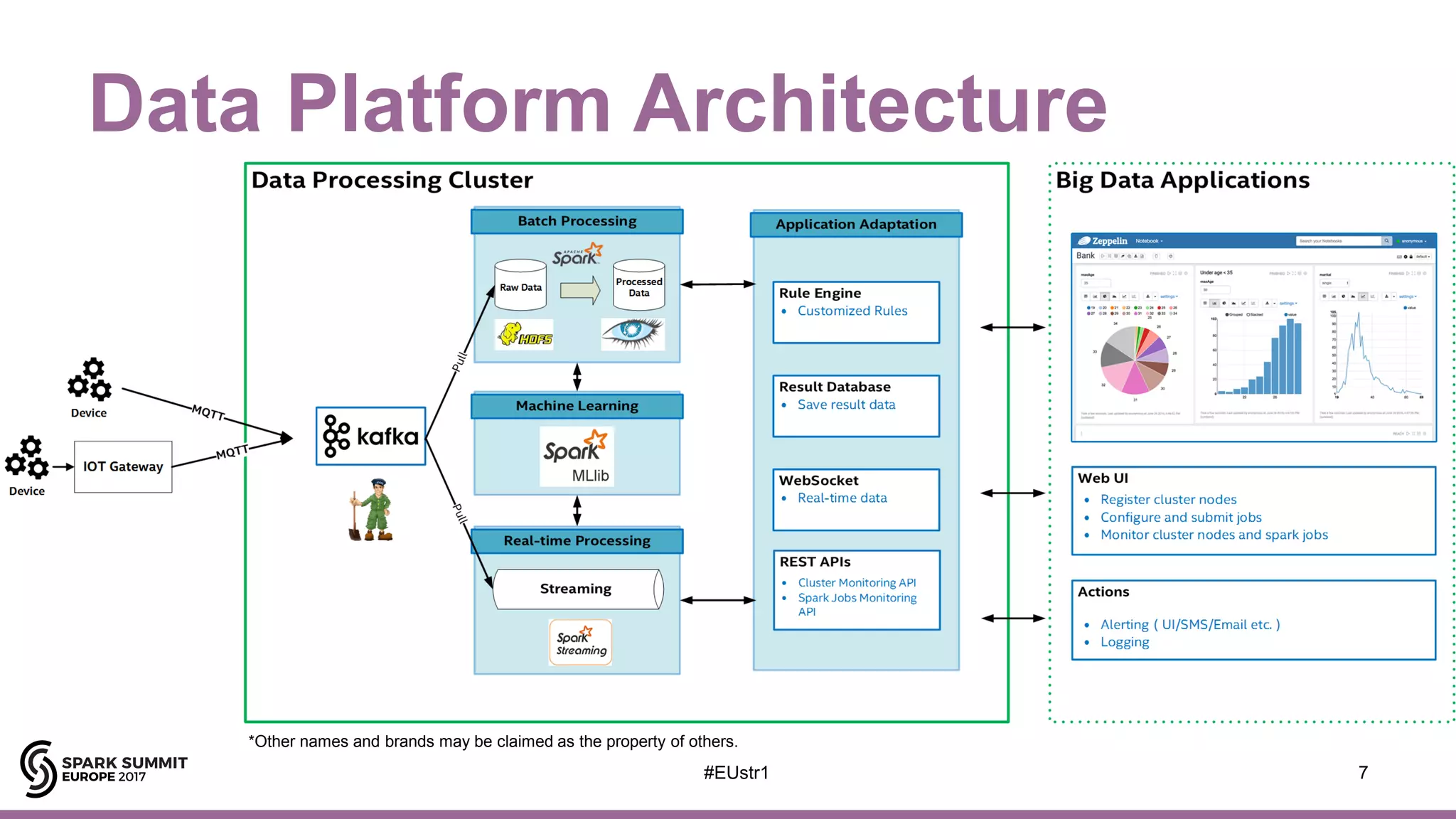
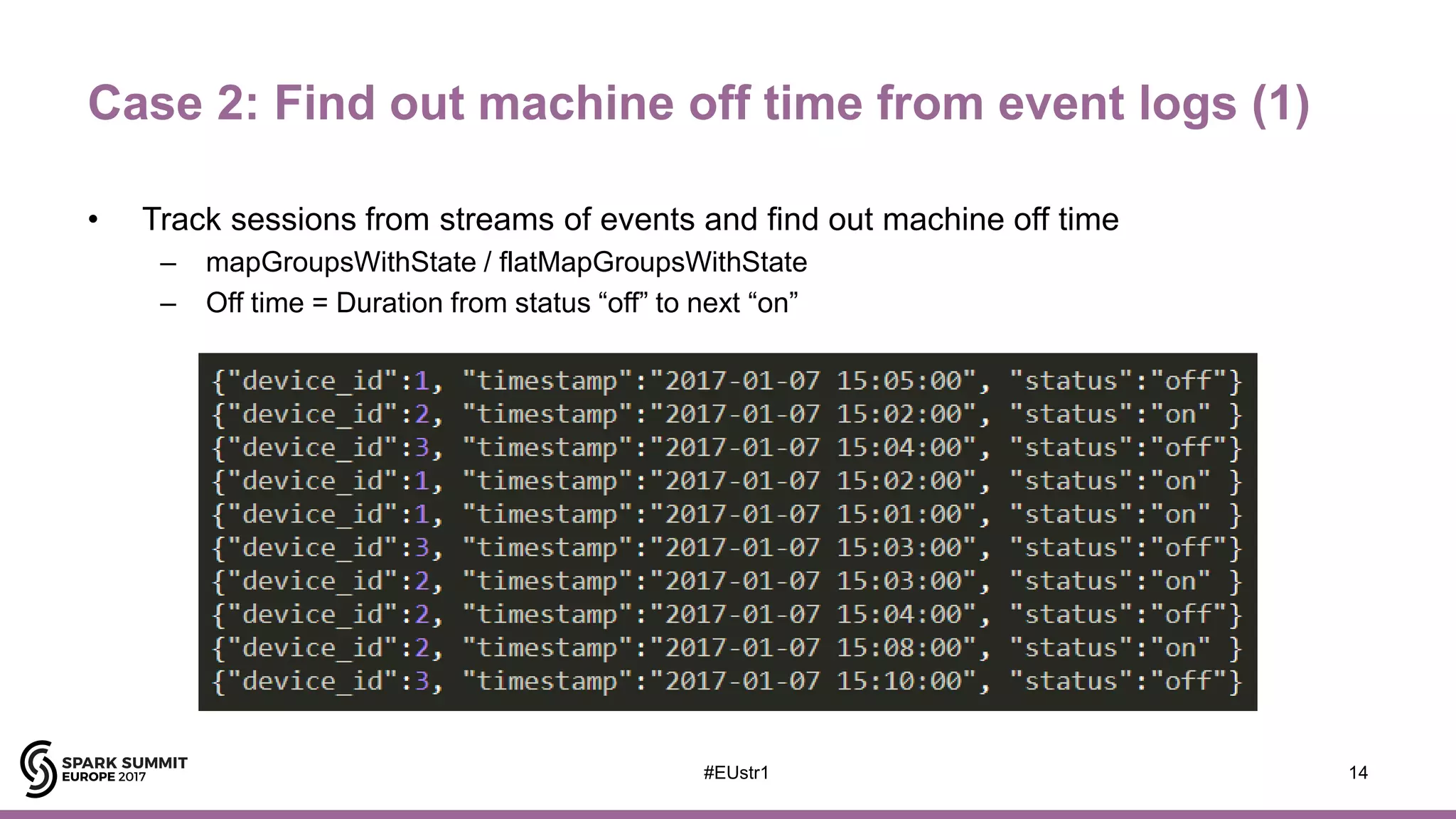
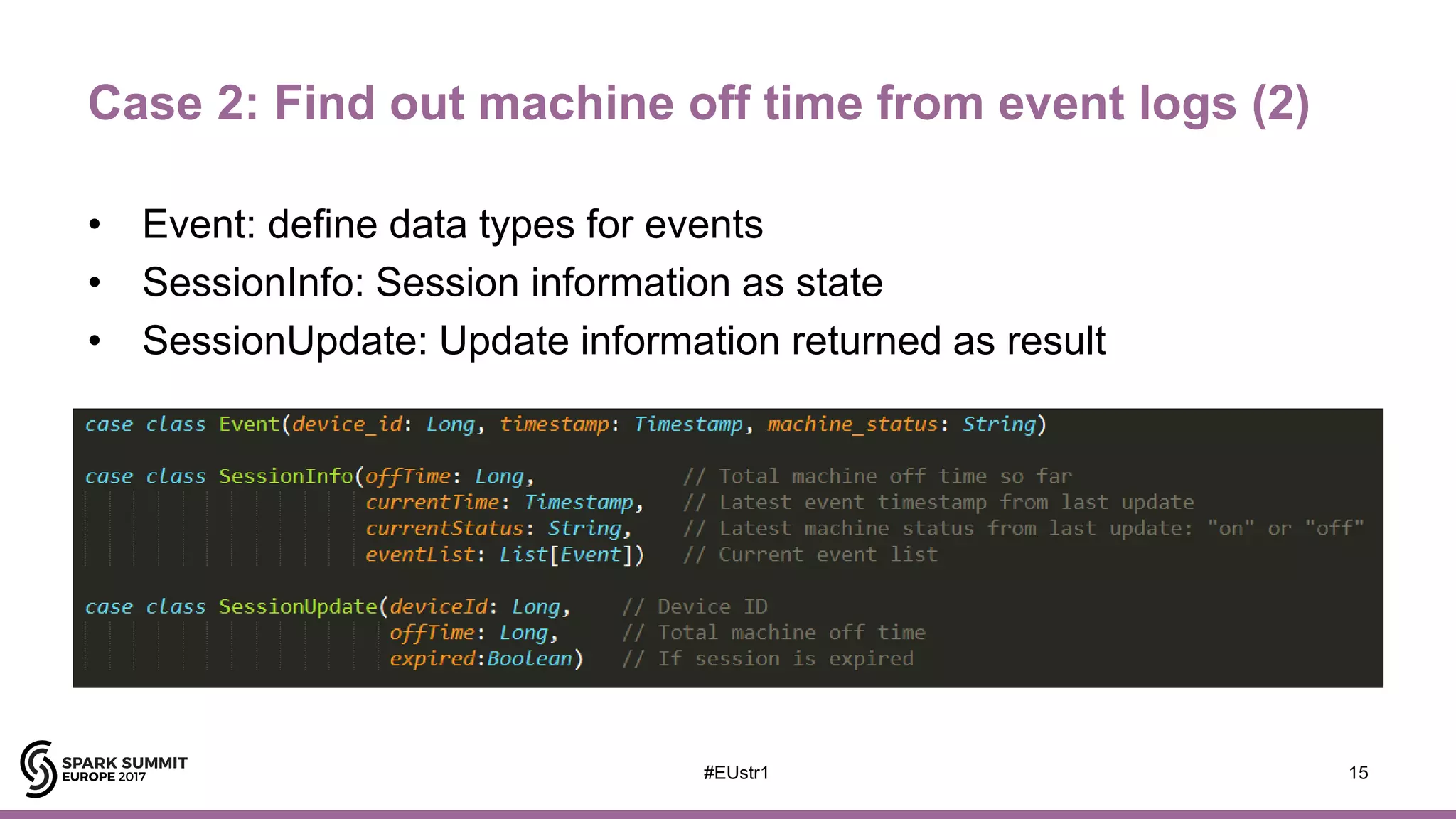
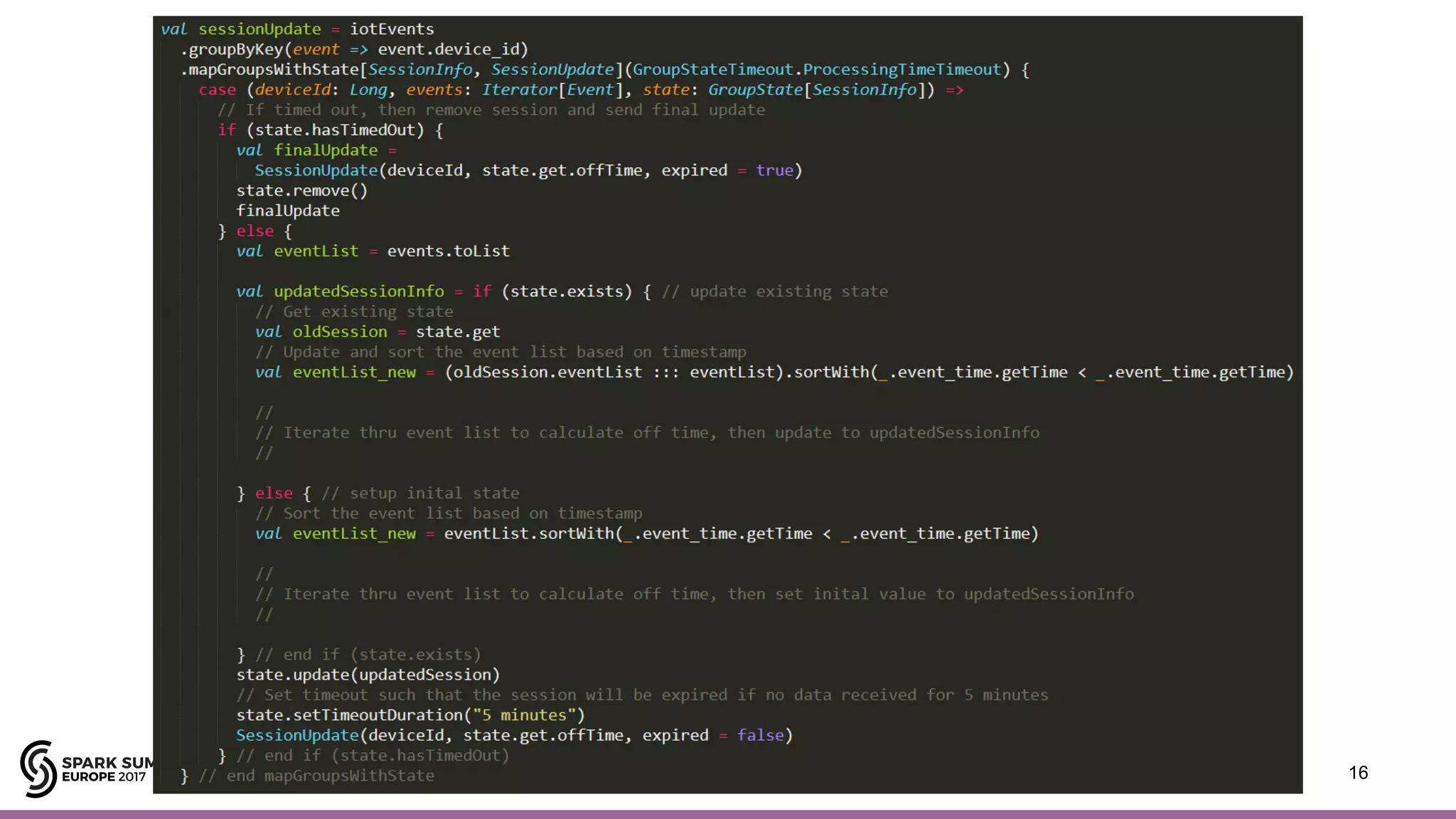
The document outlines the use of Spark Structured Streaming to build a smart manufacturing IoT data platform, focusing on enhancing efficiency in PCB manufacturing through predictive fault repair and material tracking. It details architectural features, data processing capabilities, and handling of stateless and stateful operations, along with improvement proposals for more complex event processing. Key components include real-time analytics, device management, data visualization, and the support for various data types.