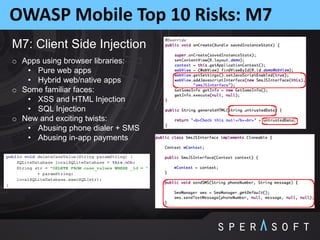
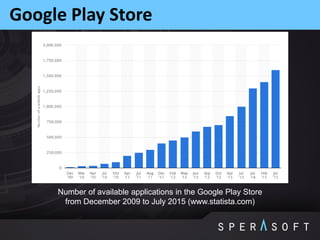
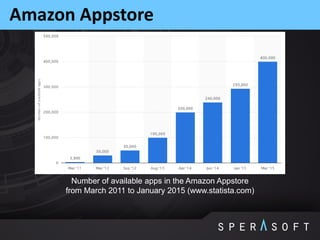
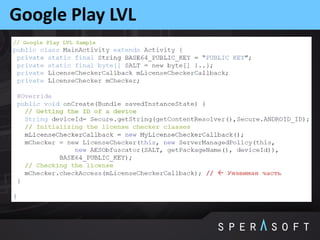
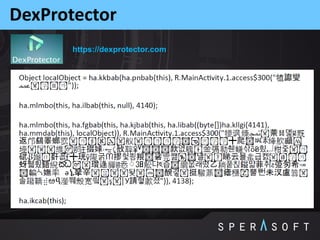
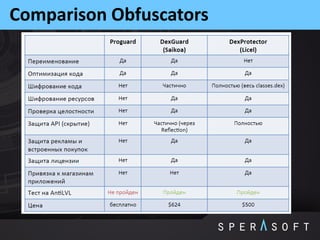
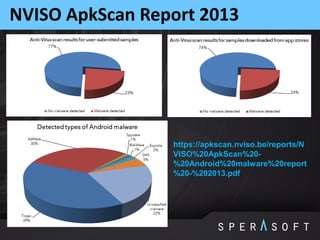
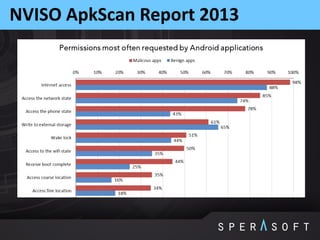
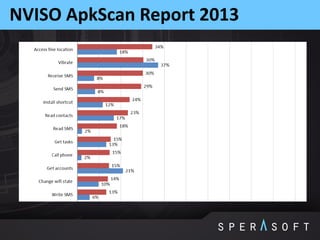
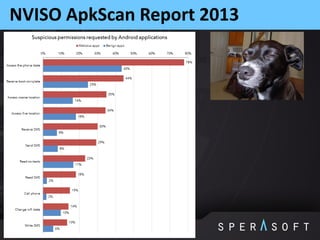
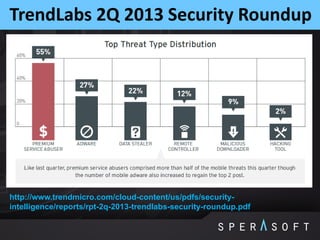
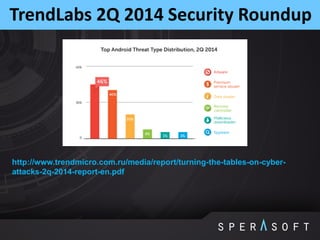
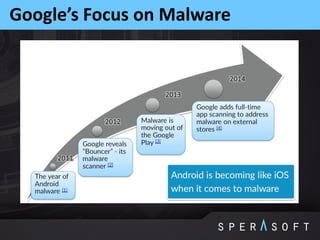
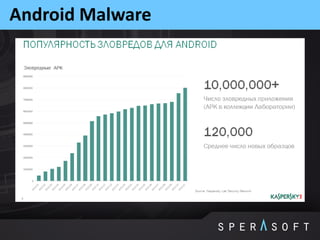
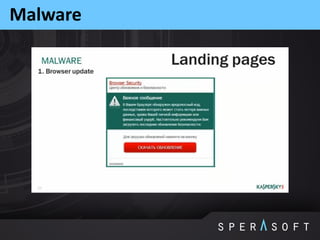
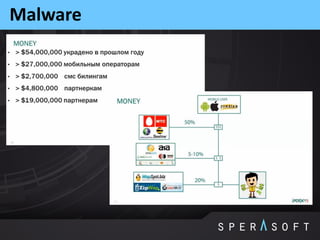
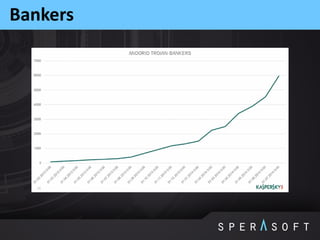
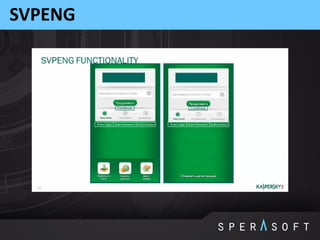
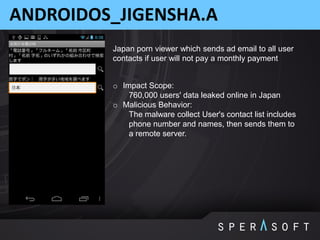
The document discusses various security threats related to Android applications. It begins by introducing the OWASP Mobile Top 10 risks framework for categorizing common mobile vulnerabilities. It then provides more details on each of the top 10 risk categories, including examples, impacts, and tips for prevention. It also discusses techniques for protecting Android apps from reverse engineering and tampering, such as code obfuscation, anti-debugging, and license verification.