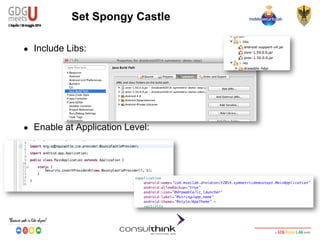
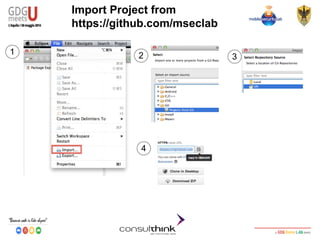
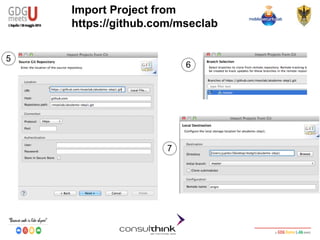
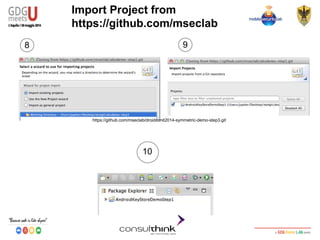
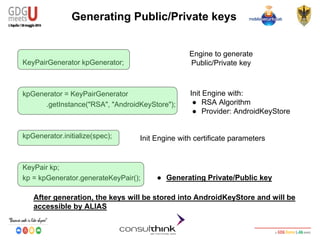
This document discusses Android key management and cryptography. It covers symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms like AES and RSA. It describes using the Android Keystore to securely store cryptographic keys and how PBKDF2 can be used to derive keys from passwords. It also demonstrates how apps can be reversed to extract hardcoded keys and discusses more secure alternatives like storing keys on a server.









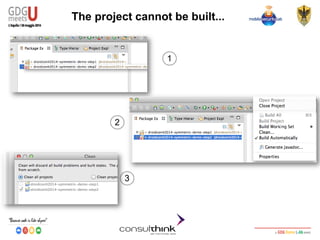
![Android Security
Key Management
Cipher Final
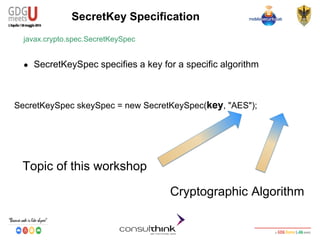
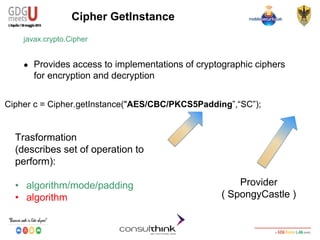
javax.crypto.Cipher
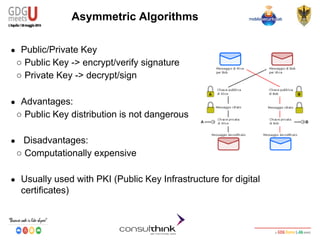
● Finishes a multi-part transformation (encryption or decryption)
byte[] encryptedText = cipher.doFinal(clearText.getBytes());
Encrypted
Text in byte
ClearText in
bytes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-23-320.jpg)











![Android Security
Key Management
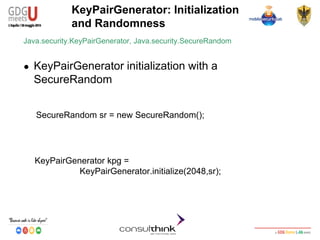
Using RSA Key: cipher example
Javax.crypto.Cipher
● Encryption
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,public_key);
● Decryption
byte[] encrypted_data=
cipher.doFinal(“GDG-Meets-U2014”.getBytes());
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE,private_key);
byte[] decrypted_data=
cipher.doFinal(cipherd_data);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-48-320.jpg)





