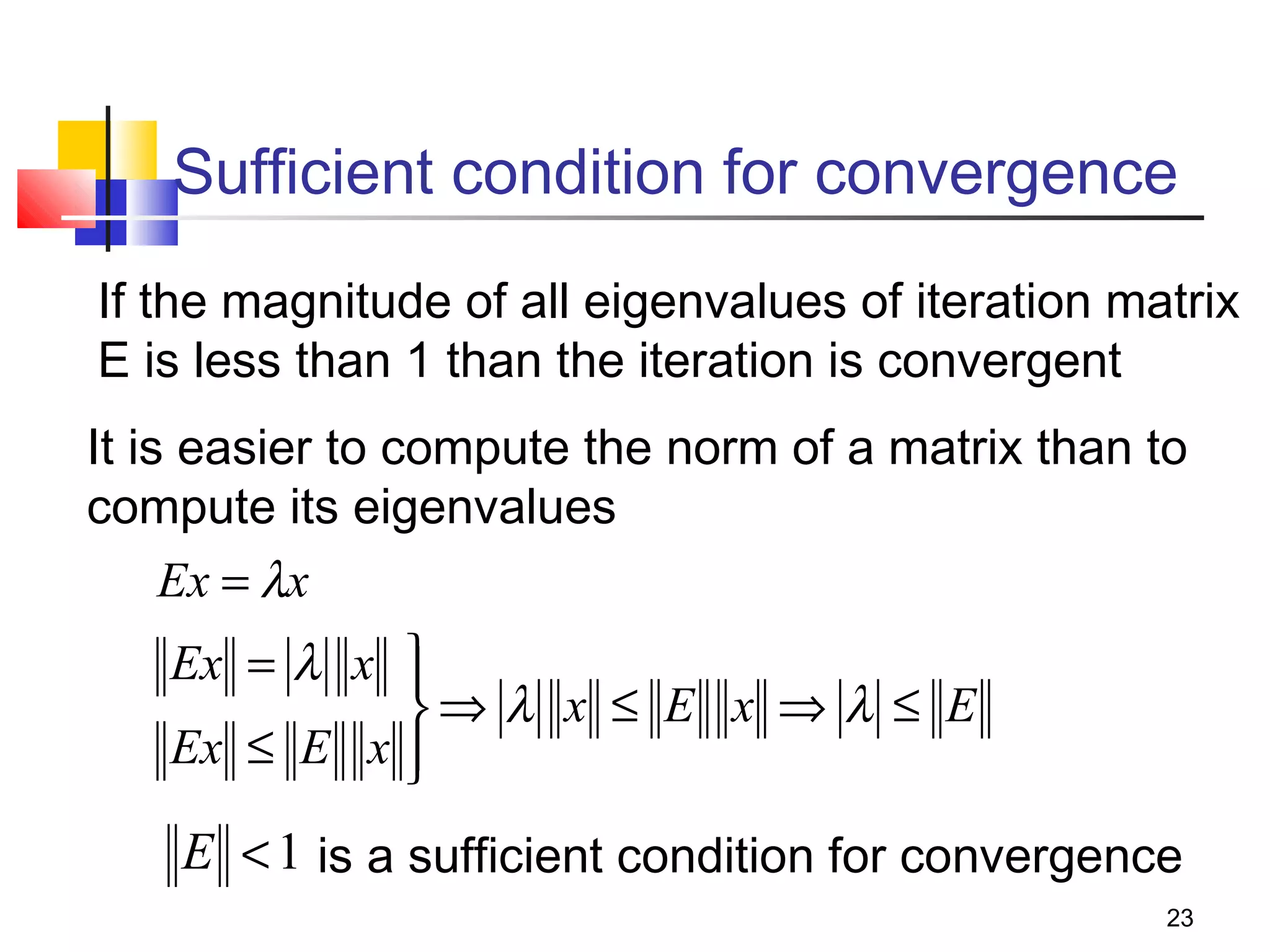
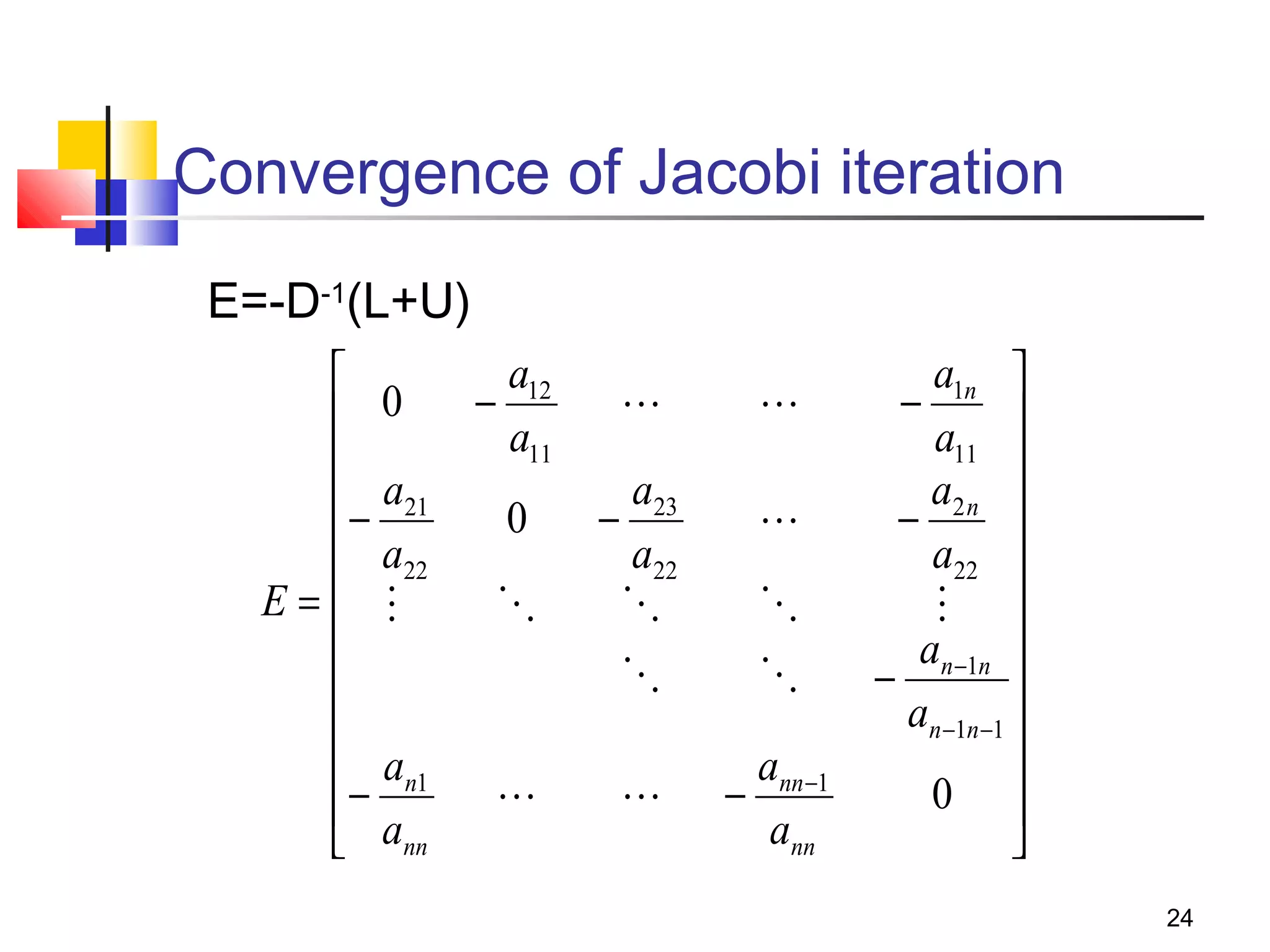
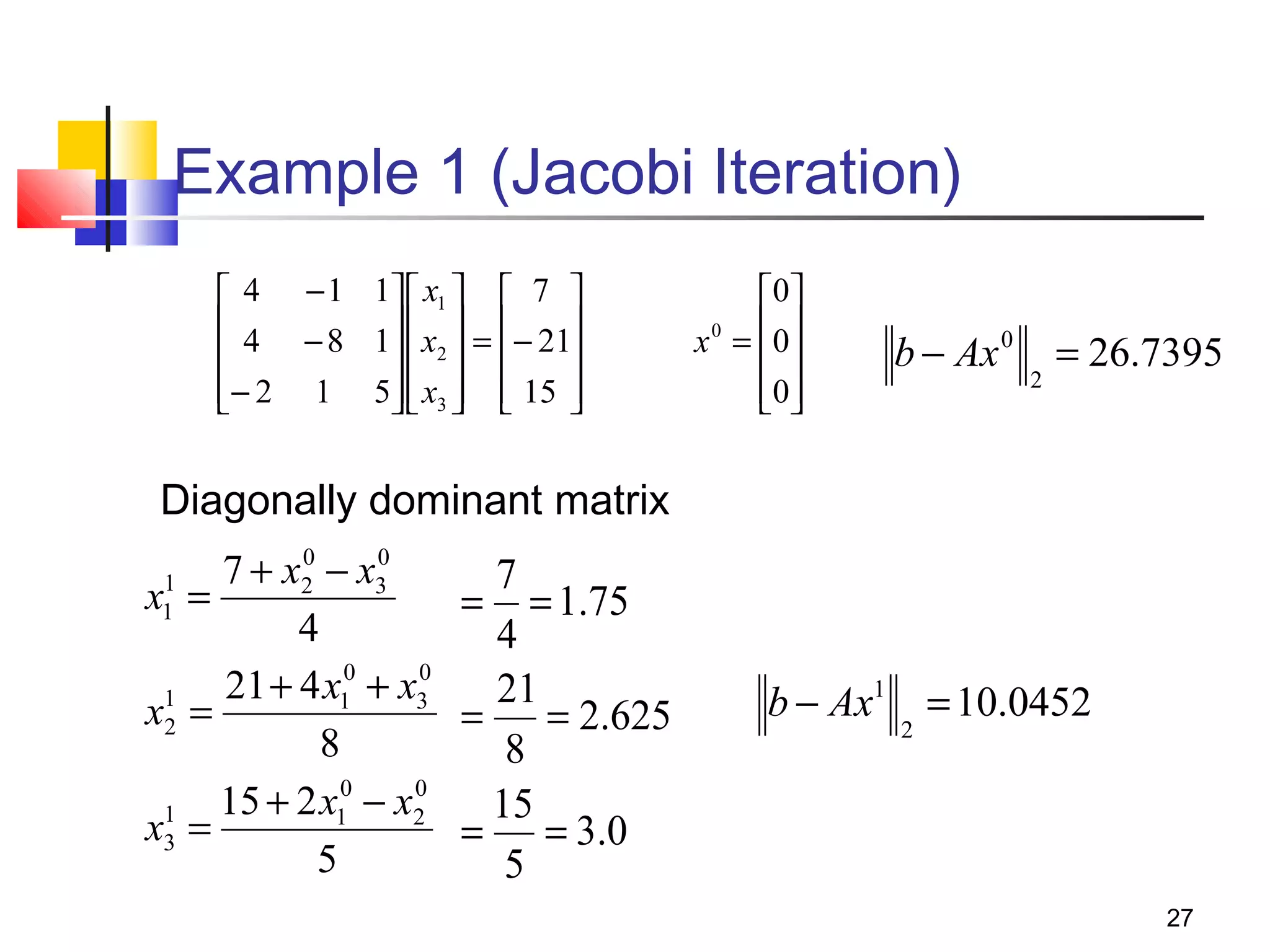
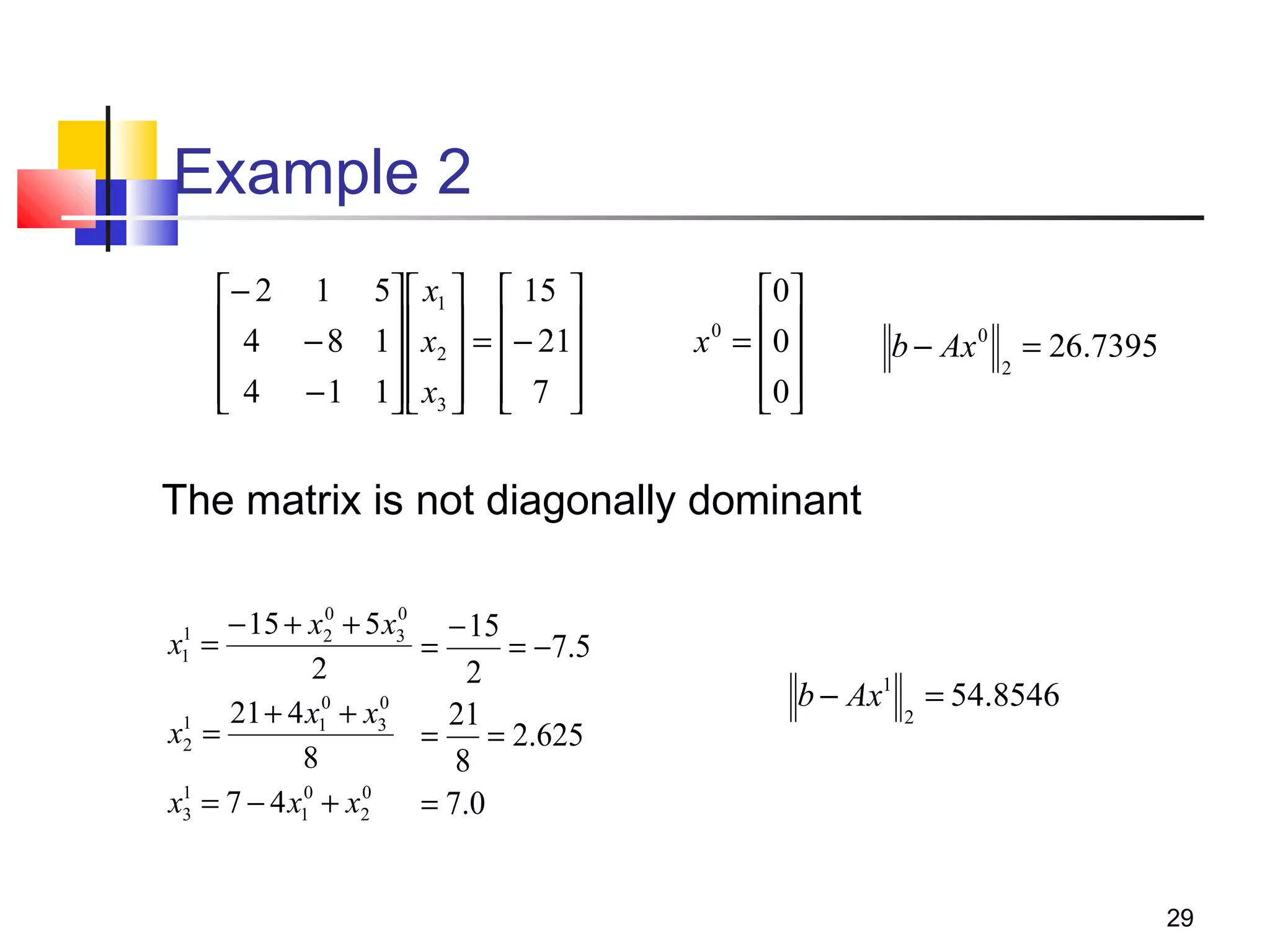
