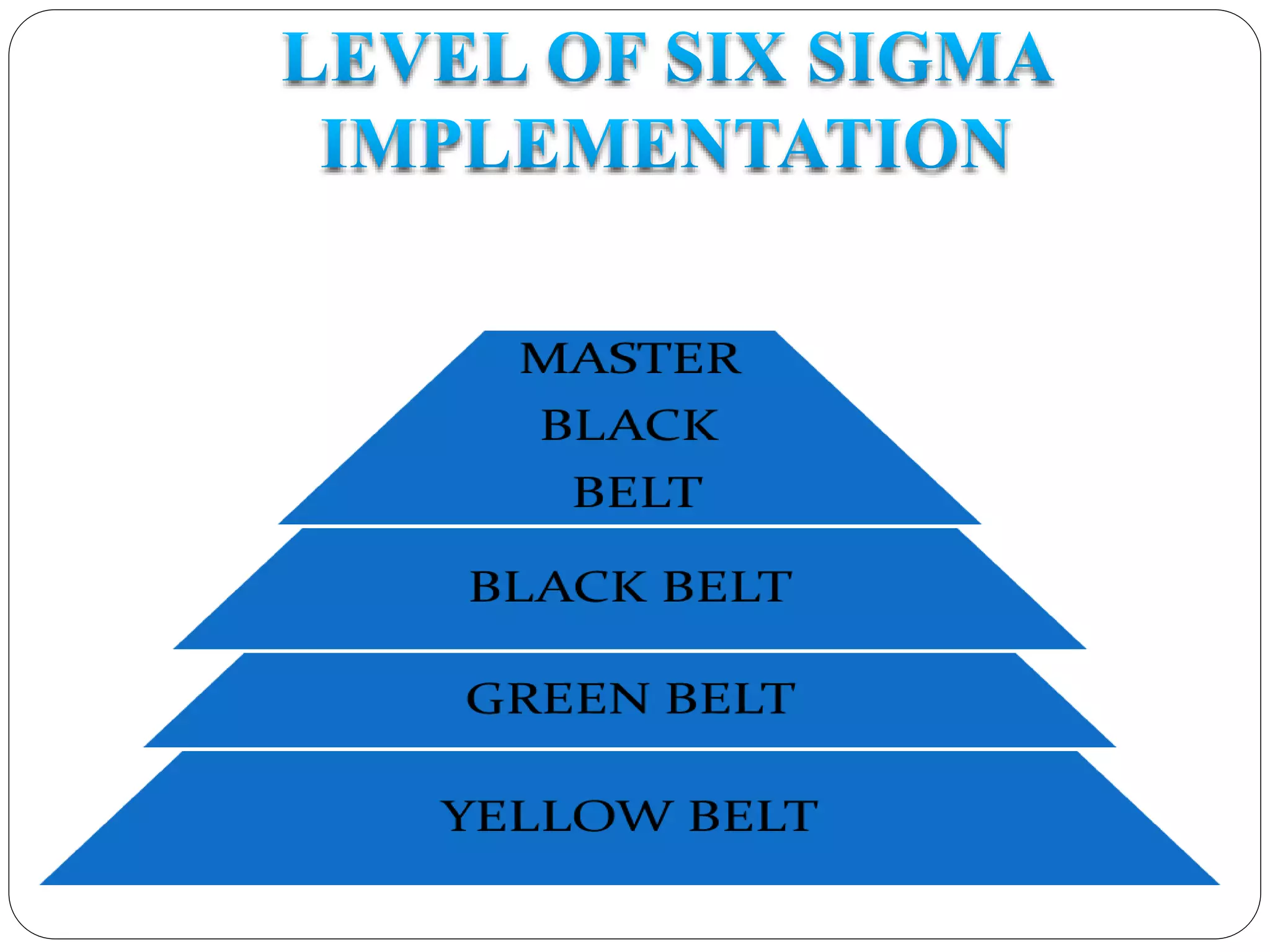
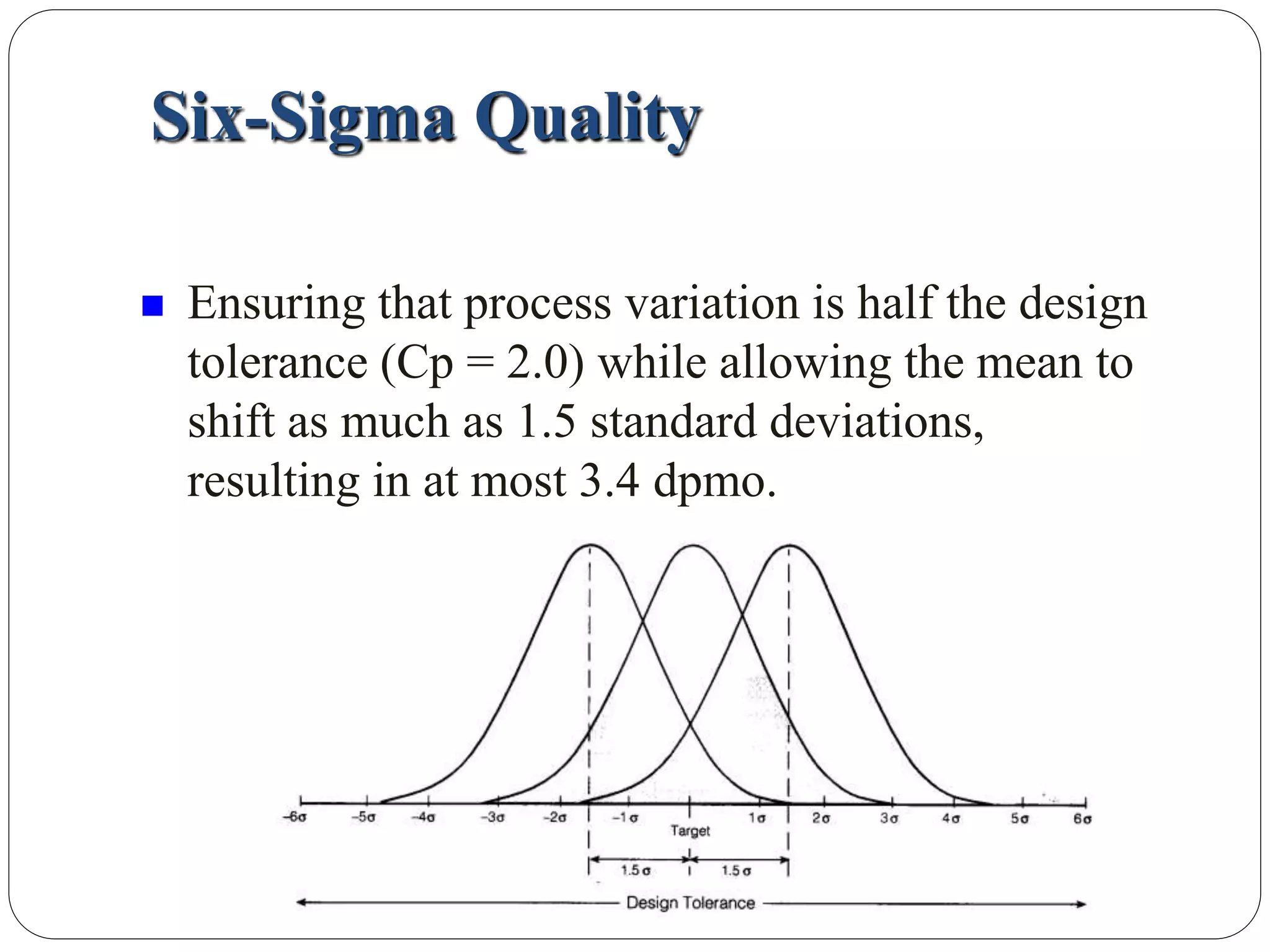
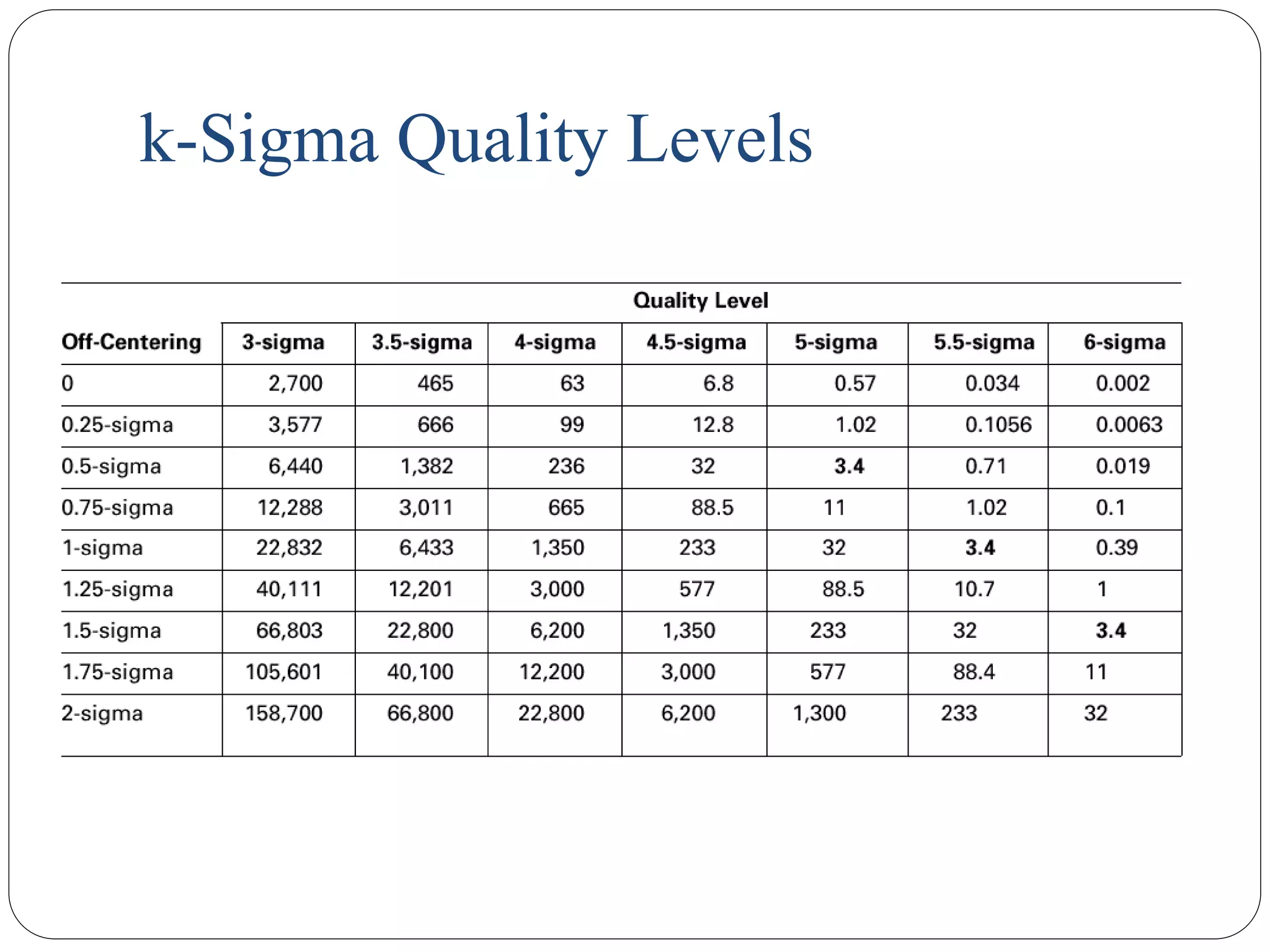
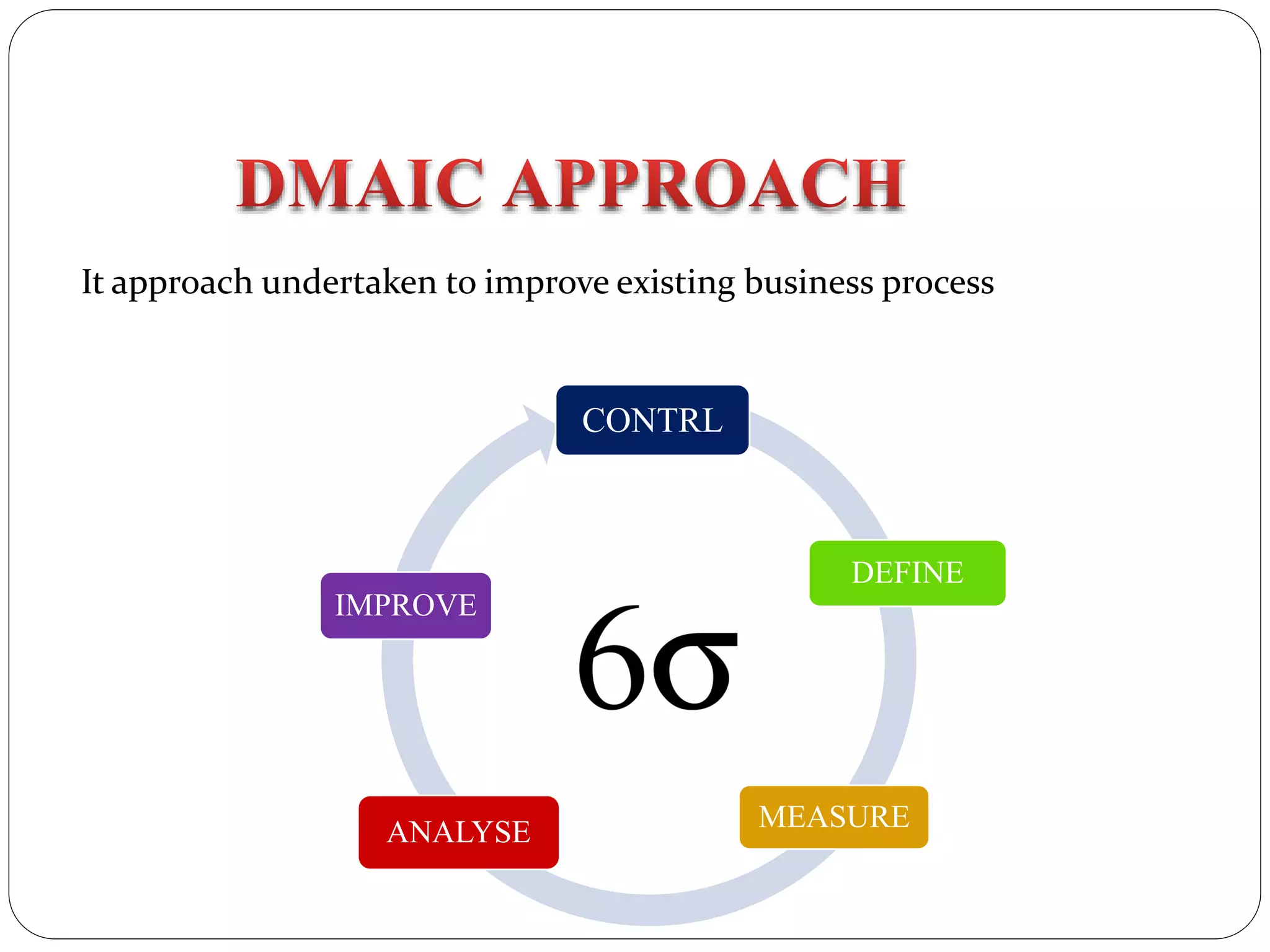
