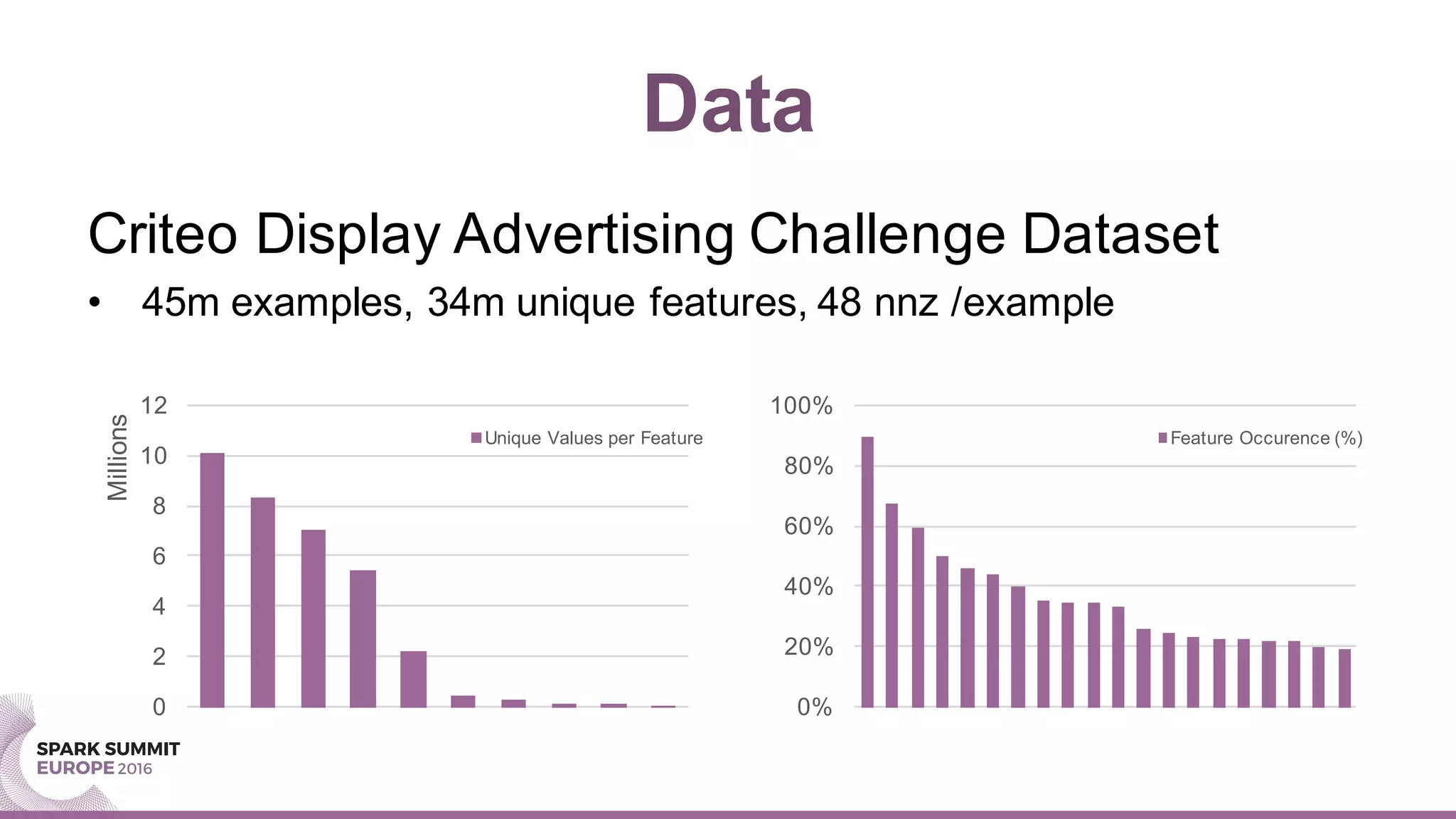
This document summarizes a presentation about scaling factorization machines on Apache Spark using parameter servers. The presentation introduces factorization machines as a method for modeling feature interactions in large datasets. It then discusses how distributed factorization machine models can be implemented on Spark using a parameter server approach, as demonstrated by the GlintFM library. Performance results show that GlintFM achieves significant speedups over the existing spark-libFM implementation on a large Criteo dataset, scaling to billions of parameters. Some remaining challenges are also outlined, along with ideas for future work.













![Feature Extraction
Solution? “Stringify” + CountVectorizer
Row(i1=u'1', i2=u'1', i3=u'5', i4=u'0', i5=u’1382’,... )
Row(raw=[u'i1=1', u'i2=1', u'i3=5', u'i4=0', u'i5=1382', ...)
Convert set of
String featuresinto
Seq[String]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4anickpentreath-161103184439/75/Spark-Summit-EU-talk-by-Nick-Pentreath-19-2048.jpg)