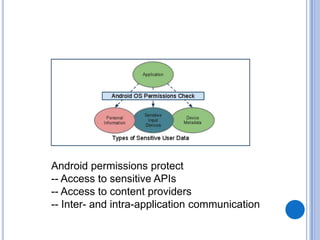
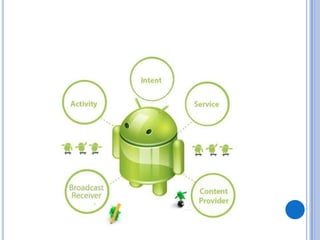
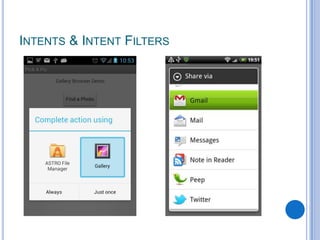
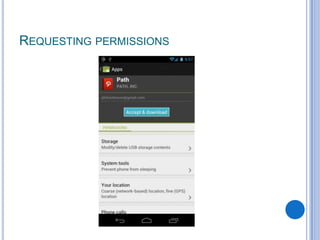
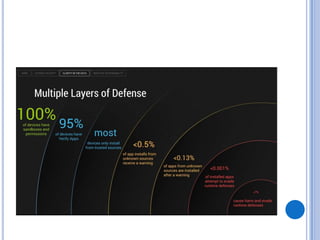
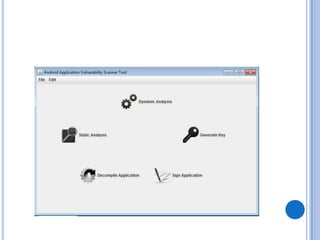
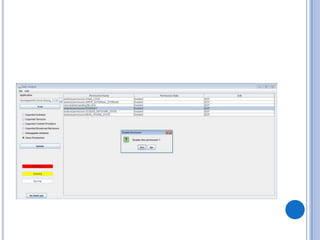
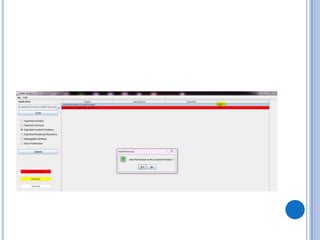
The document discusses Android security and provides an overview of key topics. It begins with Android basics and versions. It then covers the Android security model including application sandboxing and permissions. It defines Android applications and their components. It discusses debates on whether Android is more secure than iOS and outlines multiple layers of Android security. It also addresses Android malware, anti-virus effectiveness, rooting, application vulnerabilities, and security issues.