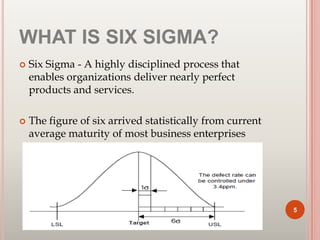
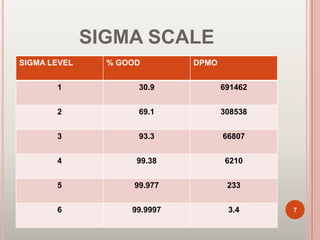
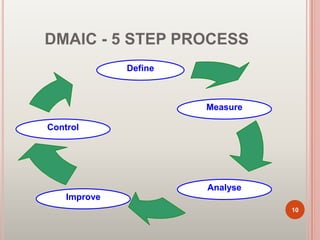
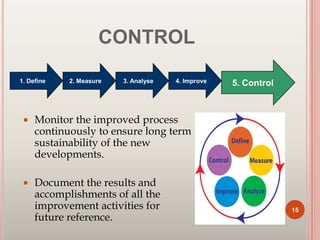
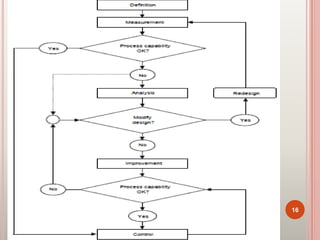
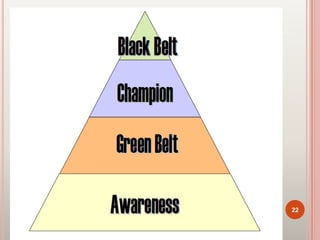
Six Sigma is a set of techniques and tools for process improvement. It was developed by Motorola in the 1980s to reduce defects but aims for near perfect processes. The goal of Six Sigma is to reduce process variation and defects to 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It uses methodologies like DMAIC for improvement and DMADV for new process design. Key benefits include increased profits by eliminating defects and accelerating improvement rates. Common roles include Champions, Master Black Belts, Black Belts, and Green Belts. Tools include control charts, Pareto charts, and design of experiments. Many major companies worldwide have implemented Six Sigma.