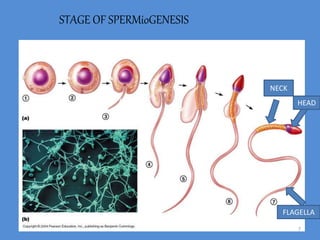
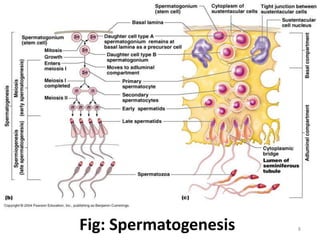
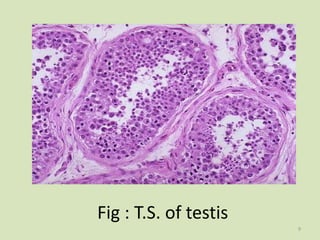
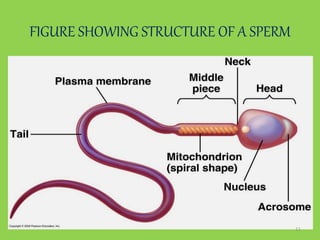
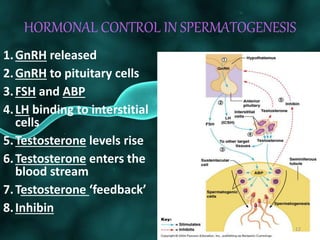
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm formation in the male reproductive system, occurring within the seminiferous tubules and involving the development of spermatids and spermatozoa. The process encompasses multiple phases: multiplication of germ cells, growth into primary spermatocytes, and maturation into secondary spermatocytes and finally spermatids, followed by spermiogenesis where spermatids are transformed into motile sperm. Hormonal control, particularly through GnRH, FSH, LH, and testosterone, regulates this process, and it results in the production of four sperm from each spermatogonium, maintaining genetic variation and chromosomal integrity across species.