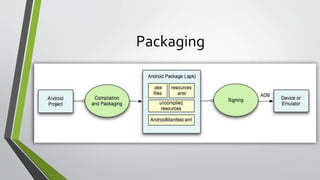
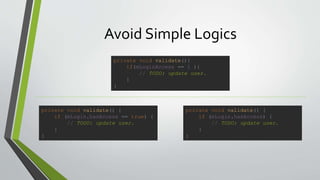
The document discusses developing secure Android apps and provides guidelines for doing so. It outlines potential attack vectors like malicious apps or files and the importance of following security best practices such as using encryption, testing third party libraries, and securing intents, logs, and webviews. The document encourages avoiding simple validation logic, using tokens for authentication, HTTPS, and provides tips for code obfuscation as well as tools that can help find vulnerabilities.