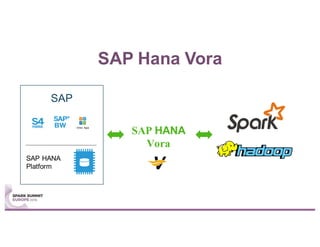
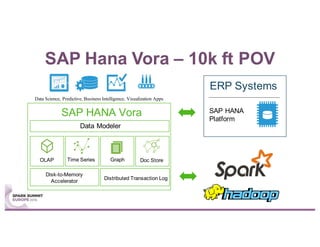
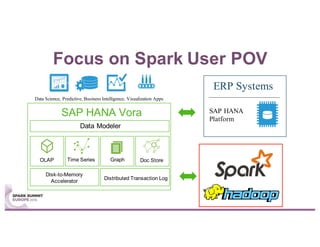
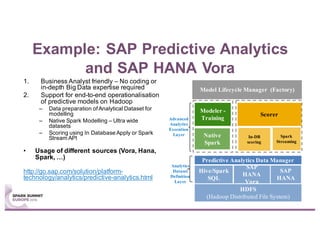
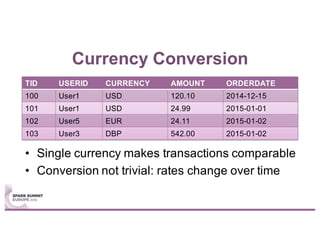
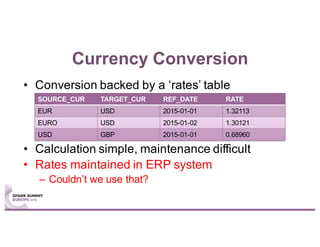
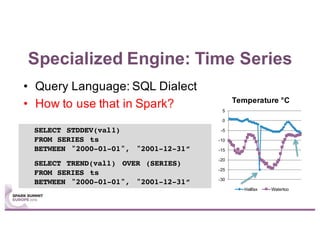
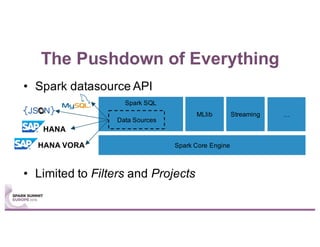
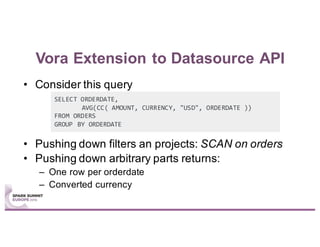
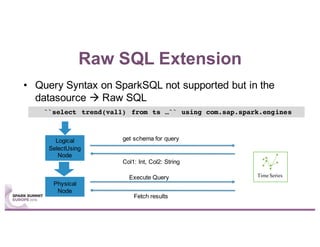
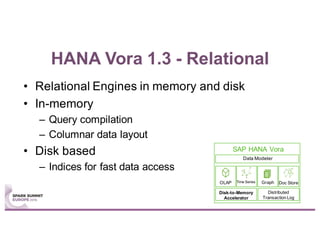
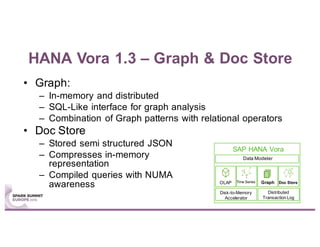
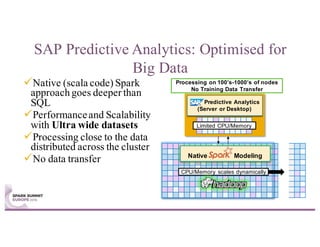
This document summarizes a talk given by Stephan Kessler at the Spark Summit Europe 2016 about integrating business functionality and specialized engines into Apache Spark using SAP HANA Vora. Key points discussed include using currency conversion and time series query capabilities directly in Spark by pushing computations to the relevant data sources via Spark extensions. SAP HANA Vora allows moving parts of the Spark logical query plan to various data sources like HANA, graph and document stores to perform analysis close to the data.