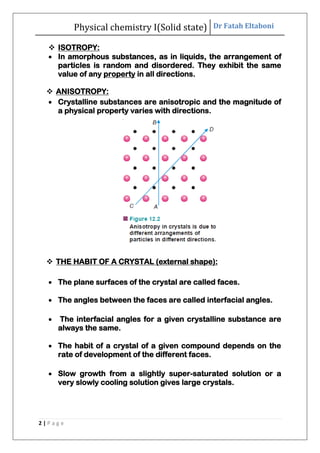
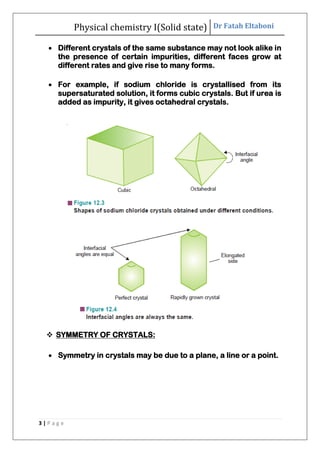
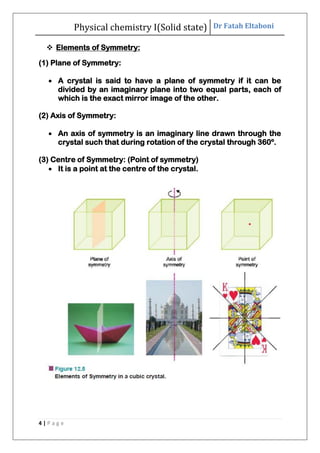
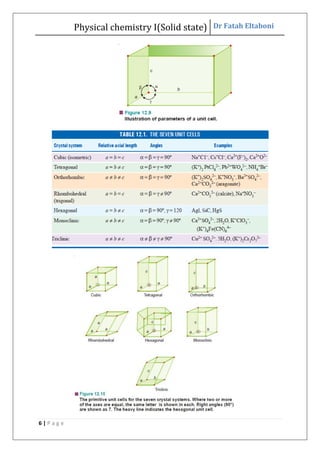
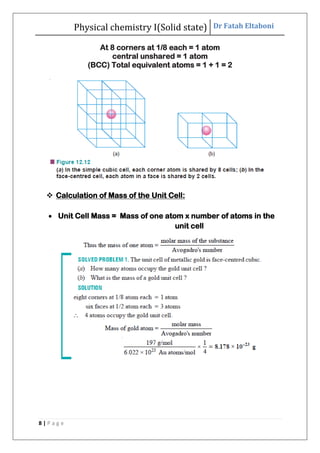
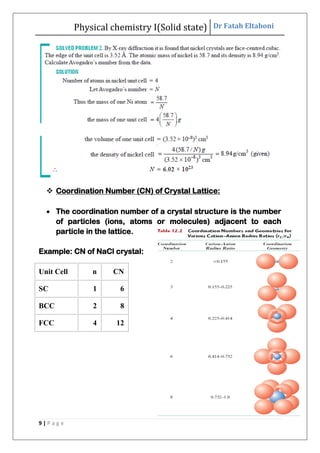
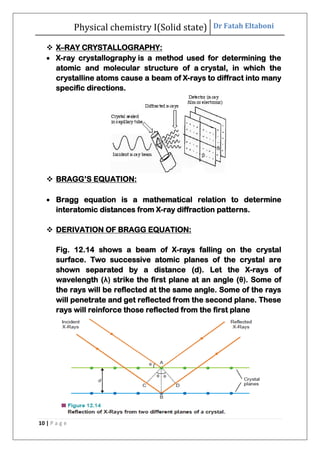
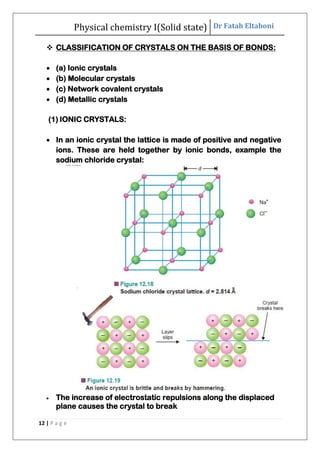
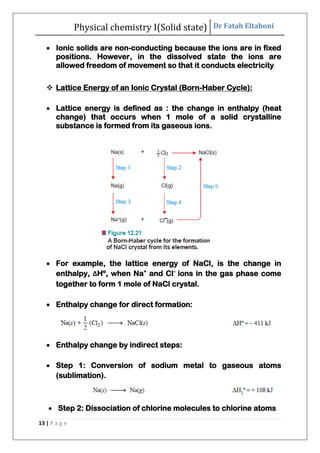
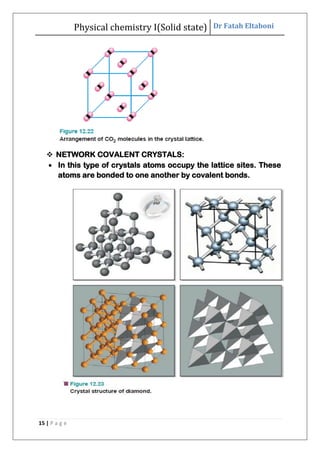
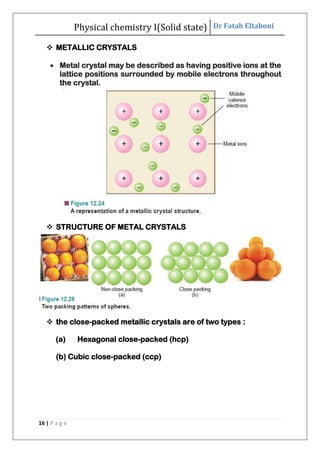
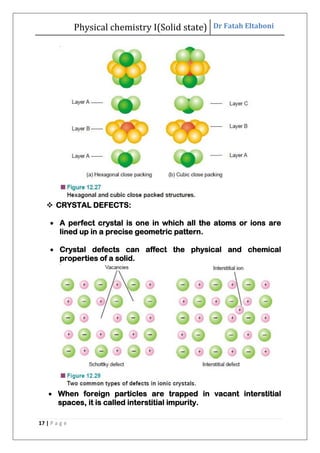
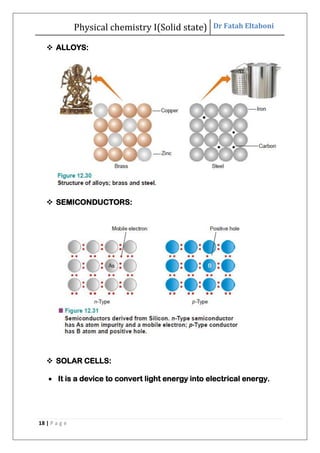
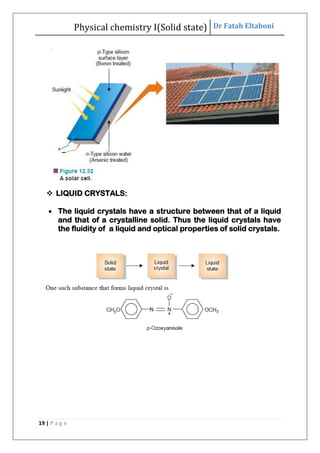
This document discusses the properties of solid state materials. It defines crystalline and amorphous solids, and describes the different types of crystal structures including simple cubic, body-centered cubic, and face-centered cubic. It also discusses crystal symmetry, unit cells, Bravais lattices, coordination number, X-ray crystallography, Bragg's law, and the different classifications of crystals based on bonding.