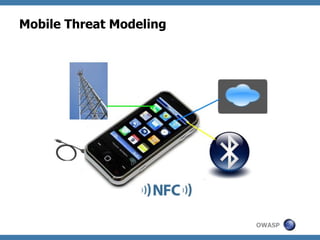
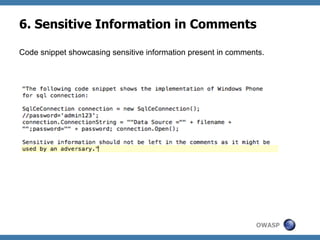
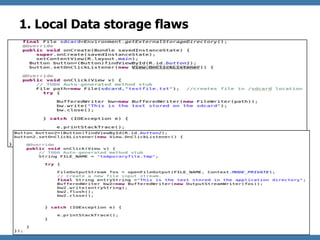
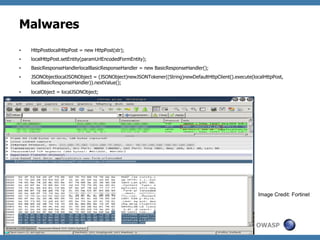
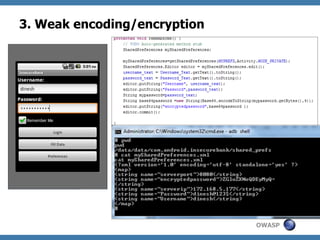
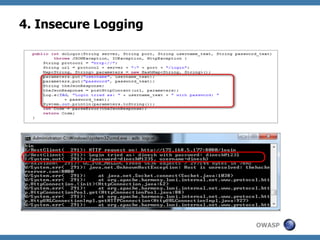
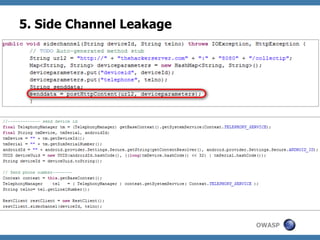
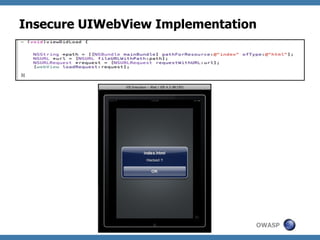
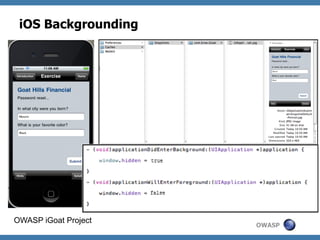
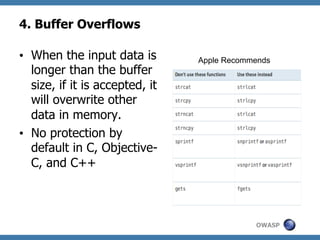
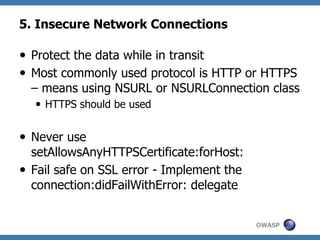
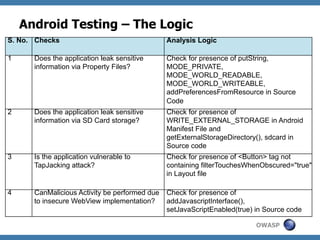
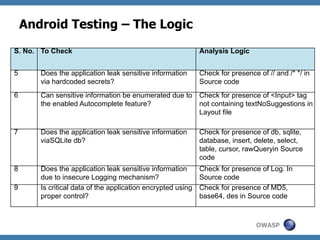
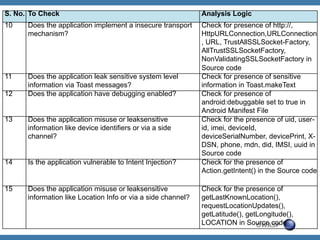
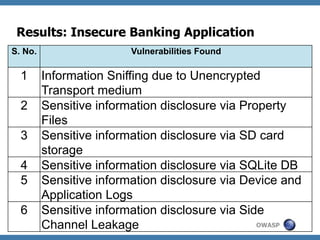
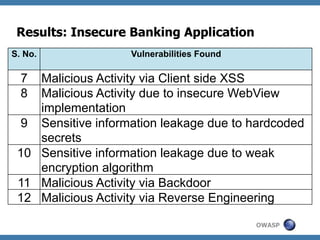
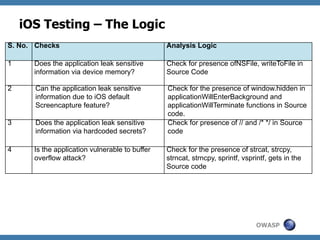
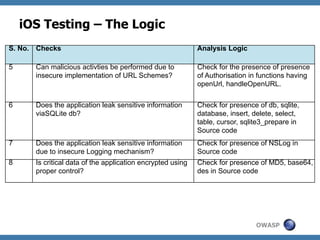
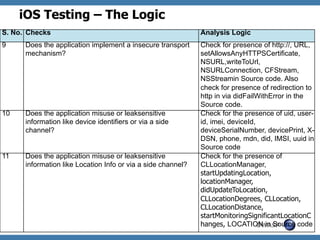
The document discusses code review techniques for advanced mobile applications. It begins with an overview of why mobile security is important given the rise in mobile usage. It then discusses different mobile application types and architectures that can be code reviewed, including native, hybrid, and HTML5 applications. The document outlines the goals of mobile application code reviews, such as understanding the application and finding security vulnerabilities. It provides the methodology for conducting code reviews, which includes gaining access to source code, understanding the technology, threat modeling, analyzing the code, and creating automation scripts. Finally, it discusses specific vulnerabilities that may be found in Windows Phone, hybrid, Android, and iOS applications.



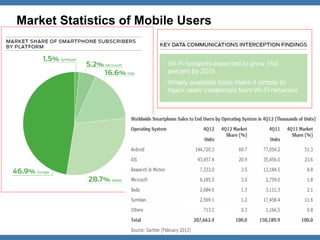
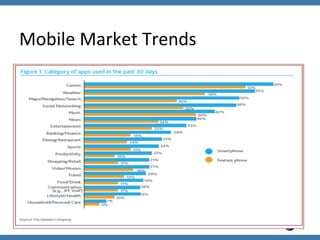








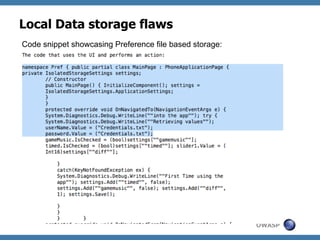
![Methodology / Study
S1:
Gaining
access
to
the
Source
code
[Development
Team
or
Decompile]
S2:
Understanding
the
Technology
used
to
code
the
applicaZon.
S3:
Build
the
Security
Threat
Model.
S4:
Derive
the
keyword
paGerns.
S5:
Analyze
the
source
code
against
list
of
keywords.
S6:
Build
the
automa'on
script
for
quick
results.
OWASP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/owaspadvanced-mobile-application-code-review-techniques-v0-131217205055-phpapp01/85/Owasp-advanced-mobile-application-code-review-techniques-v0-2-15-320.jpg)