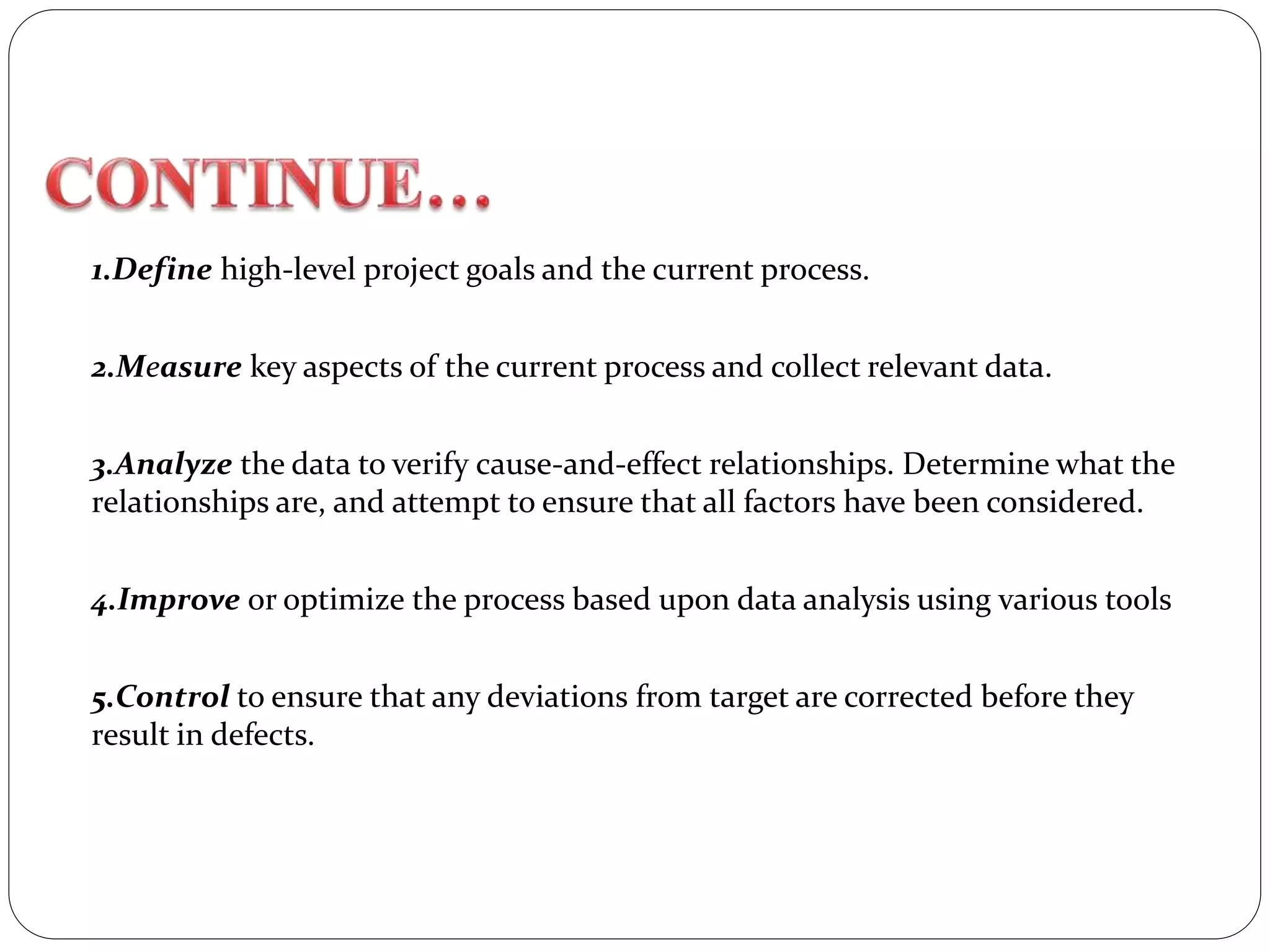
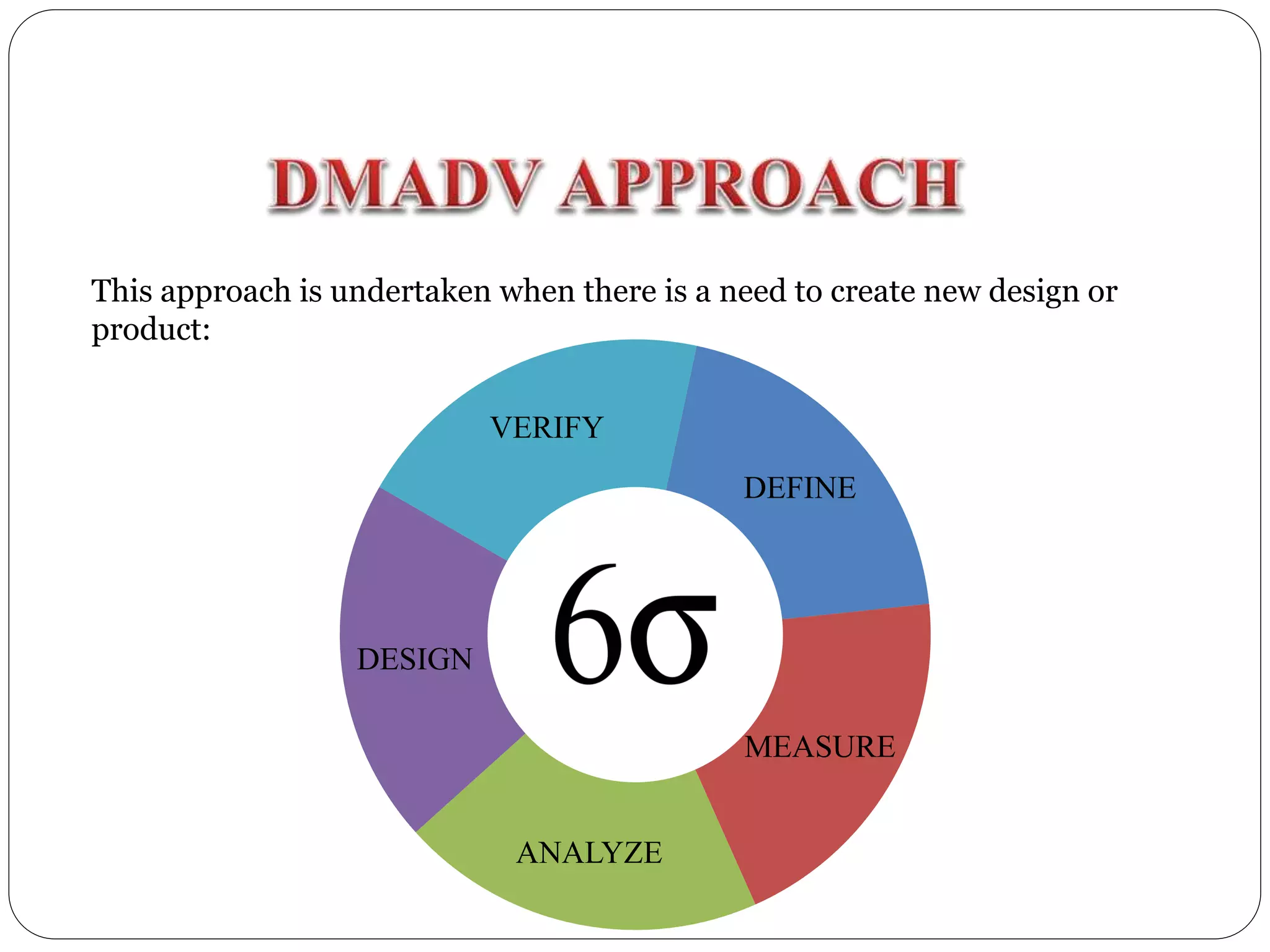
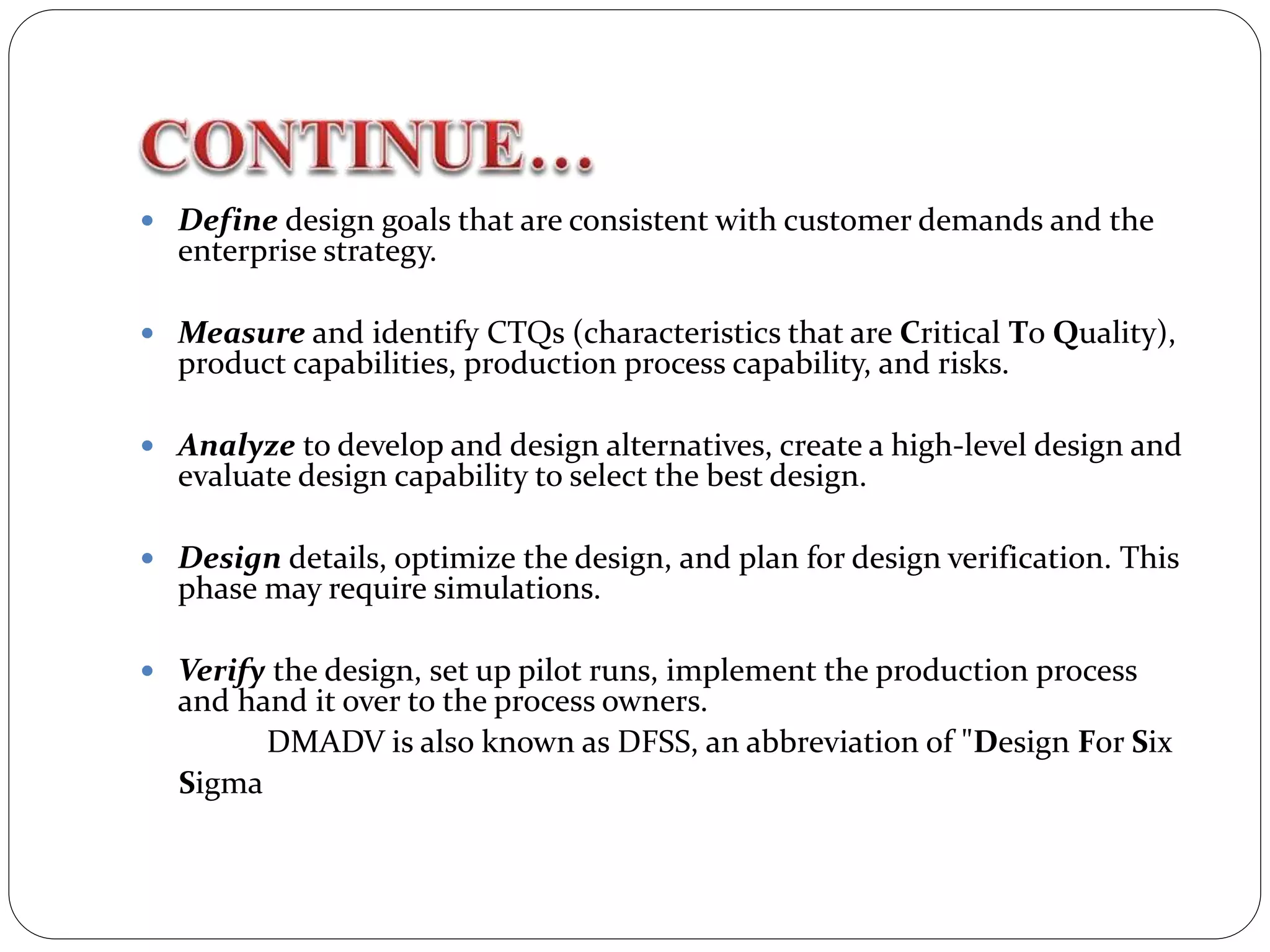
