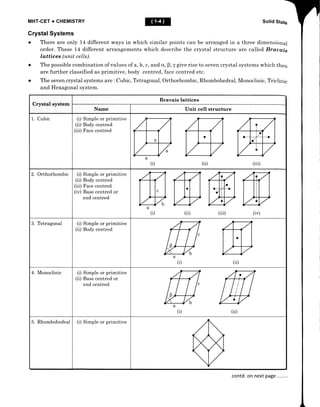
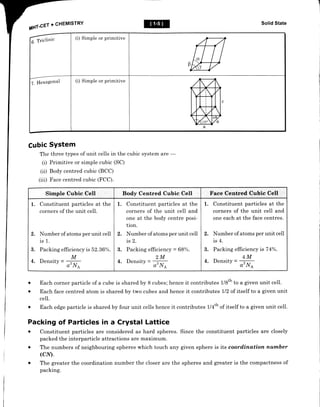
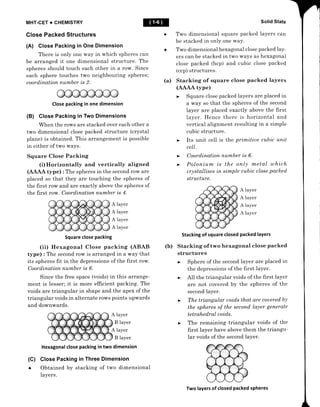
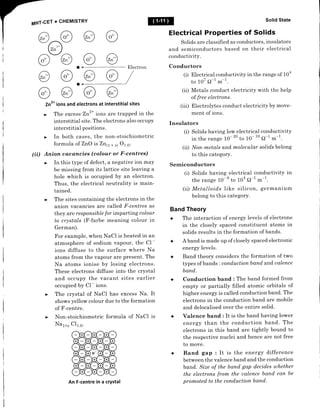
This document provides an overview of solid state chemistry. It defines solids as matter with a definite shape and volume, where the constituent particles possess fixed positions and can only oscillate. Solids are classified as crystalline or amorphous based on the ordering of particles. Crystalline solids have long-range order while amorphous solids only have short-range order. Important properties of solids discussed include density, rigidity, melting points, and electrical conductivity. The document also describes different types of crystalline solids based on bonding - ionic, molecular, metallic, and covalent network solids. Unit cell structure, crystal systems, and packing efficiency of particles in cubic unit cells are also summarized.
![MHT-CET + CHEMISTRY
lsomorphism
Two or more substances having the sarne
crystal structure are said to be isomorphous.
Isomorphous substances have the Eqme atomic
ratio.
Eryamples : NaF and MgO [atomic ratio 1 : 1],
NaNO3 and CaCO3 [atomic ratio 1 : 1 : 3] .
Polymorphism
A single substance that exists in two or more
forms or crystalline structures is said to be
polymorphous. Polymorphs of a substance are
formed under different conditions.
Polymorphs of an element are called
allotropes.
Examples ; Calcite and argonite are two
forms of calcium carbonate.
o-quartz, B-quartz andcristobalite are forms
of silica.
Diamond, graphite and fullerene are
allotropic forms of carbon.
Classification of Crystalline
Solids
(Based on the nature of constituent particles
and the forces present between them)
(l) lonic Solids
(NaCl, K2SO+, CaF2, KCI)
(i) Constituent particles are ions of opposite
charge.
(ii) Particles held together by electrostatic
(coulombic) force.
(iii) Non conductors of electricity in the solid
state. However they are good conductors
when melted or dissolved in water.
Solid State
(iv) Due to strong electrostatic forces ions are
closely packed and hence ionic solids are
hard.
(v) They are brittle as stability depends on
preservation of their geometric arrange-
ment.
(vi) High melting and boiling points.
(!l) Molecular Solids
(CIz , H2, CH+, COz, O2 on solidification and
crystalline organic compounds)
(i) Constituent particles are molecules or
unbonded single atoms of the same
substance. (in case of inert gases)
(ii) Soft solids with low melting points due
to weak intermolecular forces.
(iii) Poor electrical conductors and good
insulators.
(iv) Intramolecular forces (within the mol-
ecule) are covalent bonds.
