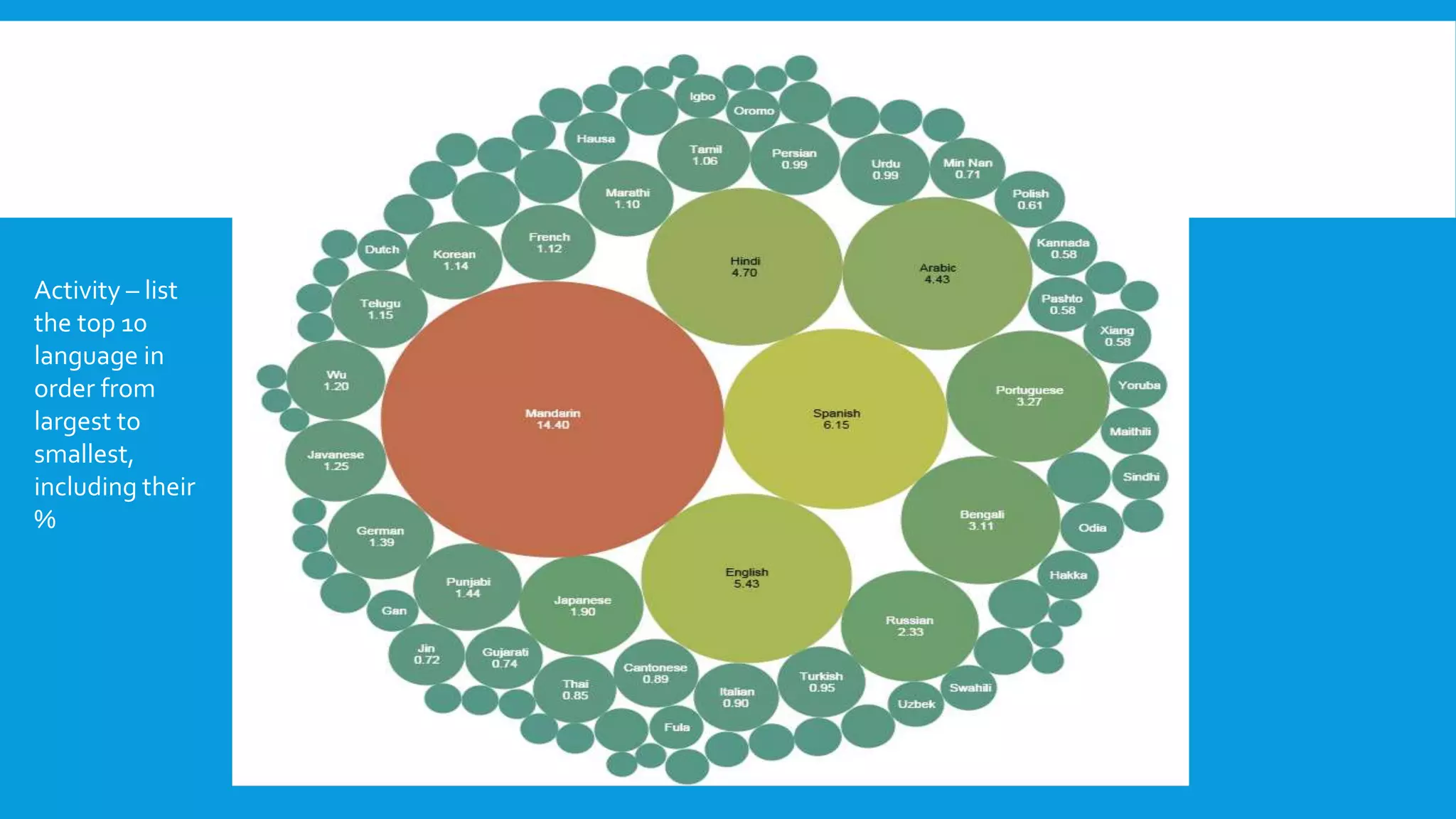
Here are some examples of abbreviations from different areas:
Academic studies - PhD (Doctor of Philosophy)
Business and finance - CEO (Chief Executive Officer)
Computing - URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
Government - UN (United Nations)
Medical - MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Internet - LOL (Laughing Out Loud)














![THE LIGHTER SIDE OFTABOO LANGUAGE
SHIFTING STANDARDS IN SOUTH PARK
Ms. Choksondik: All right children, . . . I'm supposed to clarify the school's position on the word "shit."
Stan:Wow!We can say "shit" in school now?
Kyle:This is ridiculous. Just because they say it onTV, it's all right?
Ms. Choksondik:Yes, but only in the figurative noun form or the adjective form.
Cartman: Huh?
Ms. Choksondik:You can only use it in the nonliteral sense. For instance, "That's a shitty picture of me" is now
fine. However, the literal noun form of [writes on the board] "This is a picture of shit" is still naughty.
Cartman: I don't get it.
Stan: Me neither.
Ms. Choksondik:The adjective form is now also acceptable. For example, "The weather outside is shitty."
However, the literal adjective is not appropriate. For example, "My bad diarrhea made the inside of the toilet
all shitty, and I had to clean it with a rag, which then also became shitty."That's right out!
Timmy: Sssh . . . shit!
Ms. Choksondik:Very good,Timmy.
Butters: Ms. Choksondik, can we say the expletive, like "Oh shit!" or "Shit on a shingle"?
Ms. Choksondik:Yes, that's now fine.
Cartman:Wow!This is gonna be great! A whole new word!
("It Hits the Fan." South Park, 2001)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theenglishlanguagepowerpoint-150823095700-lva1-app6892/75/The-english-language-powerpoint-16-2048.jpg)