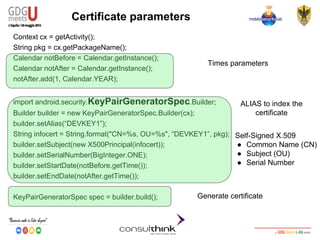


![Android Security
Key Management
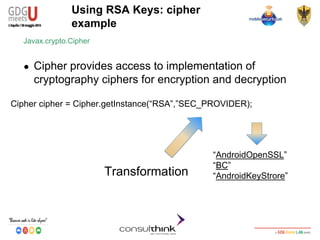
RSA Digital Signature
● Digital Signature
○ Authentication, Non-Repudiation and Integrity
○ RSA Private key to Sign
○ RSA Public Key to Verify
KeyStore.Entry entry = ks.getEntry(“DEVKEY1”, null);
byte[] data = “GDG-Meets-U 2014!”.getBytes();
Signature s = Signature.getInstance(“SHA256withRSA”);
s.initSign(((KeyStore.PrivateKeyEntry) entry).getPrivateKey());
s.update(data);
byte[] signature = s.sign();
String result = null;
result = Base64.encodeToString(signature, Base64.DEFAULT);
Access to Private/Public key identified
by ALIAS
Algorithm choice
Private key to sign
Signature and Base64
encoding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-60-320.jpg)
![Android Security
Key Management
Verify RSA Digital Signature
byte[] data = input.getBytes();
byte[] signature;
signature = Base64.decode(signatureStr, Base64.DEFAULT);
KeyStore.Entry entry = ks.getEntry(“DEVKEY1”, null);
Signature s = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
s.initVerify(((KeyStore.PrivateKeyEntry) entry).getCertificate());
s.update(data);
boolean valid = s.verify(signature);
Base64 decoding
Access to the Private/Public key
identified by ALIAS==DEVKEY1
Algorithm choice
Public Key in certificate to
verify signature
TRUE == Verified
FALSE== Not Verified](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-61-320.jpg)

![Android Security
Key Management
RSA Encryption
● Encryption
○ Confidentiality
○ RSA Public key to Encrypt
○ RSA Private key to Decrypt
PublicKey publicKeyEnc = ((KeyStore.PrivateKeyEntry) entry)
.getCertificate().getPublicKey();
String textToEncrypt = new String(”GDG-Meet-U-2014");
byte[] textToEncryptToByte = textToEncrypt.getBytes();
Cipher encCipher = null;
byte[] encryptedText = null;
encCipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding");
encCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKeyEnc);
encryptedText = encCipher.doFinal(textToEncryptToByte);
Access to Public key
to encrypt
● Algorithm
● Encryption with Public
key
Ciphered](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-63-320.jpg)
![Android Security
Key Management
RSA Decryption
Cipher decCipher = null;
byte[] plainTextByte = null;
decCipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding");
decCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE,
((KeyStore.PrivateKeyEntry) entry).getPrivateKey());
plainTextByte = decCipher.doFinal(ecryptedText);
String plainText = new String(plainTextByte);
Algorithm
Decryption with
Private key
Plaintext](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-64-320.jpg)





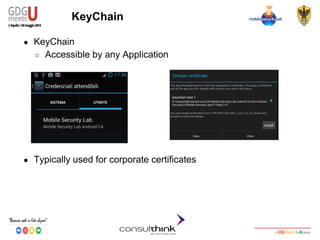
![Android Security
Key Management
Example: Import Certificates
● Import .p12 certificates
Intent intent = KeyChain.createInstallIntent();
byte[] p12 = readFile(“CERTIFICATE_NAME.p12”);
Intent.putExtra(KeyChain.EXTRA_PKCS12,p12);
Specify PKCS#12 Key to install
startActivity(intent);
The user will be
prompted for the
password](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-71-320.jpg)
![Android Security
Key Management
KeyChain.choosePrivateKeyAlias(
Activity activity,
KeyChainAliasCallBack response,
String[] keyTypes,
Principal[] issuers,
String host,
Int port,
String Alias);
Example: Retrieve the key
● The KeyChainAliasCallback invoked when a user chooses a
certificate/private key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-72-320.jpg)
![Android Security
Key Management
@Override
public void alias(String alias){
.
.
PrivateKey private_key = KeyChain.
getPrivateKey(this,alias);
.
.
X509Certificate[] chain = KeyChain.
getCertificateChain(this,”Droidcon”);
.
PublicKey public_key = chain[0].getPublicKey();
}
Example: Retrieve and use the
keys
● KeyChainAliasCallbak must implement the abstract method
alias:
Private Key
Public Key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consulthinkatgdgmeetu-aquila-2014-codelabandroidsecurity-ilkeymanagement-140605081054-phpapp01/85/Consulthink-GDG-Meets-U-L-Aquila2014-Codelab-Android-Security-Il-key-management-73-320.jpg)


