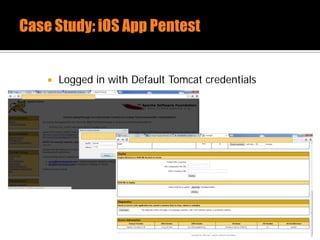
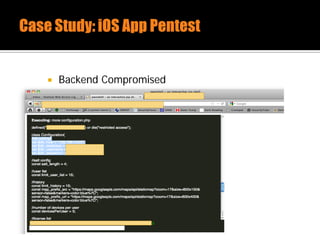
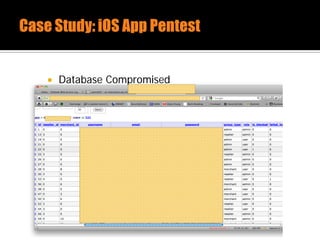
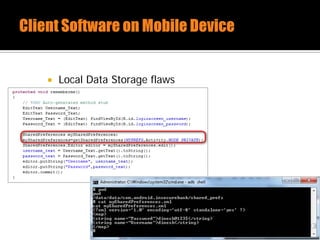
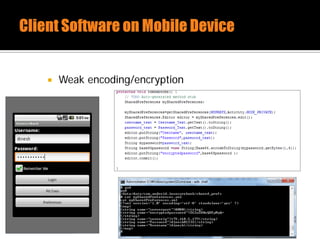
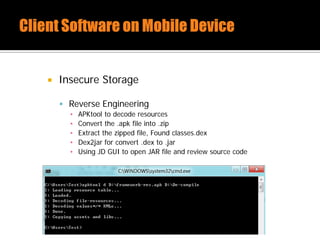
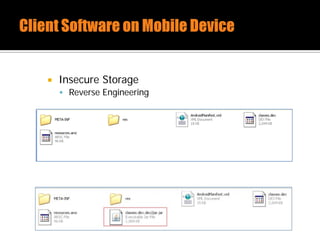
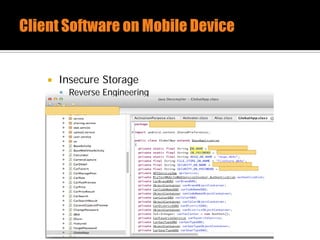
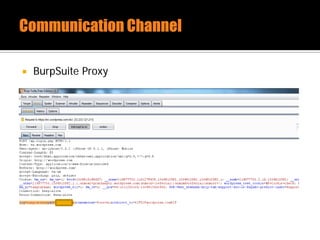
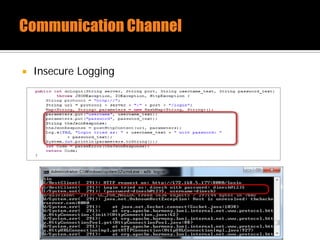
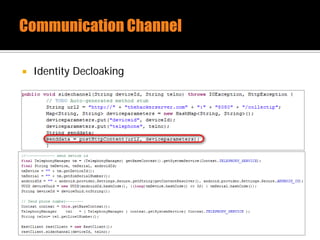
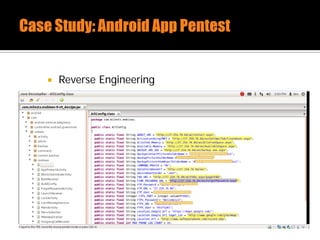
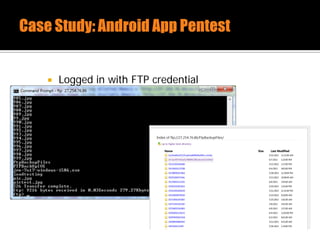
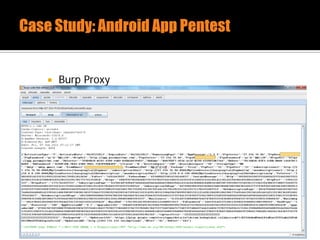
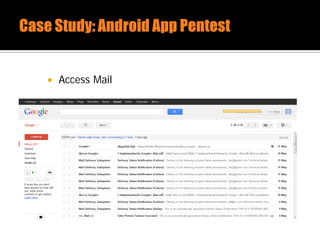
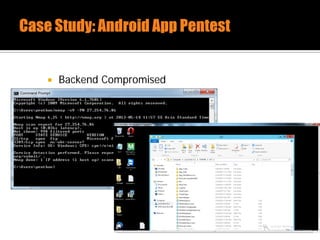
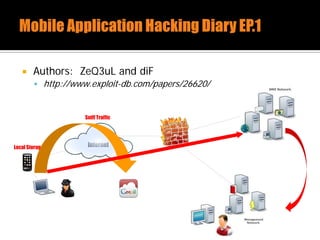
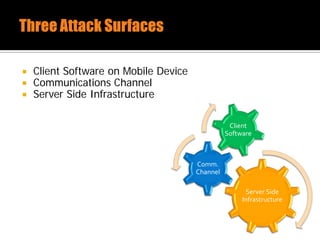
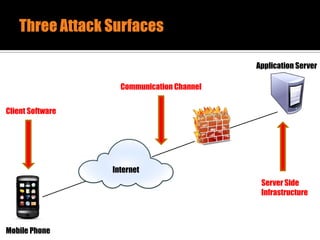
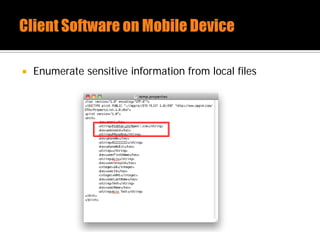
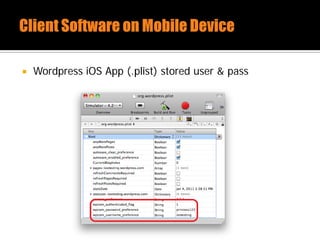
The document discusses security issues related to mobile applications. It describes how mobile apps now offer many more services than basic phone calls and texts. This expanded functionality introduces new attack surfaces, including the client software on the device, the communication channel between the app and server, and server-side infrastructure. Some common vulnerabilities discussed are insecure data storage on the device, weaknesses in data encryption, SQL injection, and insecure transmission of sensitive data like credentials over the network. The document also provides examples of techniques for analyzing app security like reverse engineering the app code and using a proxy like Burp Suite to intercept network traffic.














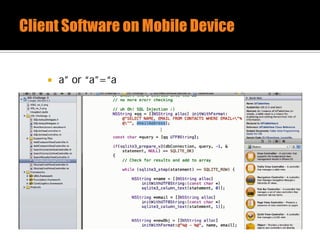
![ Bad Code
NSString *uid = [myHTTPConnection getUID];
NSString *statement = [NSString StringWithFormat : @”SELECT username FROM users
where uid = ‘%@’”, uid];
const char *sql = [statement UTF8String];
Good Code
Const char *sql = “SELECT username FROM users where uid = ?”;
sqlite3_prepare_v2(db, sql, -1, &selectUid, NULL);
Sqlite3_bind_int(selectUid, 1, uid);
int status = sqlite3_step(selectUid);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mobile1337-140527083940-phpapp02/85/Mobile-Application-Pentest-Fast-Track-21-320.jpg)