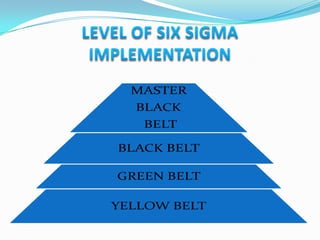
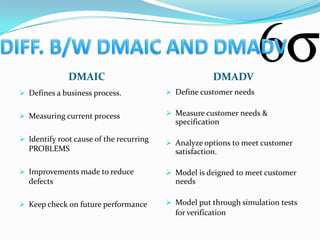
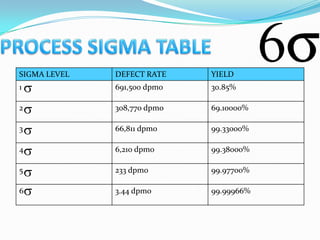
The document provides an overview of Six Sigma, including its meaning, history, implementation, and various levels of certification. Developed by Motorola in the late 1970s, Six Sigma is a statistical approach aimed at reducing defects and improving business processes, leading to significant cost savings in various industries. The document also outlines the DMADV and DMAIC methodologies for process improvement and design, detailing the training structure for different levels of Six Sigma practitioners.