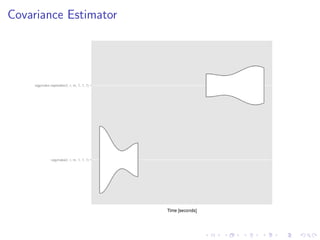
The document describes techniques for improving the computational performance of statistical analysis of big data in R. It uses as a case study the rlme package for rank-based regression of nested effects models. The workflow involves identifying bottlenecks, rewriting algorithms, benchmarking versions, and testing. Examples include replacing sorting with a faster C++ selection algorithm for the Wilcoxon Tau estimator, vectorizing a pairwise function, and preallocating memory for a covariance matrix calculation. The document suggests future directions like parallelization using MPI and GPUs to further optimize R for big data applications.
















![Vectorizing
## Bad
vec = 1:100
for (i in 1:length(vec)) {
vec[i] = vec[i]^2
}
## Better
sapply(vec, function(x) x^2)
## Best
vec^2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-140421181933-phpapp01/85/Computational-Techniques-for-the-Statistical-Analysis-of-Big-Data-in-R-18-320.jpg)
![Preallocation
## Bad
vec = c()
for (i in 1:0) {
vec = c(vec, i)
}
## Better
vec = numeric(100)
for (i in 1:0) {
vec[i] = i
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-140421181933-phpapp01/85/Computational-Techniques-for-the-Statistical-Analysis-of-Big-Data-in-R-19-320.jpg)










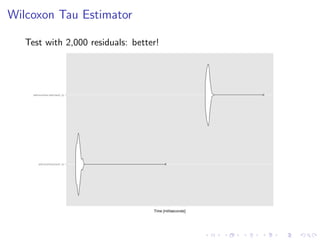
![Wilcoxon Tau Estimator
Original:
dresd <- sort(abs(temp[, 1] - temp[, 2]))
dresd = dresd[(p + 1):choose(n, 2)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-140421181933-phpapp01/85/Computational-Techniques-for-the-Statistical-Analysis-of-Big-Data-in-R-31-320.jpg)
![Wilcoxon Tau Estimator
Original:
dresd <- sort(abs(temp[, 1] - temp[, 2]))
dresd = dresd[(p + 1):choose(n, 2)]
What’s wrong?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-140421181933-phpapp01/85/Computational-Techniques-for-the-Statistical-Analysis-of-Big-Data-in-R-32-320.jpg)
![Wilcoxon Tau Estimator
Original:
dresd <- sort(abs(temp[, 1] - temp[, 2]))
dresd = dresd[(p + 1):choose(n, 2)]
What’s wrong? Bad algorithm (the sort is at least O(nlogn)),
variable gets copied multiple times](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-140421181933-phpapp01/85/Computational-Techniques-for-the-Statistical-Analysis-of-Big-Data-in-R-33-320.jpg)
![Wilcoxon Tau Estimator
Original:
dresd <- sort(abs(temp[, 1] - temp[, 2]))
dresd = dresd[(p + 1):choose(n, 2)]
What’s wrong? Bad algorithm (the sort is at least O(nlogn)),
variable gets copied multiple times
Updated with C++
dresd = remove.k.smallest(dresd)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-140421181933-phpapp01/85/Computational-Techniques-for-the-Statistical-Analysis-of-Big-Data-in-R-34-320.jpg)