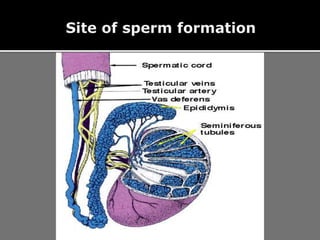
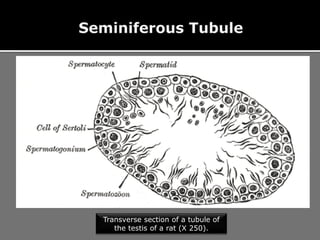
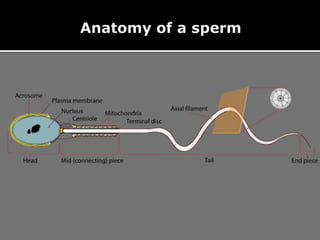
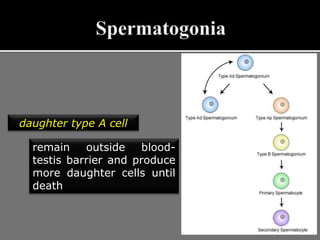
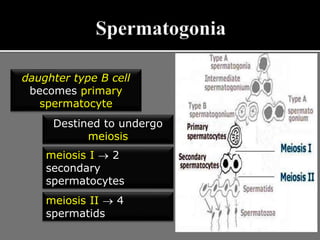
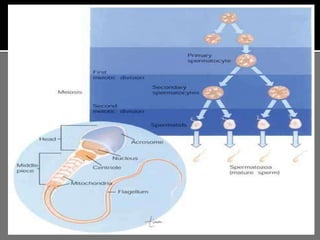
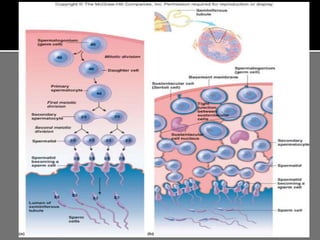
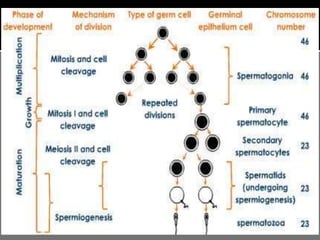
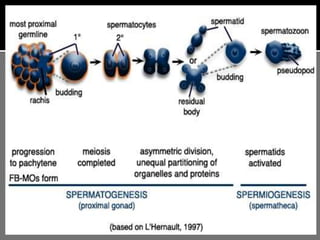
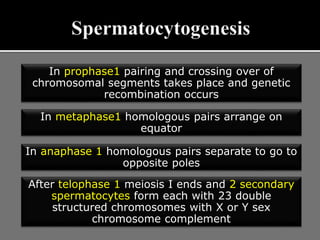
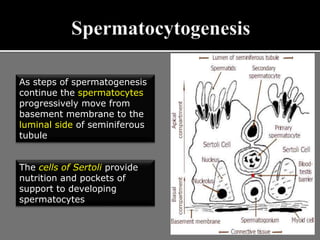
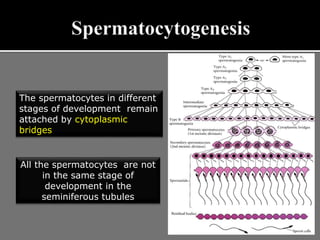
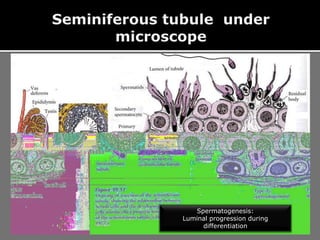
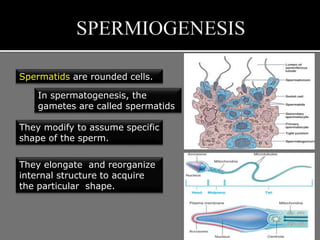
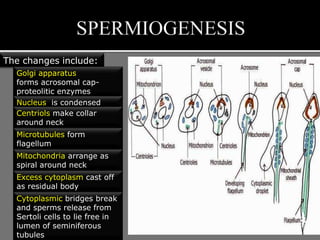
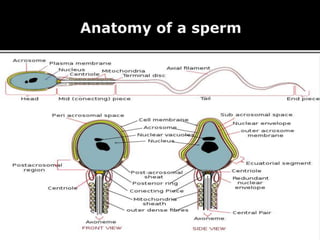
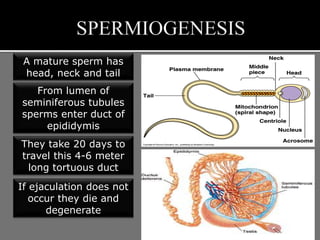
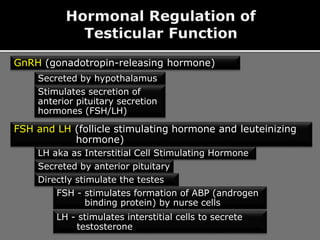
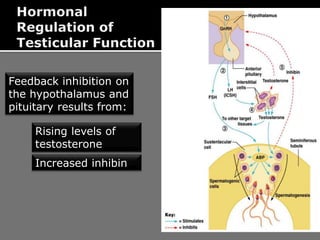
The document outlines the process of spermatogenesis, starting from spermatogonia during puberty, through meiosis, to the formation of mature sperm. It details the role of Sertoli cells in supporting and providing nutrition to developing spermatocytes, as well as the stages of cellular differentiation that lead to sperm maturation. Additionally, the document mentions the hormonal regulation of sperm production and the time required for each stage of development.