(v)'Ji,::T,:l;;lT.rorces (between the
(a) Weak dipole - dipole interaction (in
case of polar molecules)
e.g., So1id HCl, HzO, SOz
(b) Very weak dispersion or London
forces (in case of non-polar molecules)
e.g., CH4,Hz, Ar, Ne.
(c) Intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
e.9., HzO (ice), NHg, HF.
(!ll) Metallic Solids
(Metals such as Na, K, Ca, Li, Fe, Au, Ag,
co)
Crystalline solids formed by atoms of the
same metallic element held together by
a metallic bond.
Malleable and ductile.
Good electrical and thermal (heat)
conductivity.
In case of solid metal, the valence electrons
are loosely held and are hence delocalised
over the entire crystal. Hence the crystal is
considered to be an array of positive ions in
a sea of mobile electrons. The attractive
interactions between the cations and the
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Crystalline solid
Covalent
solids
(Network
solids)
Metallic
solids
Molecular
solids
Hydrogen
bonded
molecular
solids
Polar
molecular
solids
Non-polar
molecular
solids](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidstate-230228023338-20dd2b20/85/SOLID-STATE-pdf-2-320.jpg)



![MHT-CET + CHEMISTRY
Vacancy of Nae ion
Vacancy through aliovalent ion
An aliovalent ion has an oxidation state
different from that of the host ion.
A vacancy can be created by addition of
impurities of aliovalent ions.
If SrCl2 is added to NaCI during its
crystallization; the Sr2
*
ions replace Na*
ions. However to maintain electrical
neutrality; one Sr2
*
ion replaces two Na*
ions and thus creates one vacant site.
(b) lnterstitial impurity defect
interstitial spaces in the lattice structure.
the lattice sites and carbon atoms occupy
the interstitial spaces.
Iron
Carbon
Stainless steel
(lll) Non Stoichiometric Defects
+ The defects in which the stoichiometry of the
compound ls changed are called non-
stoichiometric defects.
It arises when the ratio of the number of
atoms of one kind to that of the other kind or
the ratio of the number of cations to anions
becomes different than that indicated by the
chemical formula.
Solid State
Two types of non-stoichiometric defects :
(a) Metal deficiency defect
Possible only in case of compounds of
metals showing uariable oxidation states.
In case of some ionic crystals; positive
metal ions are missing from their original
lattice sites.
the presence of a cation of the same metal
with higher oxidation, state, then that of
the missing cation.
Example : In NiO [containing Ni2* and 02- ]
Ni2* ions are missing and hence a vacancy is
created. This vacancy is filled in by Ni3* iorls
thus creating a vacant site. The composition
of NiO, then becomes Ni6.gz Or.o.
Non-stoichiometric Nio.gz Or.o
(b) Metal excess defect
The two types of metal excess defects are :
(i) A neutral atom or a,n extra positiue ion,
occupies interstitial p osition.
Excess
neutral
Zn atom
@
@
@
@
@
@
@
@
NeutralZn atom at interstitial site
When ZnO is heated it decomposes as :
ZnO + Zn2* *10, +2e-
2L/
@
@
@
@
@
@
@
@@
@@
@@
@@
@
Vacancy
@
@
@
@
.)!
?-, lt
Lln
+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidstate-230228023338-20dd2b20/85/SOLID-STATE-pdf-10-320.jpg)
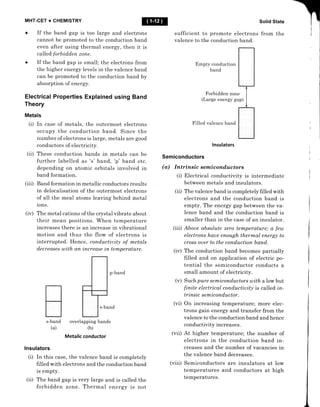








![MHT-CET + GHEMISTRY
(a) Schottky defect (b) Frenkel defect
(c) metal deficiency defect
(d) metal excess defect
118. Which of the following defects is also known
as dislocation defect?
Solid State
(b) Extrinsic semiconductors are formed by
adding an impurity.