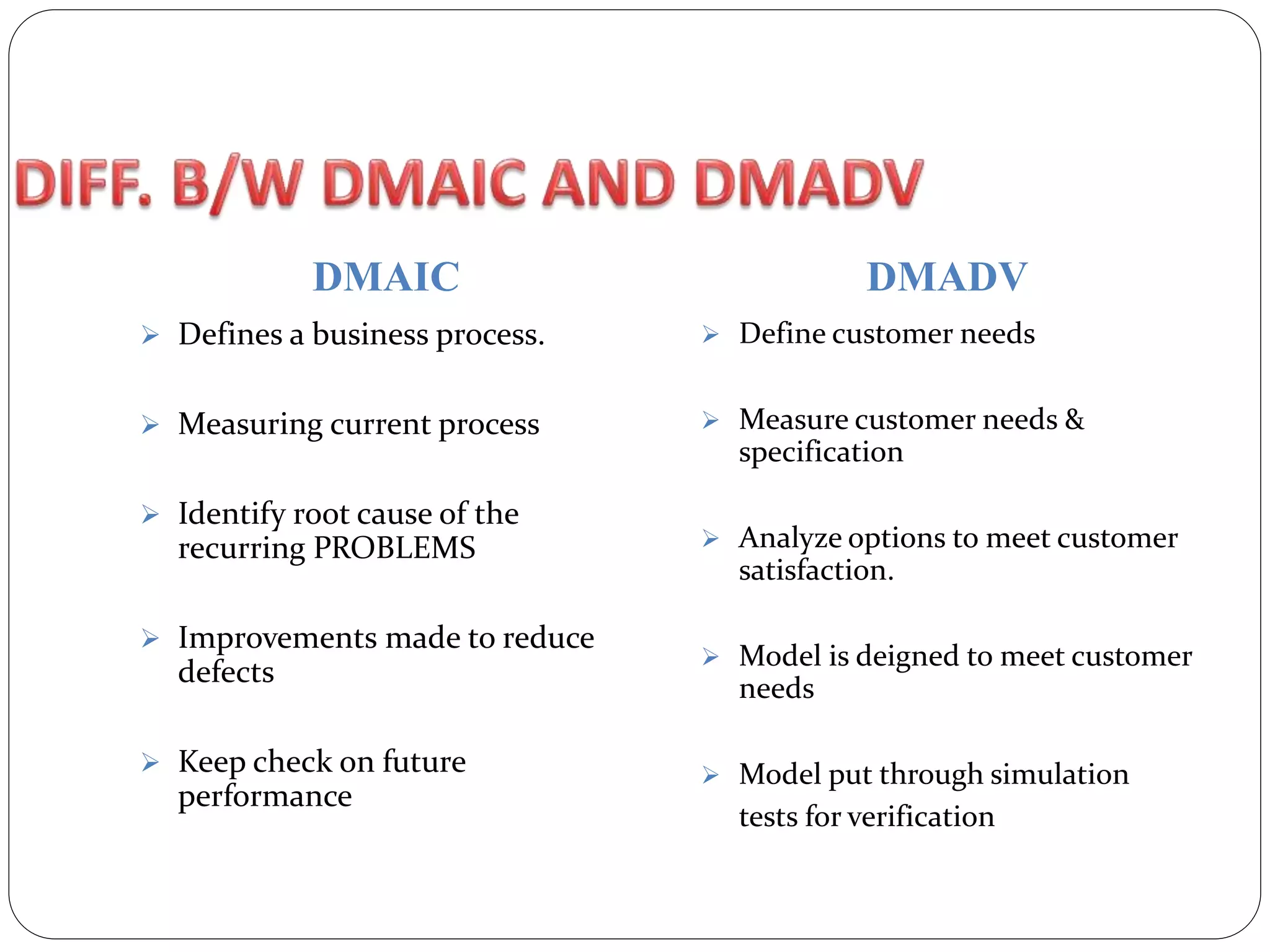
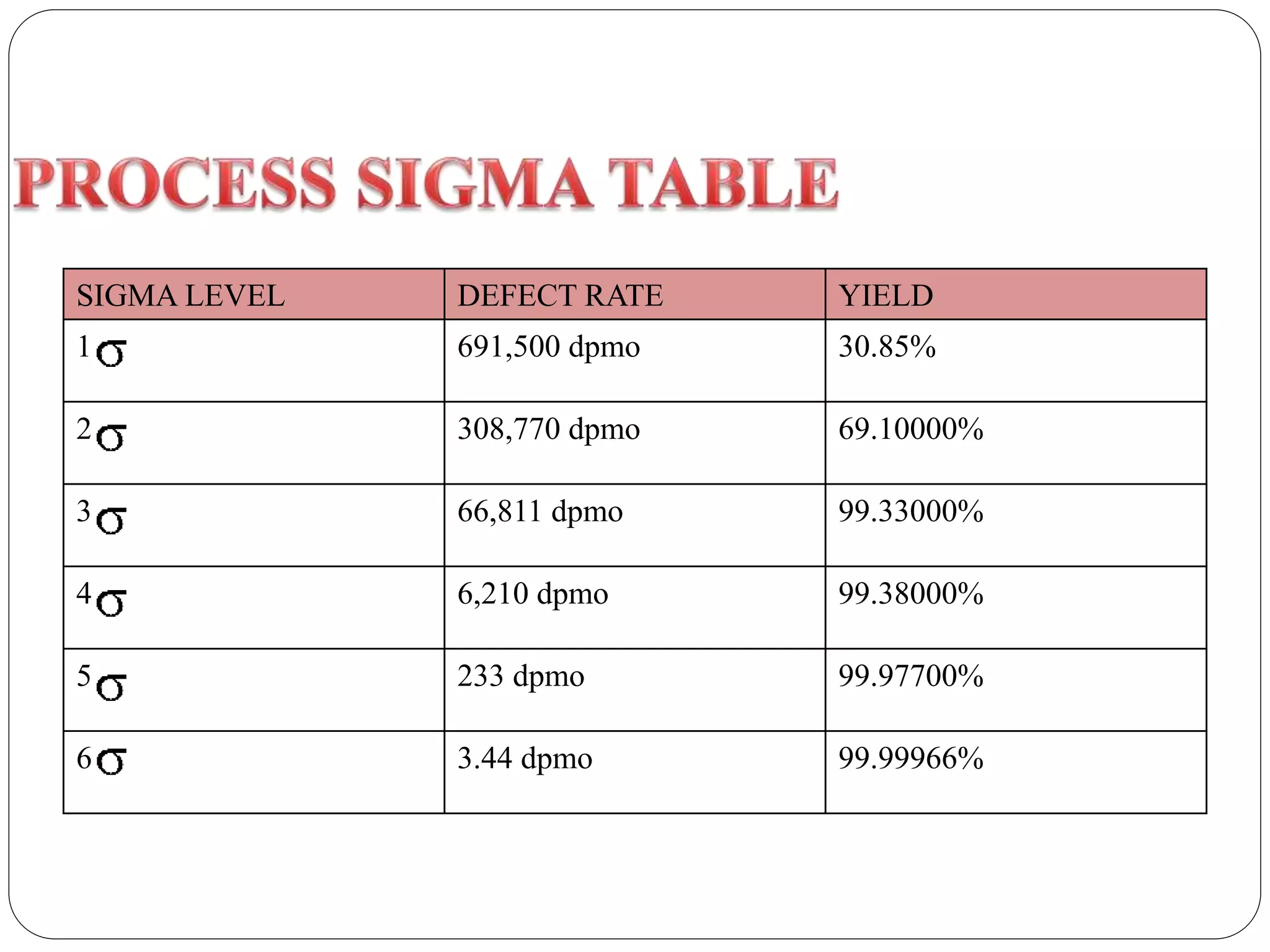
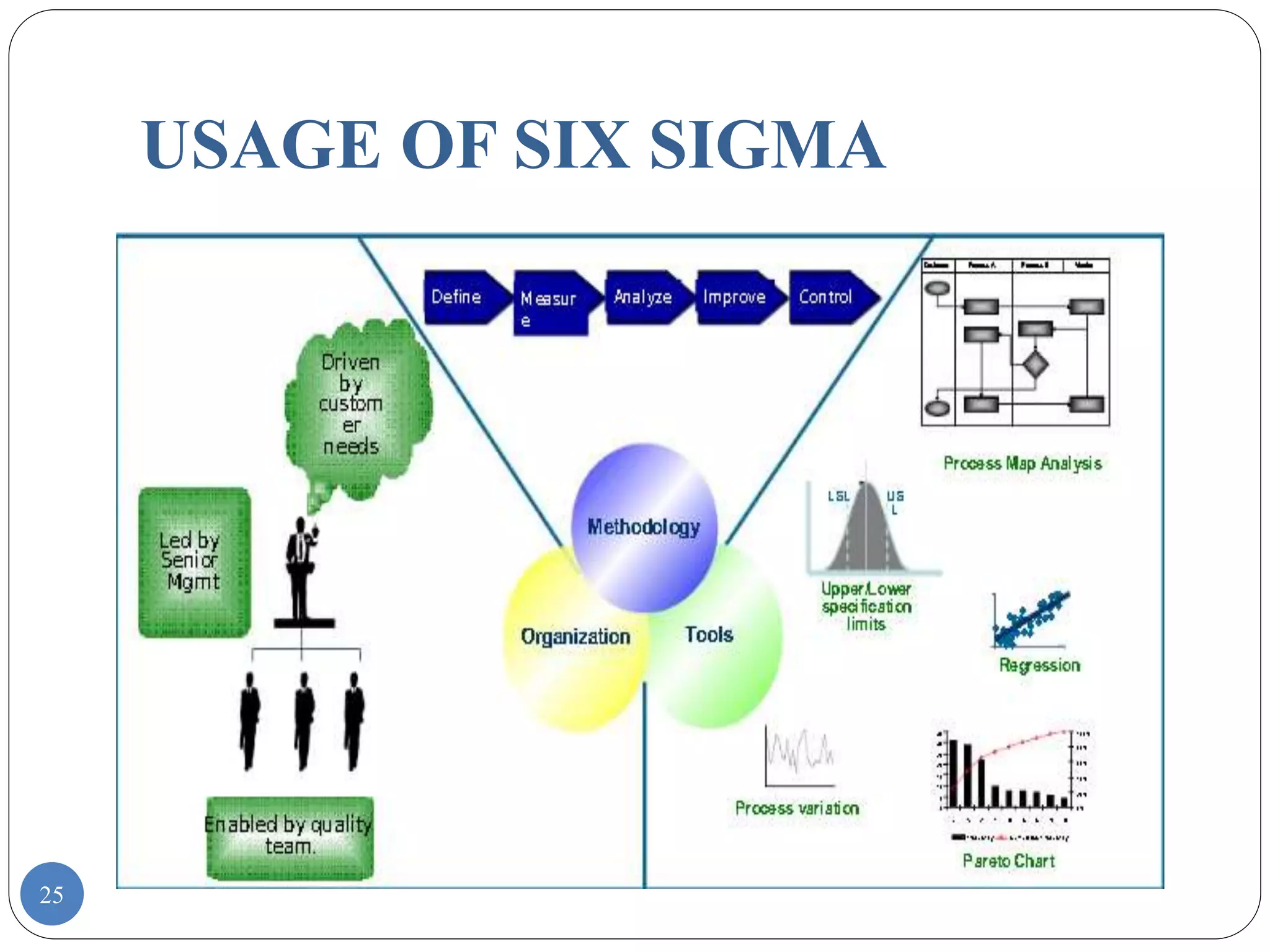
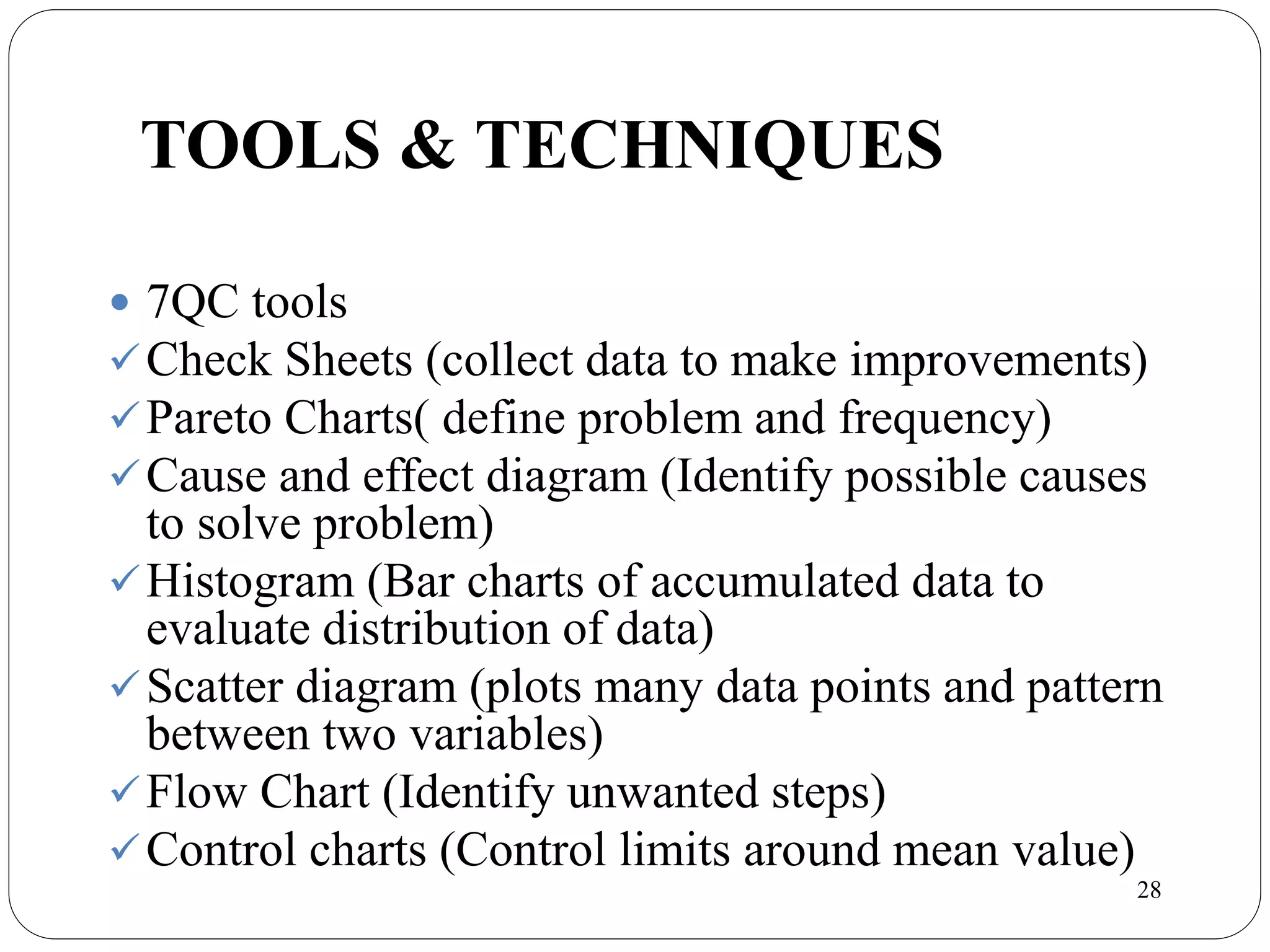
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach to process improvement originally developed by Motorola. It aims to reduce defects to 3.4 defects per million opportunities. There are two main methods - DMAIC which improves existing processes and DMADV which designs new processes. Key roles include Champions, Master Black Belts, Black Belts and Green Belts who lead projects. Statistical tools like control charts are used to analyze processes, identify issues, and implement solutions to reduce variations and defects. Widespread adoption of Six Sigma has helped many companies significantly cut costs and improve quality, including Motorola who saved over $17 billion from its Six Sigma program.