The document discusses key concepts in relational database models including:
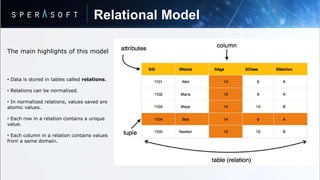
- Data is stored in tables called relations with rows and columns where rows represent records and columns represent attributes.
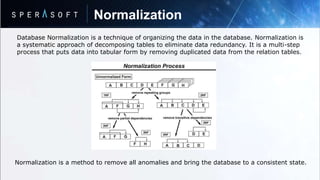
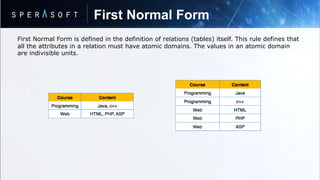
- Relations can be normalized to eliminate redundant data and optimize storage.
- Database normalization involves organizing data into tables through a multi-step process to remove anomalies.
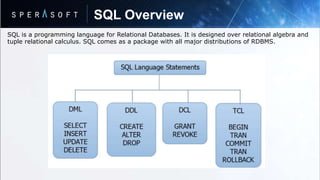
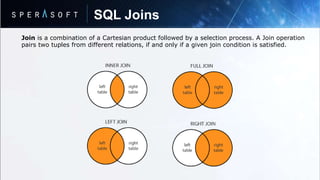
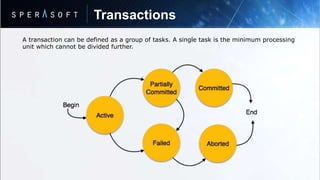
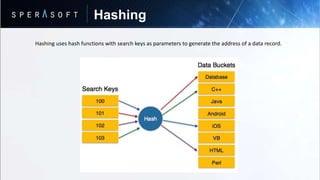
- SQL is a programming language used to interact with relational databases through operations like joins, transactions, and indexing/hashing techniques.