(c) The band gap can be crossed easily by the
electrons on supplying energy.
(d) AI1 the above.
L26. A silicon solar battery is ..
(a) n-type semiconductor.
(b) p-type semiconductor.
(c) combination of n and p-type semiconduc-
tor.
(d) used only at high temperatures.
Magnetic Properties
127. The diamagnetic substance from the follow-
ing is ..
(a) F e (b) HzO (c) Cu2* (d) CrO2
128. The ferromagnetic substance is ..
119. On doping germanium with a small amount
of gallium a type semiconductor is
obtained.
(a) F renkel
(c) Impurity
(a) n-type
(c) intrinsic
(a) Boron
(c) Phosphorus
(b) Schottky
(d) Metal deficiency
(b) p-type
(d) both (a) and (c)
(b) Carbon
(d) Arsenic
120. The true statement is :
(a) Metalloids are usually insulators above
room temperature.
(b) The size of the band gap decides the
electrical conductivity of a substance.
(c) Semiconductor prepared by adding a
dopant are called intrinsic semiconductor.
(d) Electrolytes use free electrons to conduct
electricity.
LZL Which of the following dopants would give a
p-type semiconductor with silicon?
129. The false statement is :
(a) Paramagnetic substances have unpaired
electrons.
(b) Paramagnetic substances can be magne-
tised permanently.
(c) Diamagnetic substances have all elec-
trons paired.
(d) Both (b) and (c).
(a) Gd
(c) N2
(b) benzene
(d) NaCl
122. A semiconductor of silicon can be made lB0. CrO2 is ........
n-typebyadding........ ,,; ,. A r:
(a) arsenic (b) a pentavalent impurity ja]
:iamacneti:
@) paramagnetic
(c) aluminium (d) both (a) and a,
--.---' (c) ferromagnetic
(d) a substance with no magnetic moment.
123. To get a p-type semiconductor the impuritv
added to si should have the following;;;; 131' The diamagnetic species among the following
of valence electrons ........ are """"
(a) 4 (b) 3 (c) 5 (d) 1 (a) sc3* (b) Fe3
* (") c2HsoH
r24. Band theory explains ........ (d) both (a) and (c)
(a) the difference between valence and con- 132' The magnetic moment of a substance depends
duction bonds. on """"
(b) electrical conductivity of metals. (a) the number of unpaired electrons'
(c) valencies of metals. G) the total number of electrons'
l
(d) physical properties of metals. (c) the presence of an external magnetic field'
I
125. which of the following statements is true (d) both (a) and (c)' I
i
about semiconductors? 133. Ferromagnetic materials are those, which.....
(a) Intrinsic semiconductors become conduc- (a) have large number of unpaired electrons'
tors when temperature is increased.
I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidstate-230228023338-20dd2b20/85/SOLID-STATE-pdf-22-320.jpg)
![MHT-cET+cHEMtsrRY @
27. Diamond contains sp3 hybridised carbon
while graphite has sp2 hybridised carbon
atoms.
28. Molecular solids have low melting point and
do not contain free electrons or free ions to
caruy current.
29. Copper is a metallic solid with FCC arrange-
ment while Na and Po have BCC and SCC
arrangements respectively Phosphorus is a
molecular solid.
30. Buckminster fullerene is Coo.
31. A six membered ring is fused with a five or
six membered ring.
34. A total of 7 crystal systems with 14 different
types of unit cells in total.
36. 'B' atoms at the corners of the cube.
.'. No.of Batoms-8"'-1
8
'A' atoms at the face centres of the cube each
face centre atom contributes Llz.
No. of 'A'atom = g * I
- B.
2
Formula of the compound is AB3.
37. For FCC;
Solid State
o3 = 4.76 x 10-'3 .-'
a = 3.62x 10-8.*
r = I = 1.812x 10-8.*.
2
42. hcp .... AB AB .... arrangement.
ccp .... ABC ABC arrangement.
43. AB AB type arrangement in two dimensions.
The spheres of the second layer are placed
betwe en 2 spheres of the first layer.
nM
46.
a
47.
d=
2.7 =
n=
= 3.84
Unit cell is
l/A . a3
6x1023x(4x10-8)3
2.7 x 64x 10-24 x 6 x 1023
[400pm - 4x 10-8cm]
n (27)
x l/a I atoms.
)
t in one unit ceII.
are present in Io:lr^
I
( ,-)
27
A
-+
F'CC type.
361
=-- = 127.6pm.
2x 1.414
Density =
.'. 10 =
.'. fu[ =
2J'
48. F or N close packed spheres, the number of
tetrahedral voids is '2IV' an the number of
octahedral voids is '.4/'.
Number of ions in 0.5 mol of the compound
=0.5x6x1023=3x1023
.'. Number of tetrahedral voids
= 2(Bx 1023)=6x1023
Number of octahedral voids = 3 x 1023
Total number of voids = 9 x 1023.
4M
u3 l/a
4xM
(2x10-8)3x6x1023
10x8x10-24x6x1023
l/A
4
49. 49 = 40
mol
2 atoms are
=12
L2 g contain
contain
50x6x1023
4
6 x 1023 atoms 50 g wilt
- 25 x 1023 atoms.
L2
38. Since CsCI is a BCC unit cell with Cs* at the
body centre position and Cl - at the corners
of the unit cell.
Distance between Cs* and Cl -.
1
=, xBodYdiagonal
=
1*.E a-Ji o
22
39. For SCC;
M
.'. 0.1 l/A atoms
unit cells.
50. Atoms of Q are in ccp arrangement. F or every
atom of Q there are 2 tetrahedral voids.
Atoms of P occupy (1/3)'d of these voids.
Number of voids occupied - 2t + = ?.
33
RatioofP and a = : : l=2:3. PzQg.
J
51. The primitive unit cell is same as the simple
cubic cell.
52. Greater the coordination number more com-
pact is the packing and lesser the void space.
(4
-t_
.40
presen
d=
l-
D
au
200
6x 1023 xoB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidstate-230228023338-20dd2b20/85/SOLID-STATE-pdf-24-320.jpg)

![MHT.CET + CHEMISTRY
1
1 g NaCl = rr" x 6 x 1023 molecules
4 molecules of NaCI are present in one unit
ceII t '.' it shows F CC arrangement.]
#
x 6 x 1023 molecules are present in
' 2.56 x lO21 unit cells.
72. In NaCI, each CI - ion is surround.ed by 6 Na+
ions and each Na* is surrounded by six Cl -
ions. Hence, CN of both ions is 6.
7 3. BCC lattice.
.'. Distance between nearest neighbours
_ Ji o
- .6 * 6
-
22
7 4. For simple cubic system,
a 350
g.EA"
r = 2= Z =I75pm
77 . Volume of 1 sphere = +" 13 .
3
Since BCC lattice has 2 spheres per irnit ceII.
Totalvolume - 2xlnrn =
8
n13.
33
78. There were 6 atoms of A at face centres. If
the face centred atoms along one of the axes
is removed, then 2 atoms of A are removed.
No. of A atoms per unit cell
11
= 8x- + 4x- -3
82
(corners) (face centred)
No. of B atoms per unit cell
= Dx! + 1 -,1
(edge centres) (bodY centre)
Hence, the resultant stoichiometry is AsBn.
[NaCl structure .'. B occupies the voids at
the edge centres and at the body centre.]
81. Body diagonal is Jg
".
= 1.732 x 400 = 692.8 pm
83. For BCC,
2M
Solid State
F e1o.g) S(r.o)
Let the number of F e2* be r.
The number of Fe3* be (0.9 - r)
2x+3(0.9-x)+(-2)-0
2x+2.7-3x-2-0
.'. x - 0.7.
Number of F e2* = 0.7
Number of Fe3* = 0.2
Ratio of
Fe3* 0.2
0.28.
Fe2* 0.7
85. 2(r*+r-)=o 2(r*+r_)=500
r**r_ = 250.
86. 02* : ,L2* : B*
(ccp (occupies (occupies
arrange- tetrahedral octahedral
ment) voids) voids)
1
1 : 2"2 : lx1
1
1 , i : l=2:1:2.
.'. Formula of the compound is AB2Oz.
87. 2 (r*+ r-) = a .'. 2 (110 + r--)=508
r_ = 144 pm.
88. r- o:
2J'
Diameter = 2r =
J, 1.414
- 288 pm
89. Both Cs* and I - have large atomic size.
95. KCl has FCC structure.
1 mole = 6 x 1023 molecules of KCI
4 molecules in 1 unit celI
.'. 6 x 1023 molecules - 1.g x 1023 unit cells
96. It is a ccp structure.
.'. Number of oxide ions (O2 - ) are 4.
.'. Total negative charge - 4 x (- 2) - - 8
Let number of AI 3*
be r and number of Mg'*
be .y.
@
84
d=
5.0 =
o3=
a=
l/A . a3
2x6.9
6x 1023 xo3
2x6.9
Total positive
3r+ 2Y=8
charge-3x+2y
(to balance the negative
charge due to oxide ions)
is the only value satisfying
2.3 x
cm.
10- 23
.*3
x-2andY=l
the equation.
n - fraction of octahedral holes occupied by
r), 2 1
lrr
4 2'
6 x 1023
2.84 x 10- 8
I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidstate-230228023338-20dd2b20/85/SOLID-STATE-pdf-26-320.jpg)
![MHT.GET + CHEMISTRY
m - fraction of tetrahedral voids occupied by
Ms'* = +.
8
97 . F or each Sr2* ion introduced two Na* ions
are removed; creating a cation vacancy.
10-
a
mol percent of SrCl2 is added.
'.'. 100 mol NaCI are doped with 10- 4
mol
100
moI NaCl,
= 10- 6
mol SrC12 is added.
No. of Sr2* ions added
= 10-6 x 6 x 1023 = 6 x 1017
No. of cation vacancies = 6 x 1017.
106. Since pairs of ions are missing at lattice
points mass of the crystal decreases but vol-
ume remains same. Hence, density decreases.
L07 . On heating ZnO loses oxygen and turns
yellow.
The excess Zn2* ions are trapped in the
interstitial sites and electrons also occupy
interstitial po sitions .
zno
o
, zn2* **o, +2e_
2
108. The holes created by missing anions are
occupied by electrons. These sites are called
F-centres and are responsible for colour in
the crystal.
110. The oxide is Ms.gsO.
For one mole of the oxide; moles of 02 - - 1.
moles of M - 0.98.
Let, moles of M 3*
= *
.'. Moles of M 2+
- (0.98 - x)
On balancing charges;
[3r] + t(0.e8 - x) 2) + l- 2l -- 0
000
M3* M2* 02-
x - 0.04
% ofM 3*
Solid State
1 11. Metal deficiency defect occurs with metals
showing variable valency.
FeS, FeO, NiO.
It4. Since it is a metal oxide O
2- is present. A
has oxidation state 2+.
3: J, ilT #"1," ;:t";1, i J :lil;^'.
115. In brass alloy, copper is the host element and
zrrtc is the impurity.
116. A crystal showing interstitial defect either
has the same or higher density.
Schottky defect is shown by elements having
high ionic character.
119. Germanium (group 14) is doped with a
trivalent impurity gallium (group 13). Hence,
a p-type semiconductor is obtained.
120. Metalloids behave as conductors at higher
temperature.
Greater the band gap lesser is the probability
of electrical conductivity. Electrolytes carry
current with the help of free ions.
1-zL Since boron (group 13) is trivalent.
127. CrO2; Fe + ferromagnetic
Cu2* -+ paramagnetic
128. Benzere, N2 and NaCl are diamagnetic.
L29. Ferromagnetic substances can be magnetised
permanently.
131 . 2rS. : [Ar] 3d1 4s2
sc3* [Ar] Bdo4so
Since, S.'* and CzHsOH have no unpaired
electrons, they are diamagnetic.
132. Greater the number of unpaired electrons
greater is the magnetic moment.
L34. Since all electrons are paired, they are dia-
magnetic and the number of electrons with
clockwise and anticlockwise spin should be
same.
135. Maximum magnetic moment.
SrC12.
For 1
10-4
x 100 - 4.08 %](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidstate-230228023338-20dd2b20/85/SOLID-STATE-pdf-27-320.jpg)