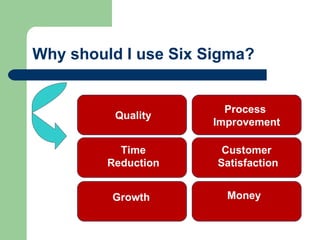
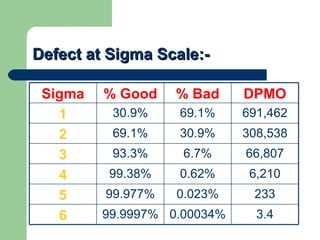
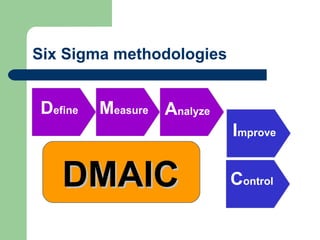
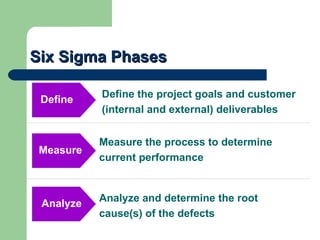
This document provides an introduction to Six Sigma, including an overview of what it is, why it's used, key concepts like defects per million opportunities (DPMO) at different sigma levels, and the DMAIC methodology involving define, measure, analyze, improve, and control phases. It also outlines some common Six Sigma tools and roles like Green Belts, Black Belts, Master Black Belts, Champions, and executive leadership. The goal of Six Sigma is to improve quality, reduce defects and variation in processes, and increase customer satisfaction.