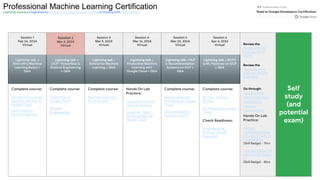
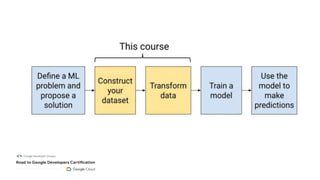
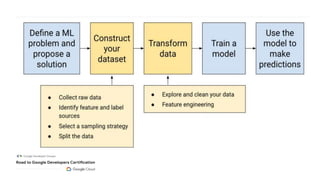
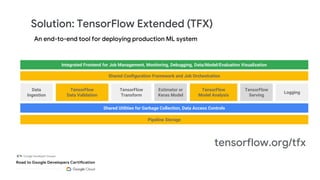
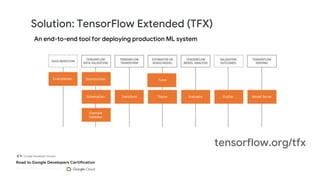
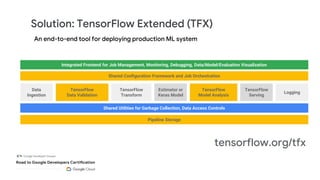
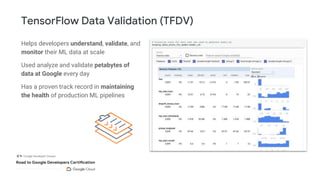
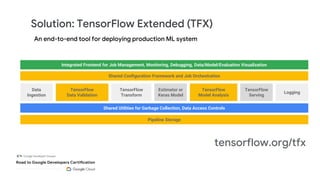
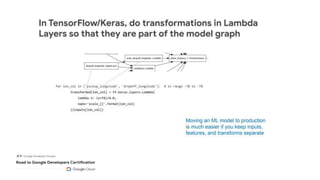
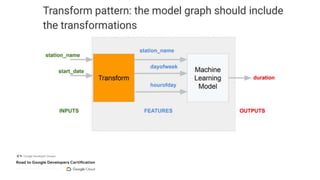
This document outlines the schedule and content for a professional machine learning engineer certification program co-hosted by Google Developer Groups. Key topics covered include data ingestion, feature engineering, and production ML systems using TensorFlow Extended (TFX). Participants are encouraged to complete hands-on labs and review sample questions in preparation for the certification exam.











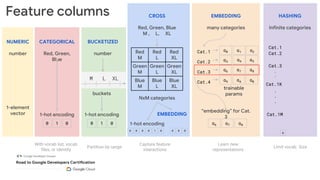



![Different cities in California have markedly different housing prices. Suppose you
must create a model to predict the housing prices. Which of the following sets of
features, or features crosses could learn city-specific relationships between
roomsPerPerson and housing price?
A. Three separated binned features: [binned latitude], [binned longitude],
[roomsPerPerson]
B. Two feature crosses: [binned latitude x roomsPerPerson] and [binned longitude
x roomsPerPerson]
C. One feature cross [latitude x longitude x roomsPerPerson]
D. One feature cross [binned latitude x binned longitude x binned roomsPerPerson]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2024-03-02session2-pmle1-240308190649-b78f5a39/85/Certification-Study-Group-Professional-ML-Engineer-Session-2-GCP-TensorFlow-Feature-Engineering-47-320.jpg)
![Different cities in California have markedly different housing prices. Suppose you
must create a model to predict the housing prices. Which of the following sets of
features, or features crosses could learn city-specific relationships between
roomsPerPerson and housing price?
A. Three separated binned features: [binned latitude], [binned longitude],
[roomsPerPerson]
B. Two feature crosses: [binned latitude x roomsPerPerson] and [binned longitude
x roomsPerPerson]
C. One feature cross [latitude x longitude x roomsPerPerson]
D. One feature cross [binned latitude x binned longitude x binned roomsPerPerson]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2024-03-02session2-pmle1-240308190649-b78f5a39/85/Certification-Study-Group-Professional-ML-Engineer-Session-2-GCP-TensorFlow-Feature-Engineering-48-320.jpg)