Embed presentation
Downloaded 91 times






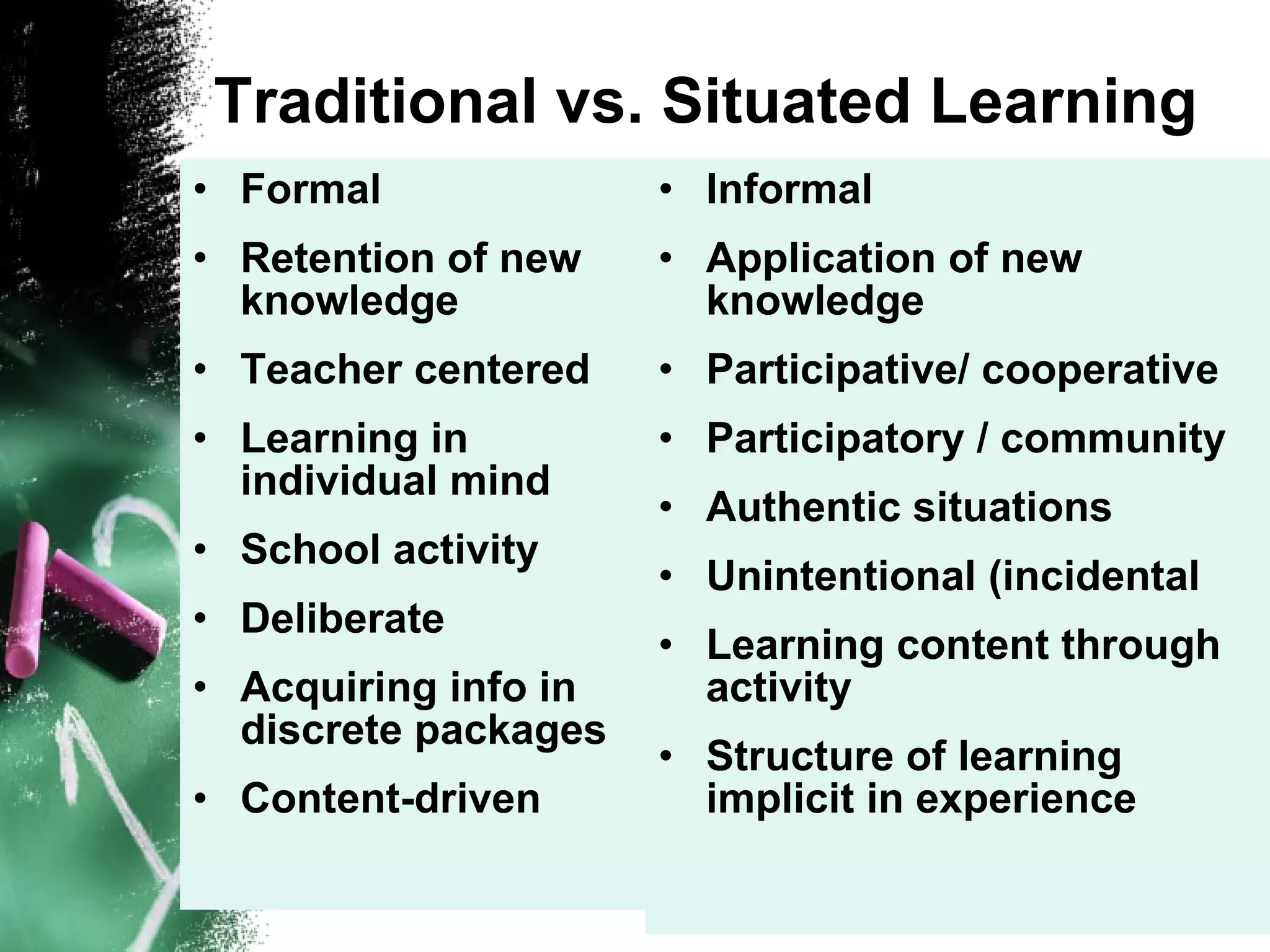

The document discusses situated learning and communities of practice. Situated learning suggests that knowledge is acquired through everyday situations and transfers only to similar contexts. Learning is a social process that occurs through authentic activities rather than acquiring discrete facts. Traditional learning focuses on retention of new knowledge through a teacher-centered approach, while situated learning emphasizes applying knowledge through participation in a community of practice and learning the content embedded within real-world contexts and activities.







