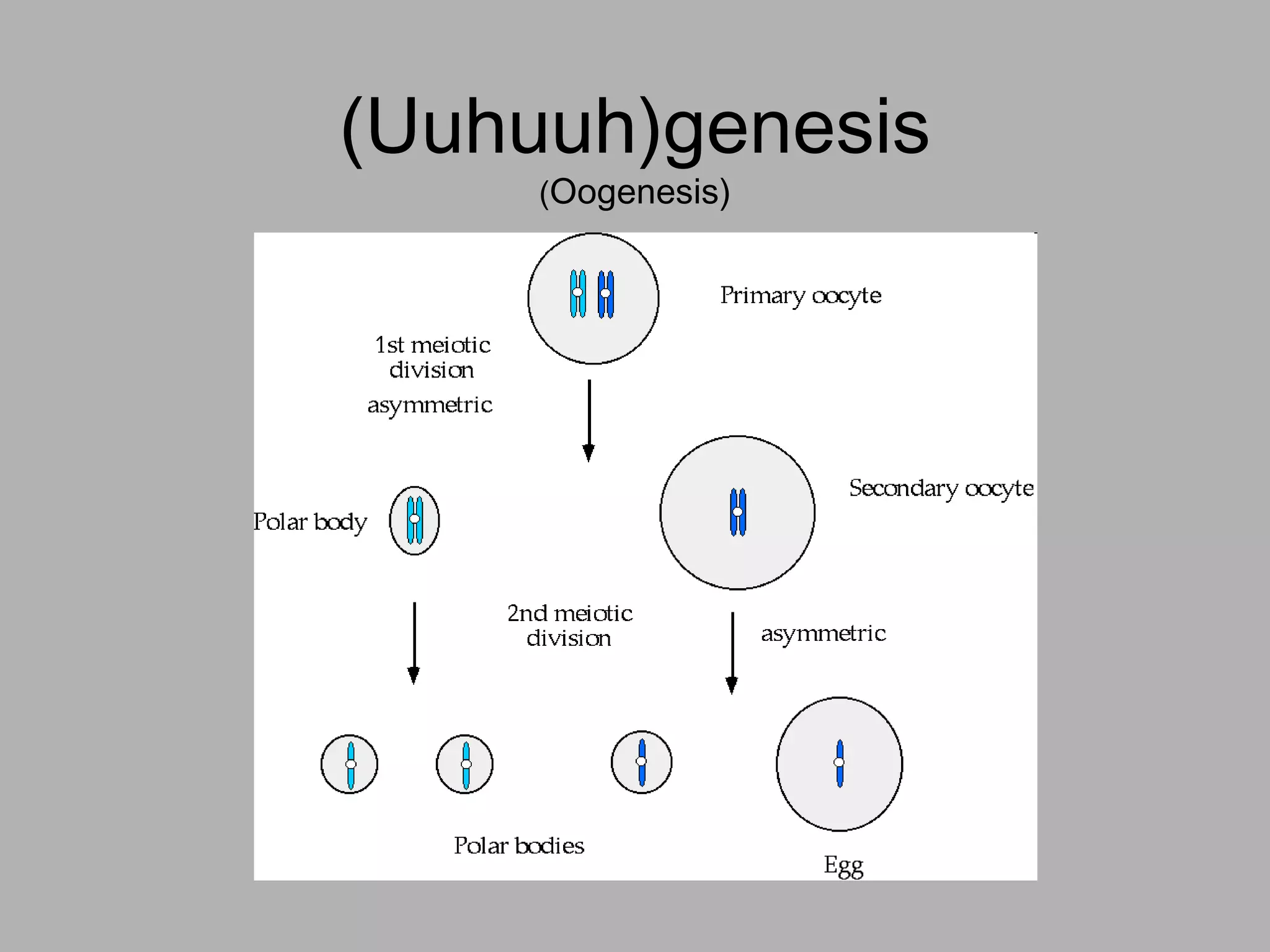
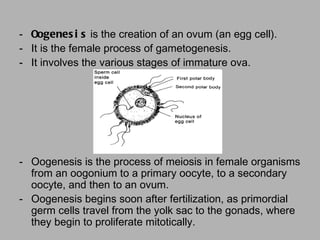
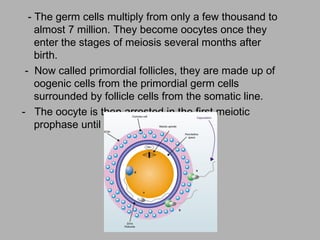
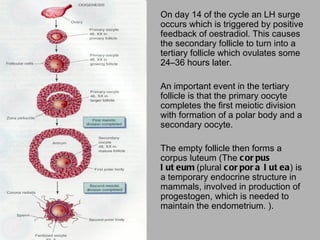
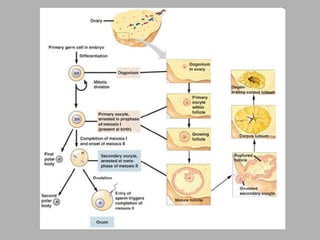
Oogenesis is the process by which ova (egg cells) are produced in female organisms. It begins with primordial germ cells that proliferate into millions of oocytes through mitosis after birth. During puberty, a few oocytes begin to develop each month, though usually only one is released. The oocyte undergoes the first meiotic division, producing a secondary oocyte and polar body. If fertilized by a sperm, it will complete the second meiotic division.