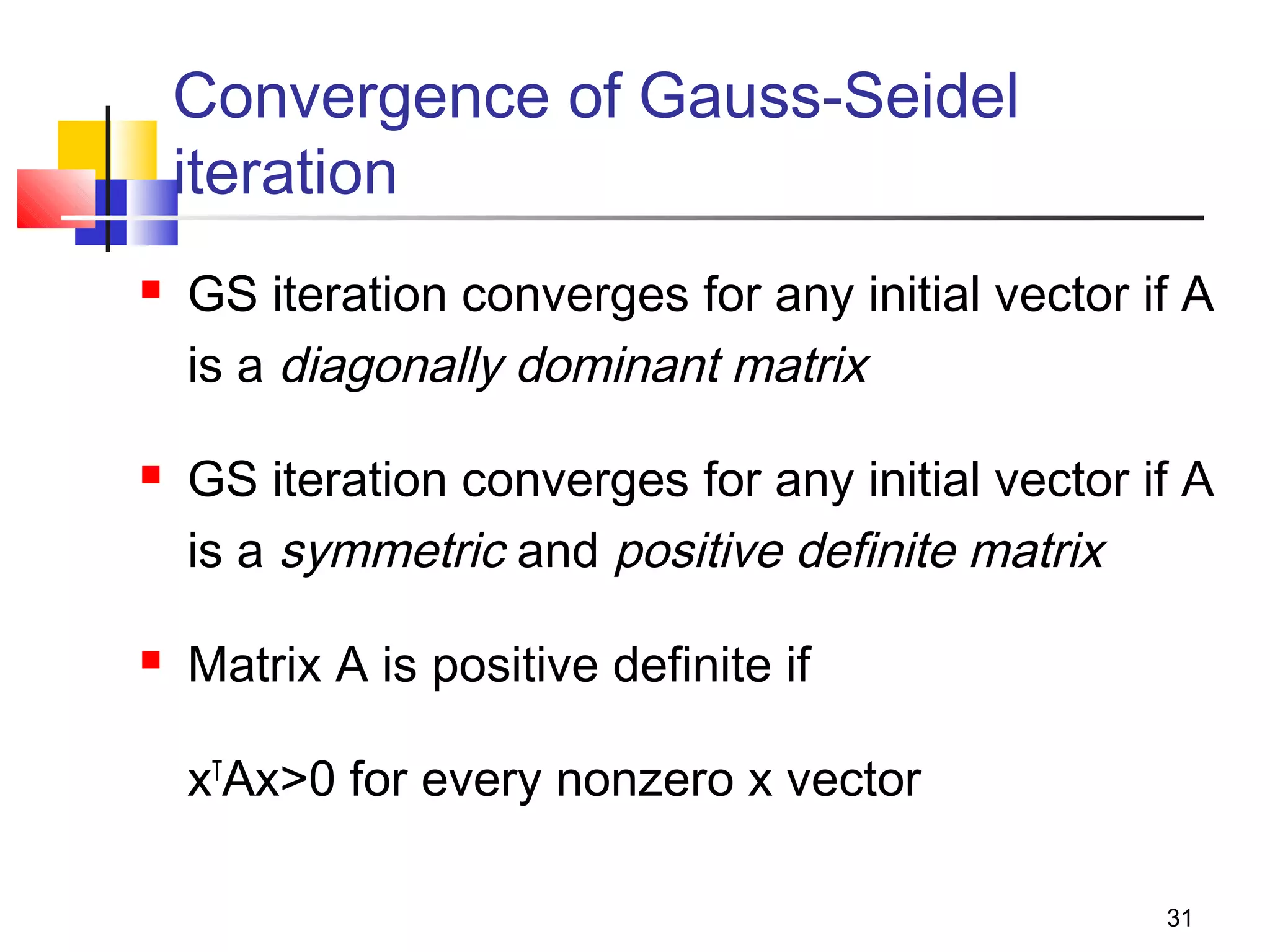
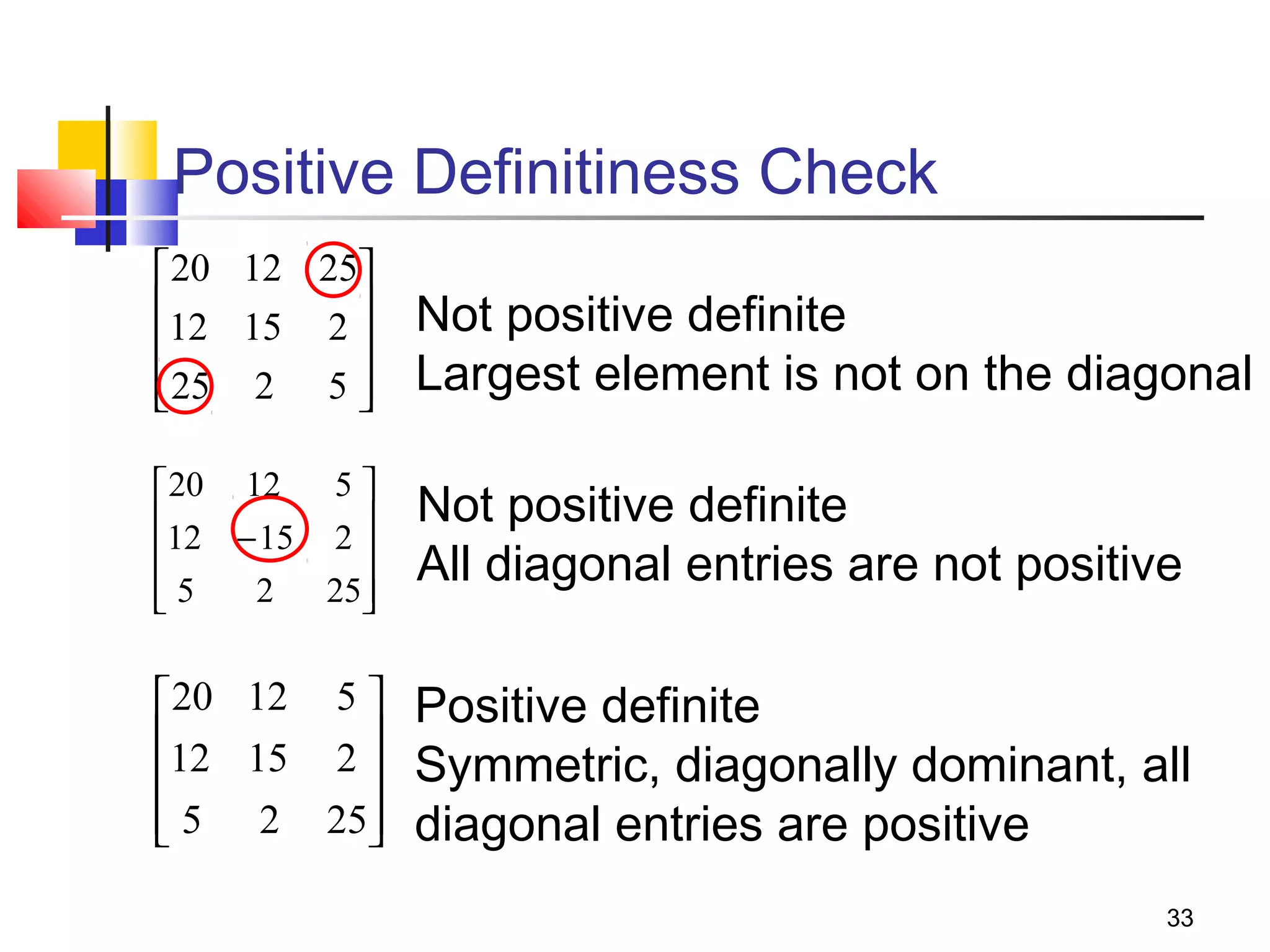
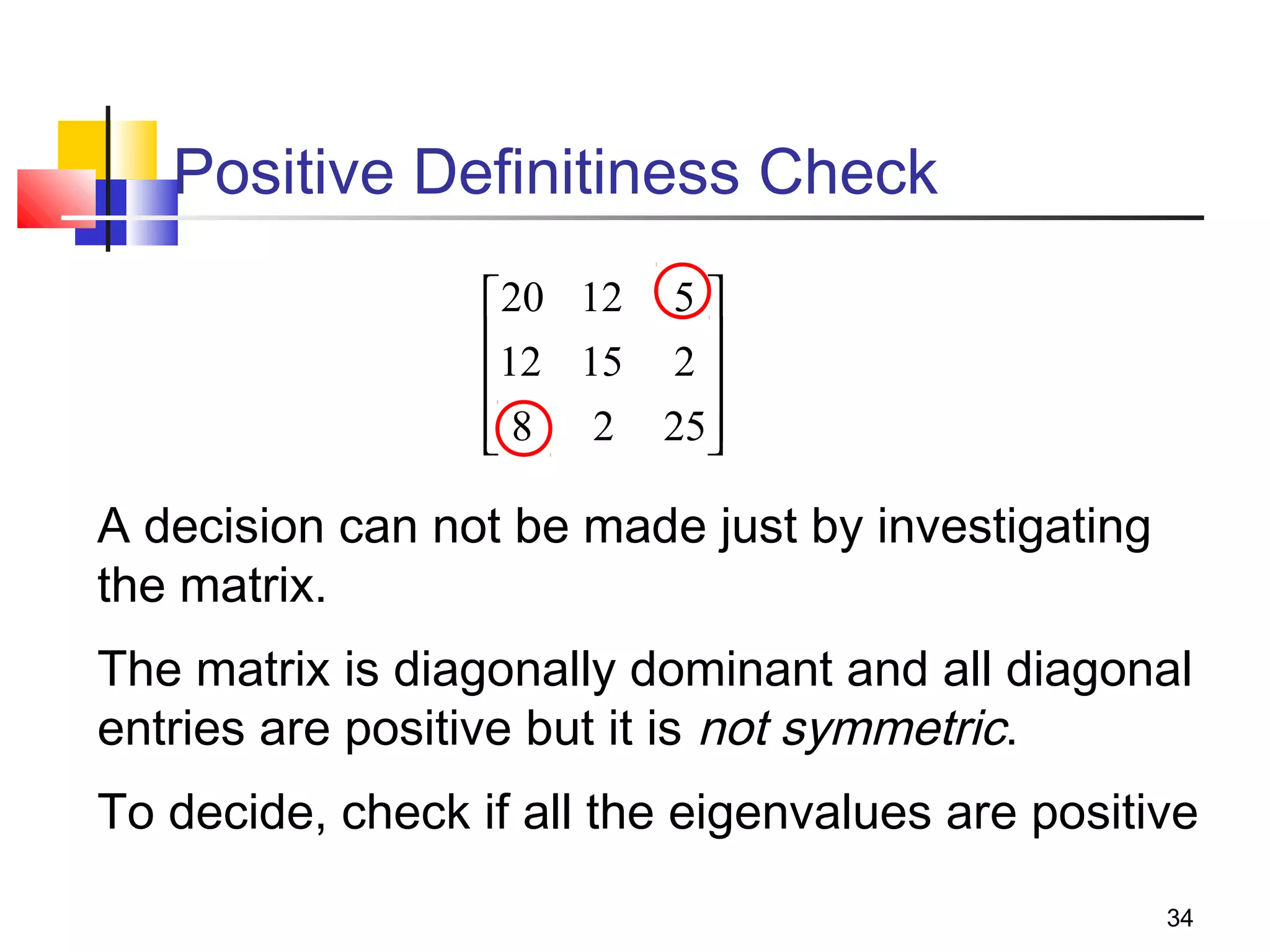
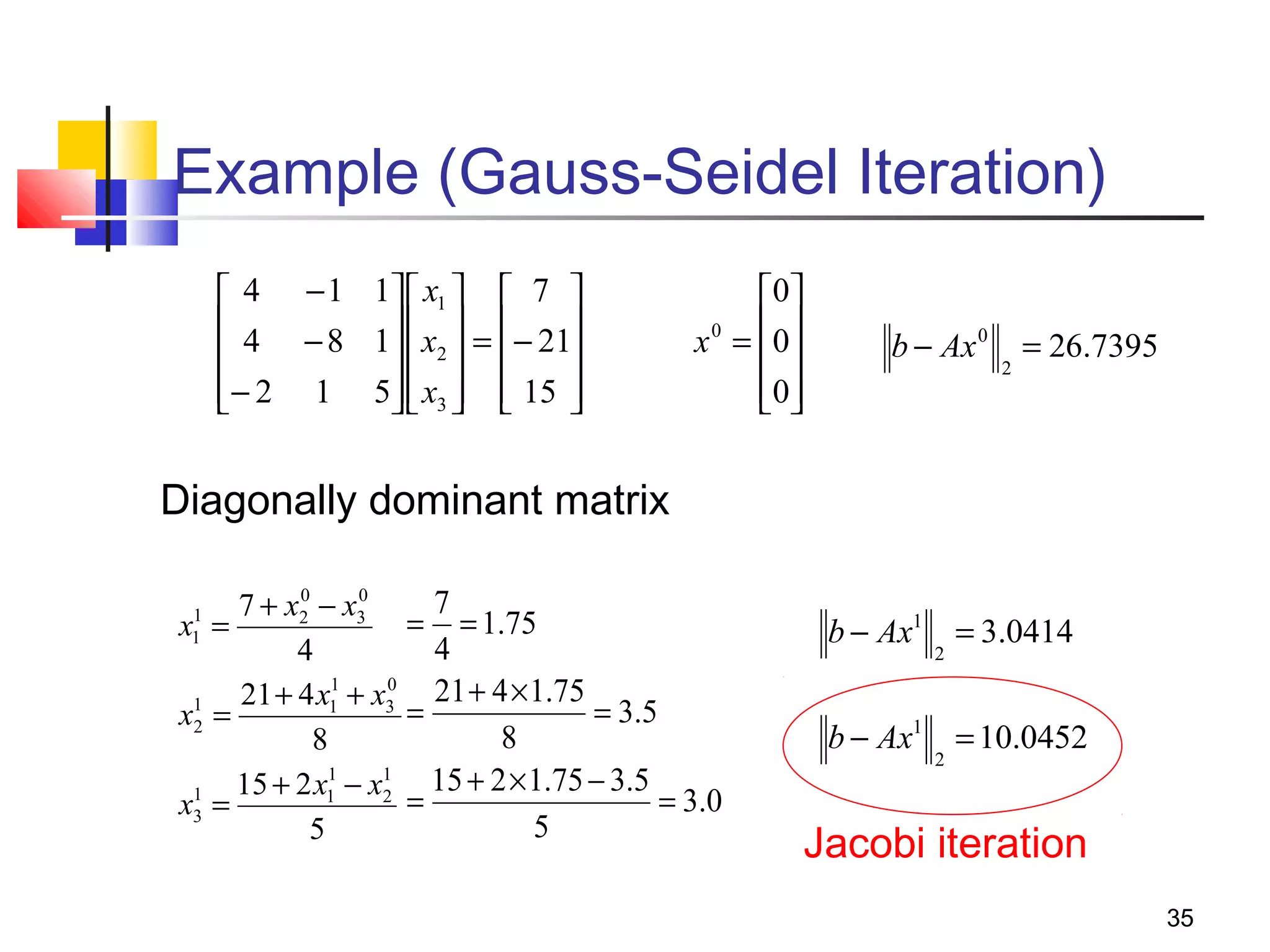
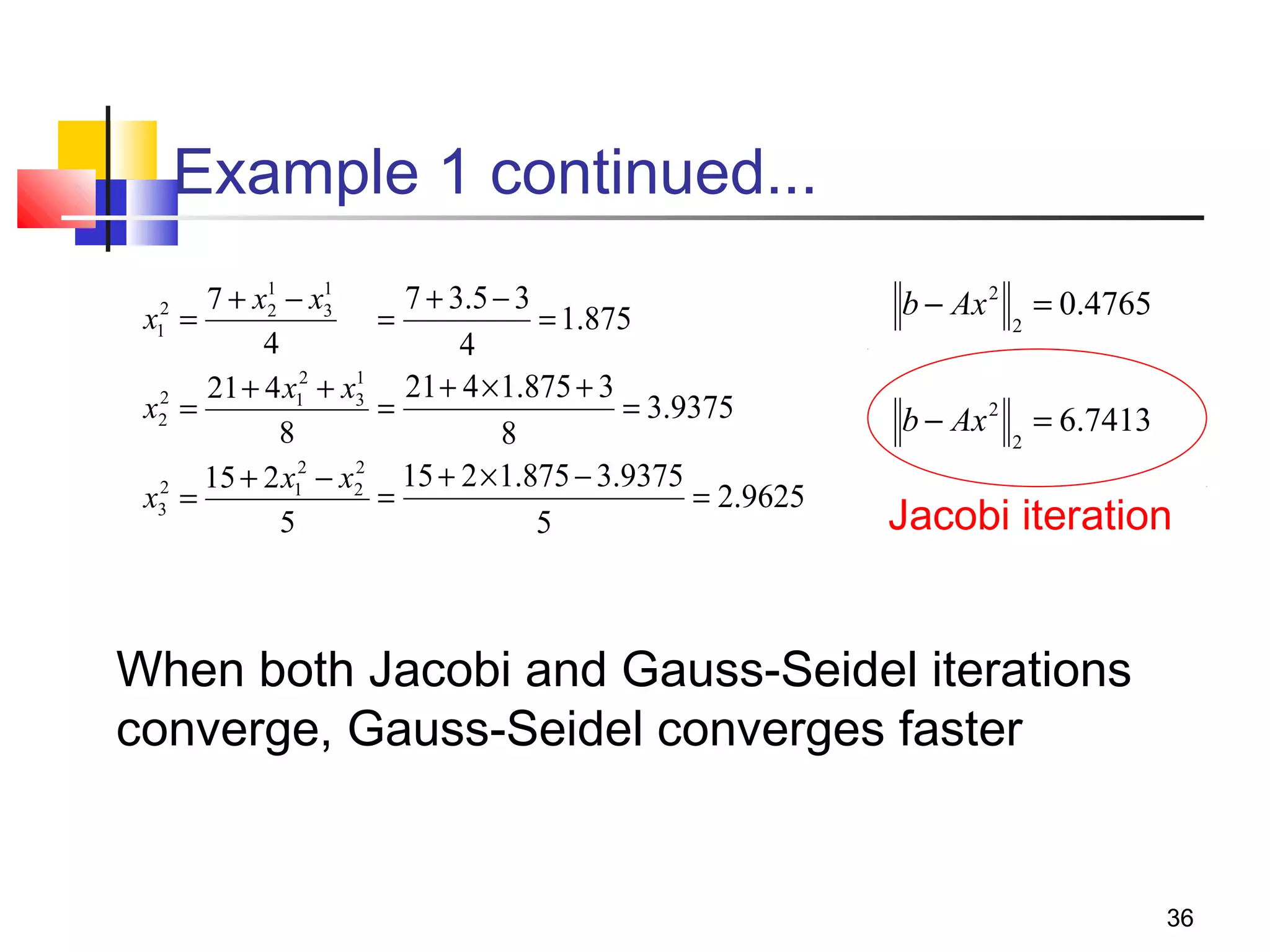
