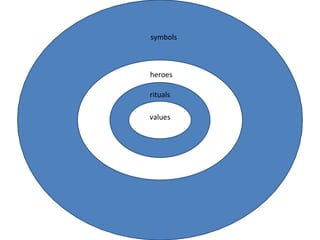
Codes can refer to any system of communication between two or more people. A diglossic situation exists when a society has two distinct codes with clear functional separation, such as one code for formal contexts and another for informal contexts. Ferguson identified four languages that exhibit diglossia: Arabic, Swiss German, Haitian Creole and French, and Greek. Bilingualism is the ability to use two languages effectively while multilingualism involves the ability to use more than two languages. Code-switching and code-mixing are strategies used in multilingual societies where speakers shift between languages. Pidgins and creoles develop from contact between languages, with creoles becoming stabilized first languages. The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis