Embed presentation
Downloaded 70 times
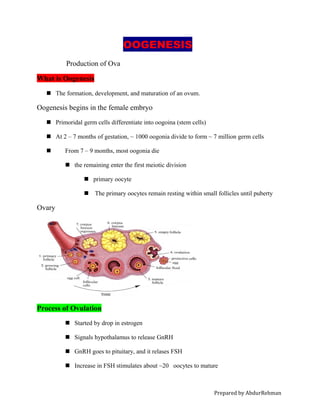


Oogenesis begins in the female embryo with primordial germ cells differentiating into oogonia that divide to form millions of germ cells. During gestation most oogonia die off while the remaining enter the first meiotic division to become primary oocytes that remain in the ovaries in a non-dividing state. At puberty, a drop in estrogen signals the release of hormones that stimulate around 20 primary oocytes to mature through meiosis I to become secondary oocytes with one being ovulated from its follicle while the others are reabsorbed. If the ovulated oocyte is fertilized, the empty follicle forms the corpus luteum which produces hormones to support pregnancy.