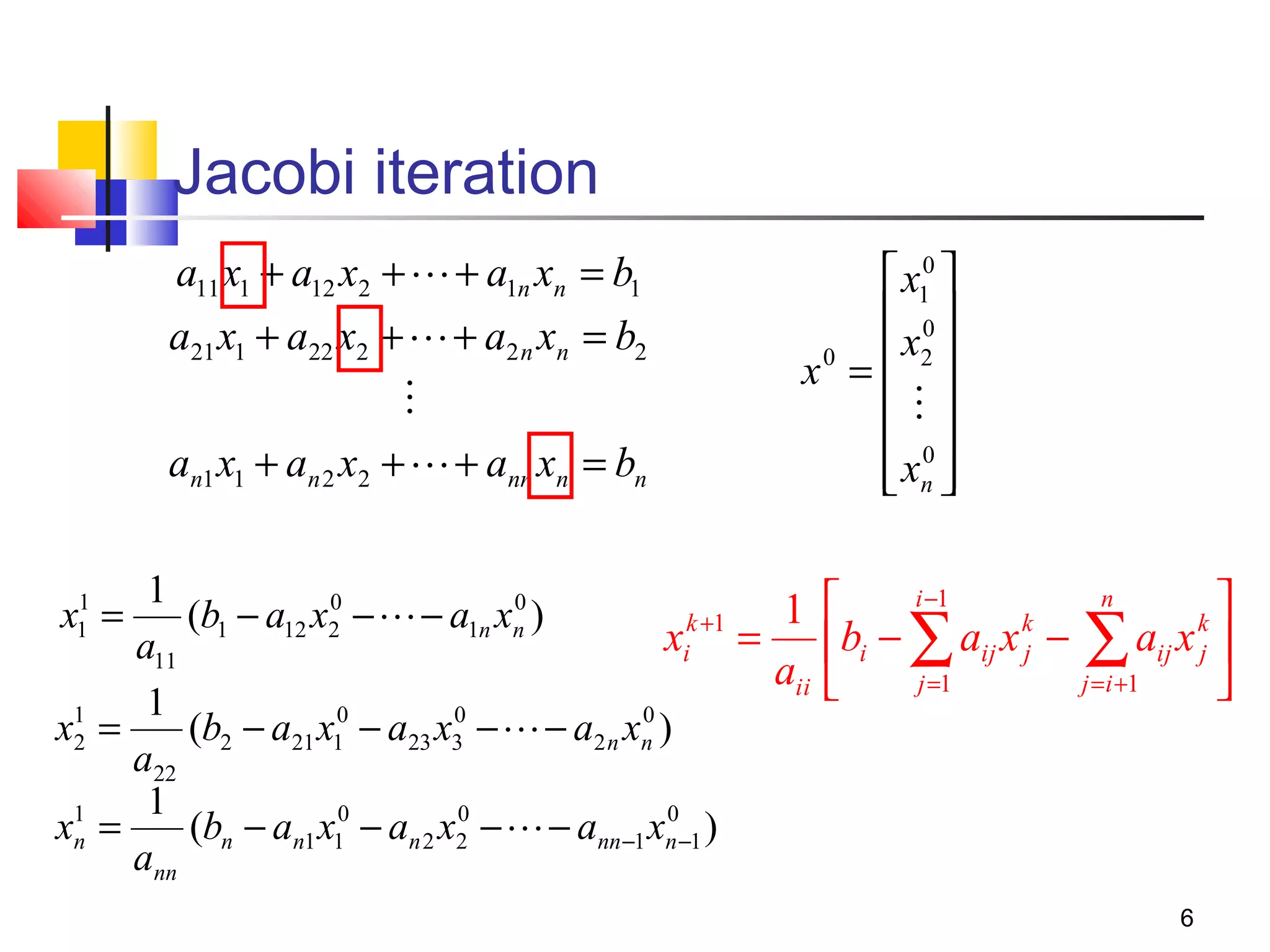
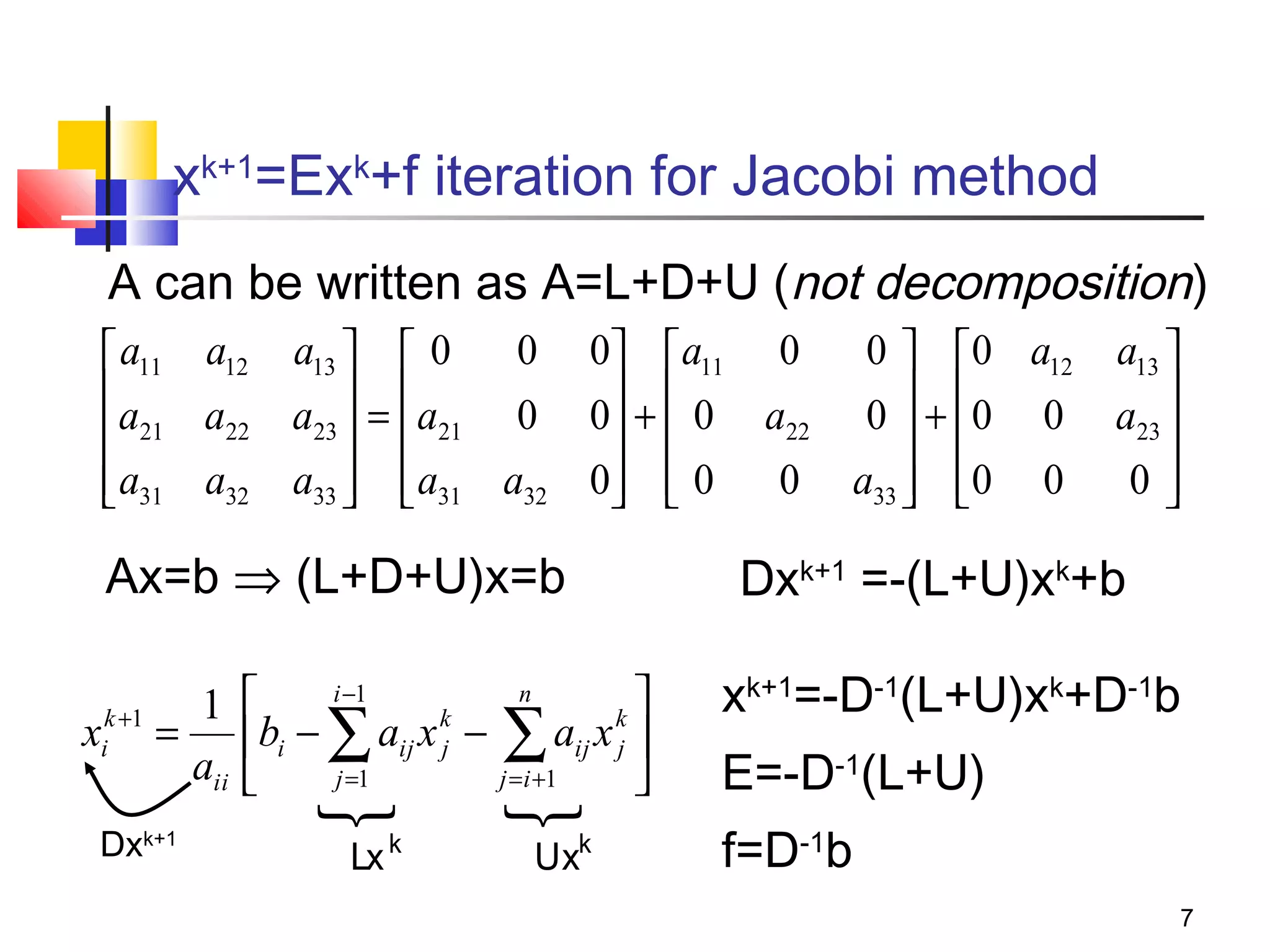
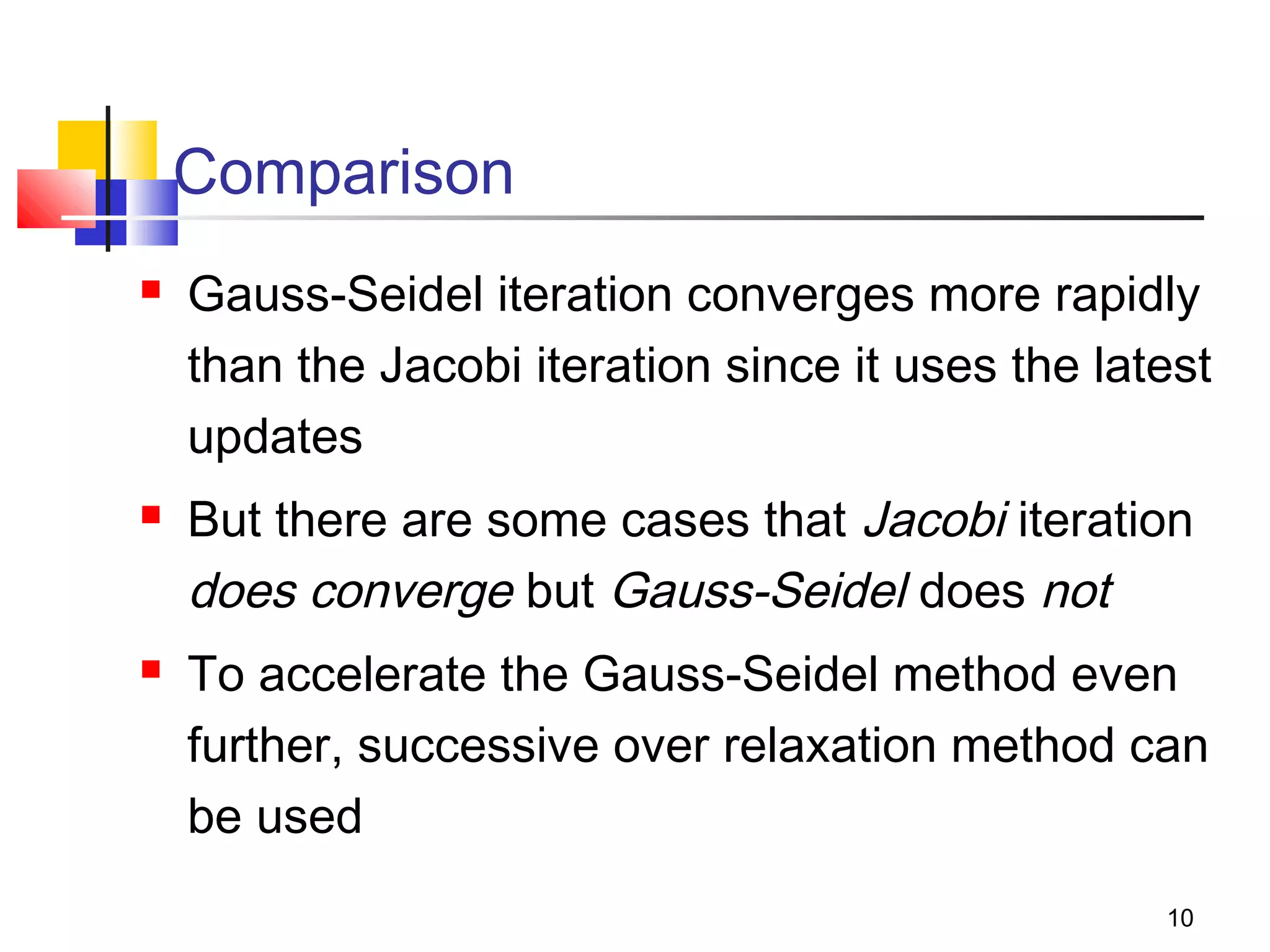
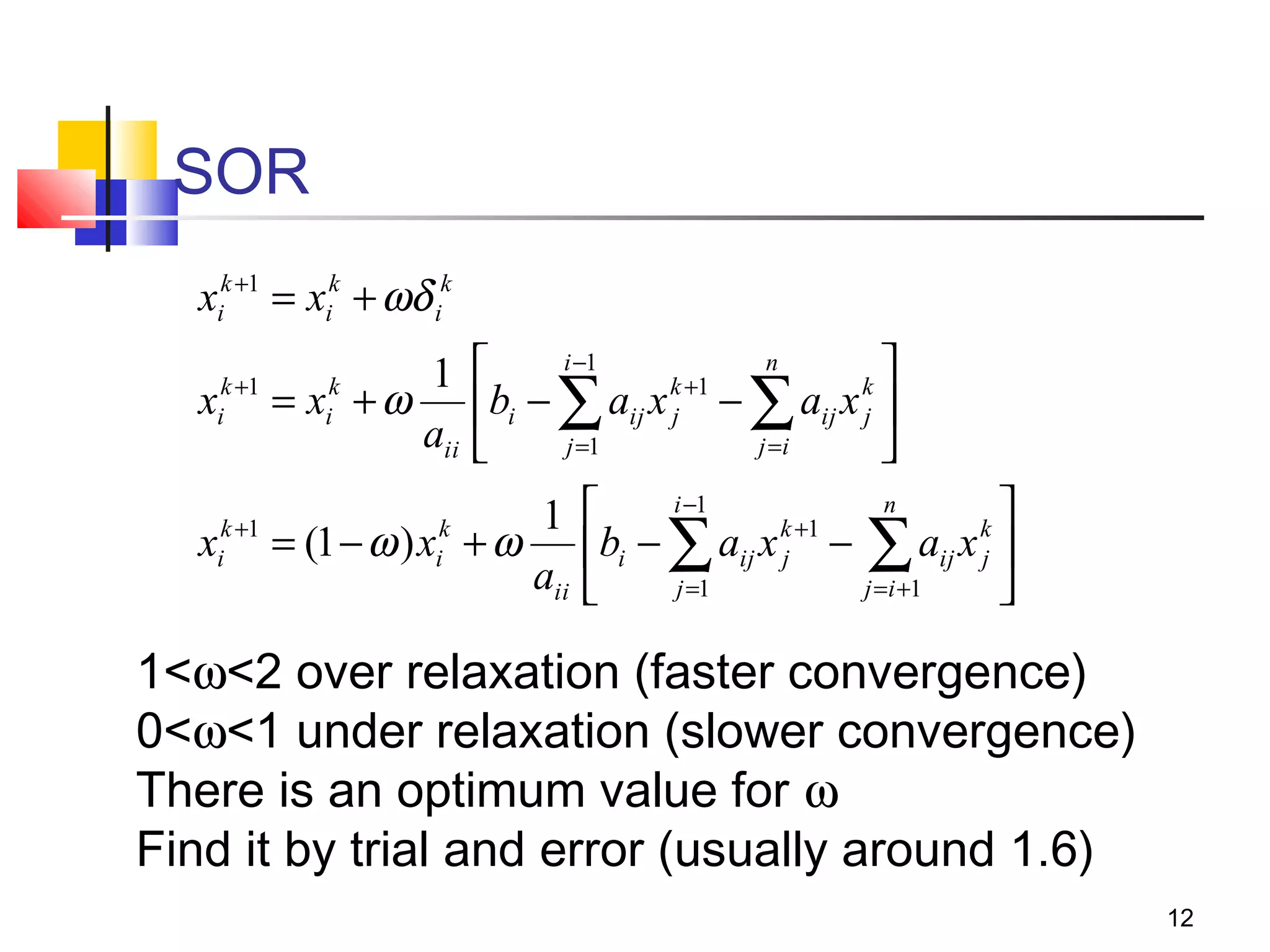
Iterative solution methods start with an initial approximation for the solution vector and iteratively update the vector at each step by using the system Ax=b. Different iterative methods like Jacobi, Gauss-Seidel, and Successive Over Relaxation represent the system in the form x=Ex+f and generate the next approximation. The iterative method converges if the spectral radius of E is less than 1 as the number of iterations increases. Different convergence criteria like the norm of the residual vector can be used to check when the iterations have converged to the solution.






![x(k+1)=Ex(k)+f iteration for SOR
1
k +1
k
xi = (1 − ω ) xi + ω
aii
i −1
n
k +1
k
bi − ∑ aij x j − ∑ aij x j
j =1
j = i +1
Dxk+1=(1-ω)Dxk+ωb-ωLxk+1-ωUxk
(D+ ωL)xk+1=[(1-ω)D-ωU]xk+ωb
E=(D+ ωL)-1[(1-ω)D-ωU]
f= ω(D+ ωL)-1b
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convergencecriteria-131111132129-phpapp01/75/Convergence-Criteria-13-2048.jpg)