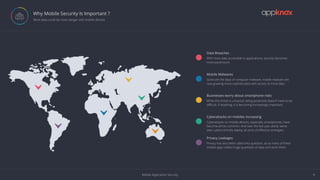
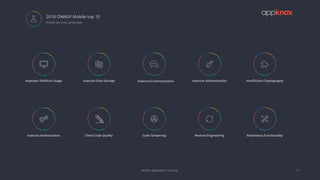
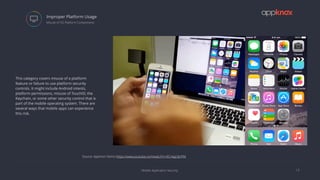
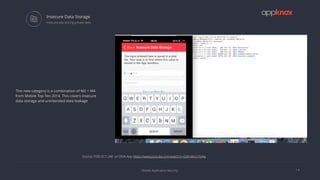
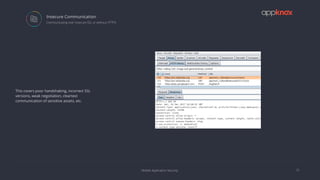
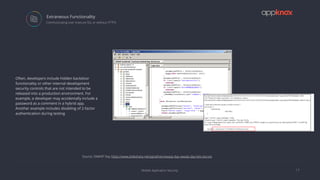
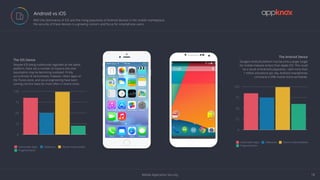
The document discusses the critical importance of mobile application security amidst increasing cyber threats, data breaches, and privacy concerns. It outlines common vulnerabilities such as poor authentication, insecure data storage, and insufficient cryptography, while referencing the OWASP Mobile Top 10 list as a guideline for identifying risks. The document further highlights the challenges developers face due to fragmented platforms and the necessity for robust security measures in mobile applications.