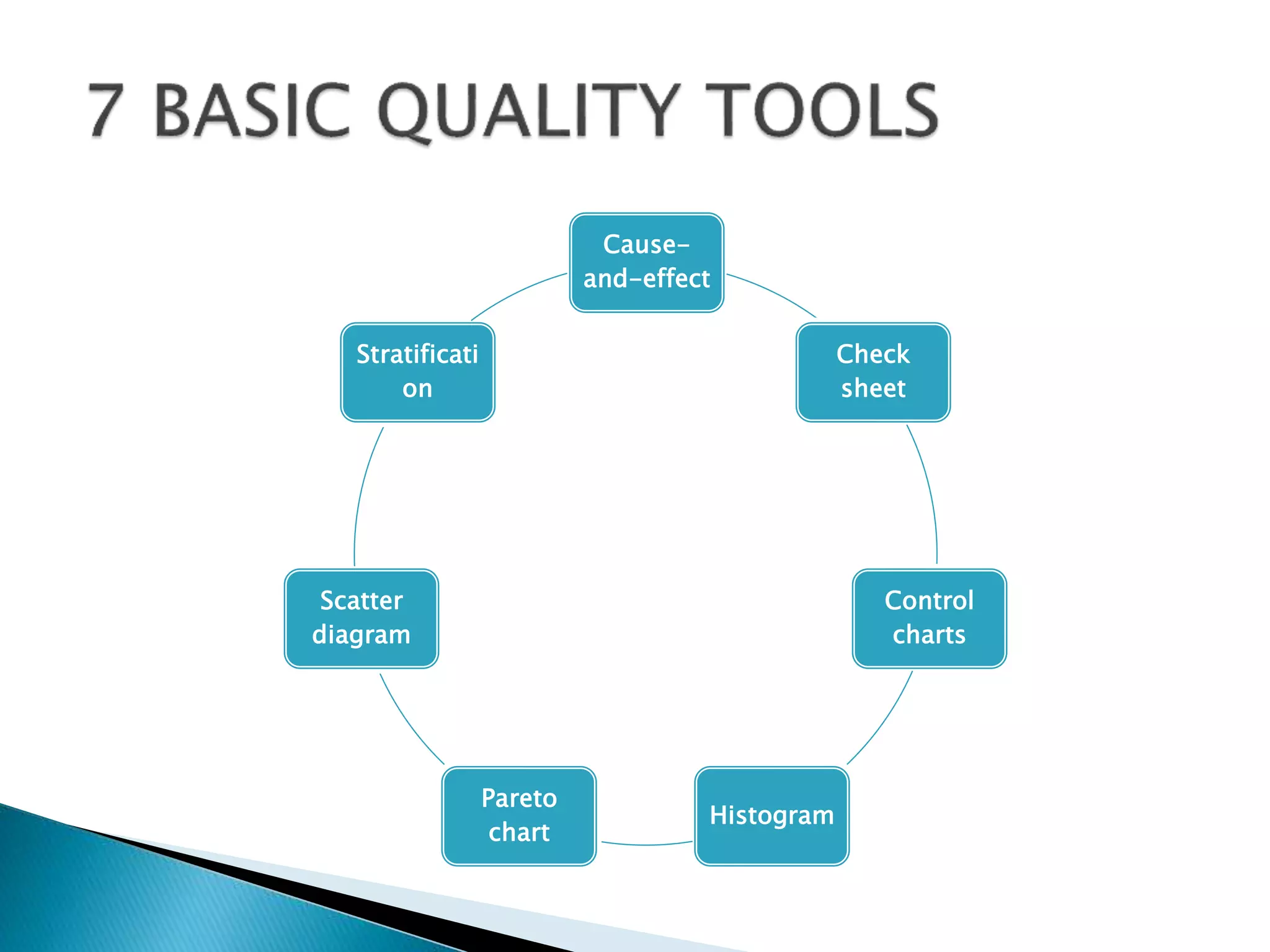
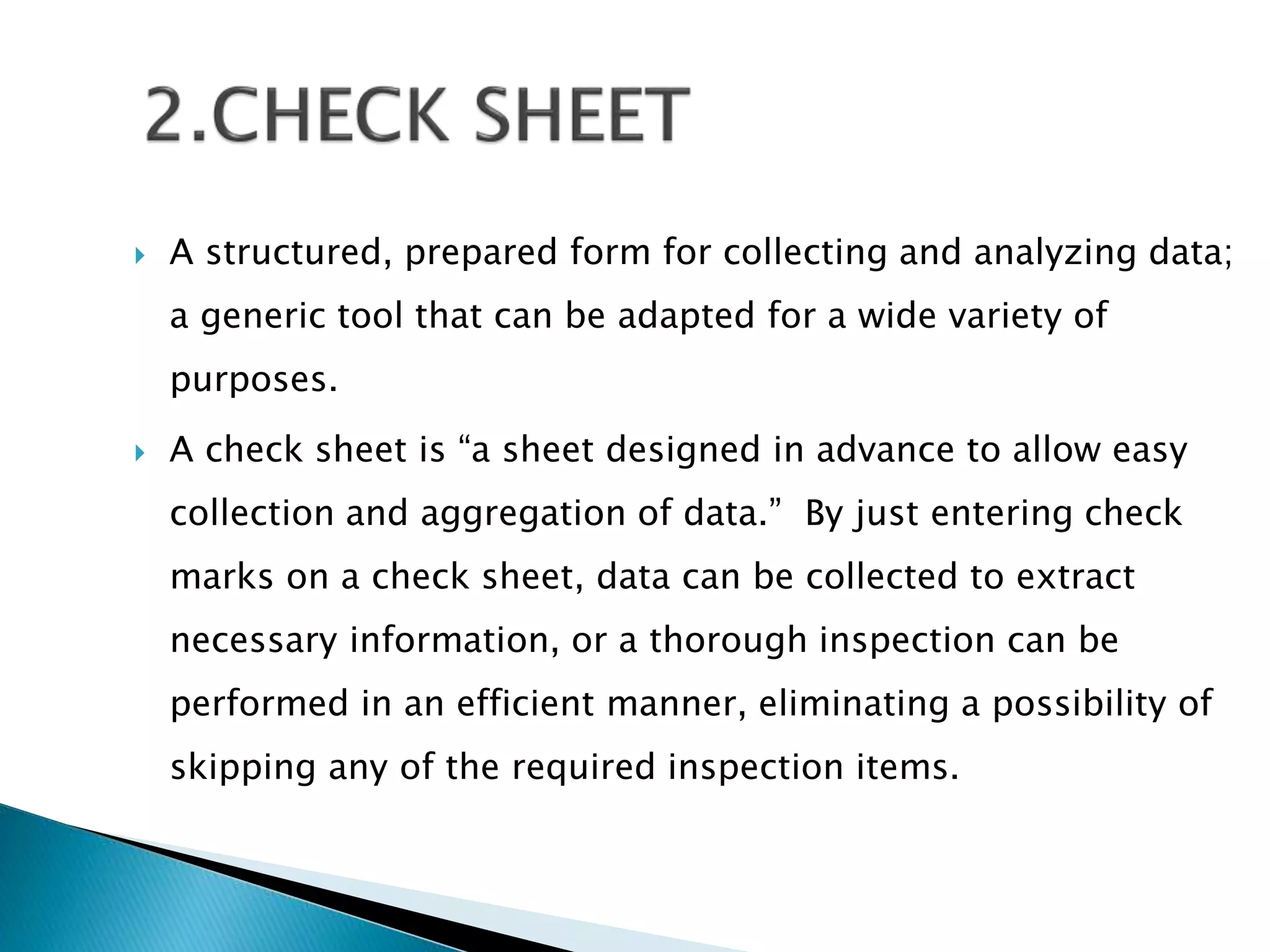
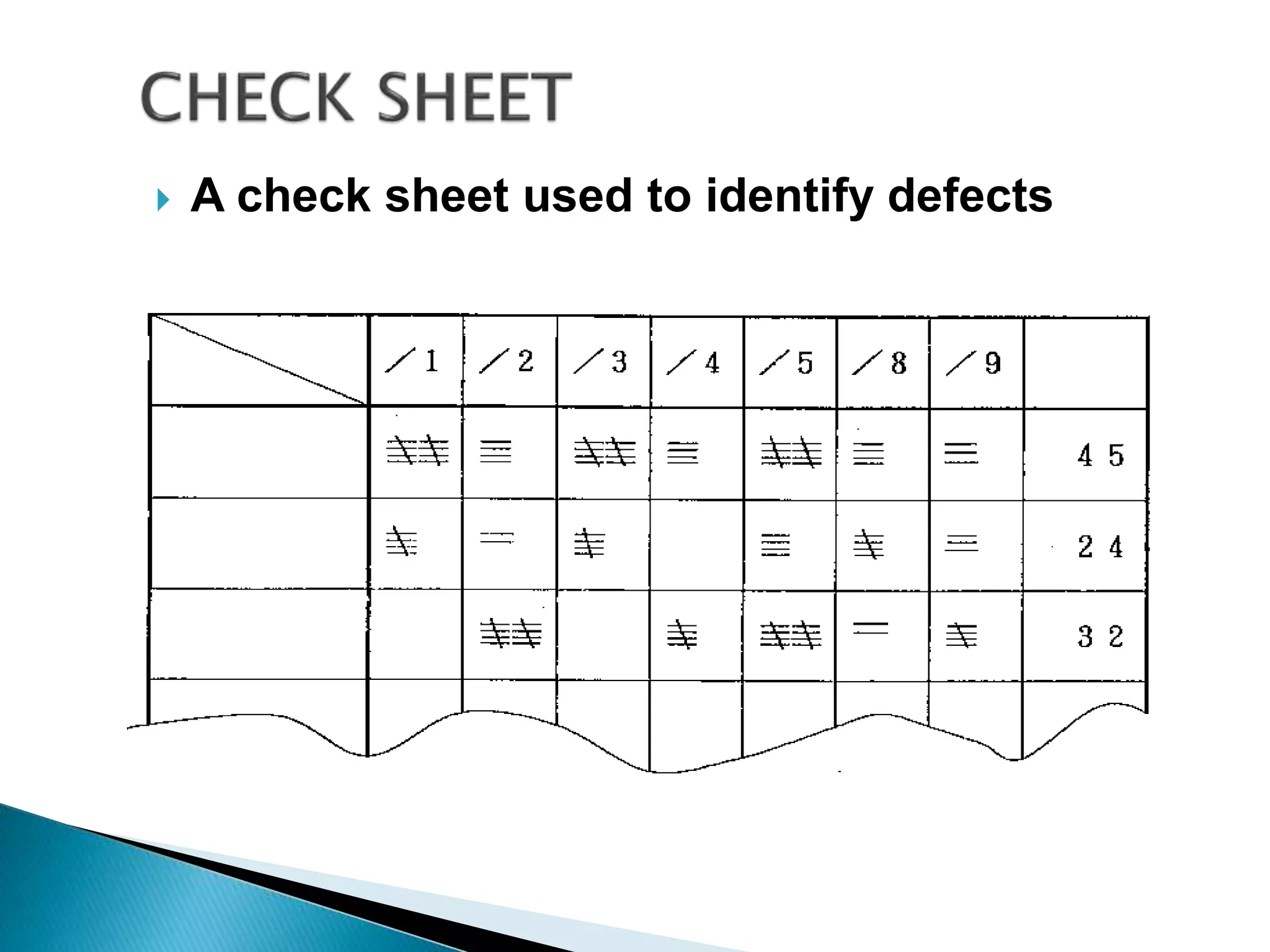
The document discusses 7 quality tools: cause-and-effect diagram, check sheet, control chart, histogram, Pareto chart, scatter diagram, and stratification. It provides descriptions of each tool and guidelines on when they should be used, such as for identifying causes of problems, collecting data, analyzing processes over time, determining if a process is stable, and separating data into categories for clearer analysis.