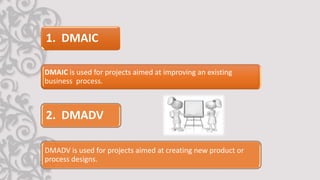
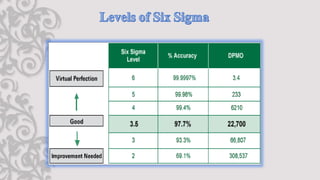
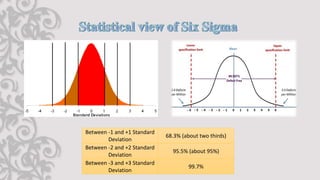
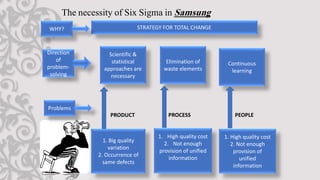
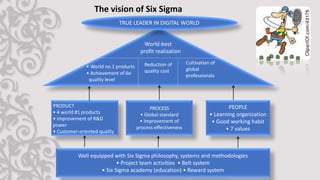
The document discusses Six Sigma, a statistical approach to process improvement. It was developed by Motorola in the 1970s to improve quality by identifying and removing defects. Six Sigma aims to reduce variation and prevent deficiencies through techniques like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify). It utilizes belts, champions, masters belts, and executives for implementation. Case studies show how Samsung adopted Six Sigma to remedy defects, reduce costs, improve cycle time, and increase customer satisfaction.