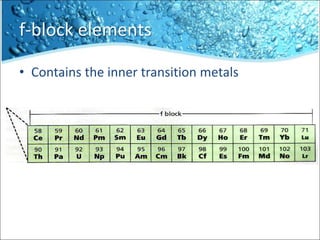
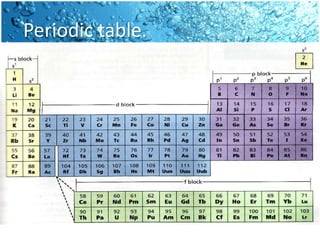
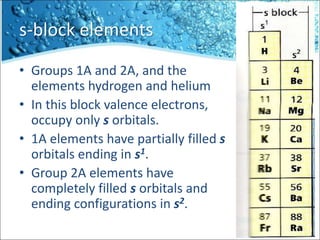
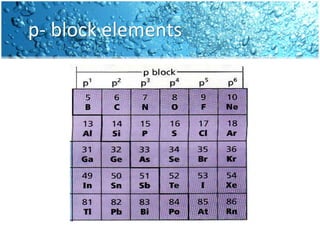
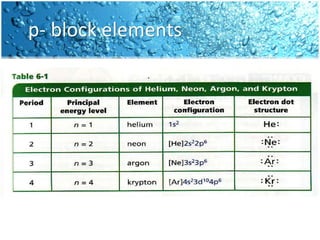
The periodic table is divided into blocks based on the orbital being filled with electrons - s-block, p-block, d-block, f-block. The s-block contains groups 1 and 2 whose elements have electrons filling the s orbital. The p-block spans groups 3 through 8 and contains elements with electrons filling p orbitals. The d-block is the largest block and contains the transition metals, whose elements have electrons filling the d orbital. The f-block contains the inner transition metals and its elements have electrons filling the 4f or 5f orbitals.




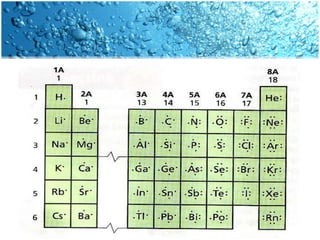





![• For example:
• scandium (Sc) [Ar]4s23d1
• titanium (Ti) [Ar]4s23d2
• The five d- orbitals can hold a total of
ten electrons; thus the d- block
spans ten groups.
d- block](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spdfblocks1-101120143409-phpapp01/85/Spdf-blocks-1-15-320.jpg)