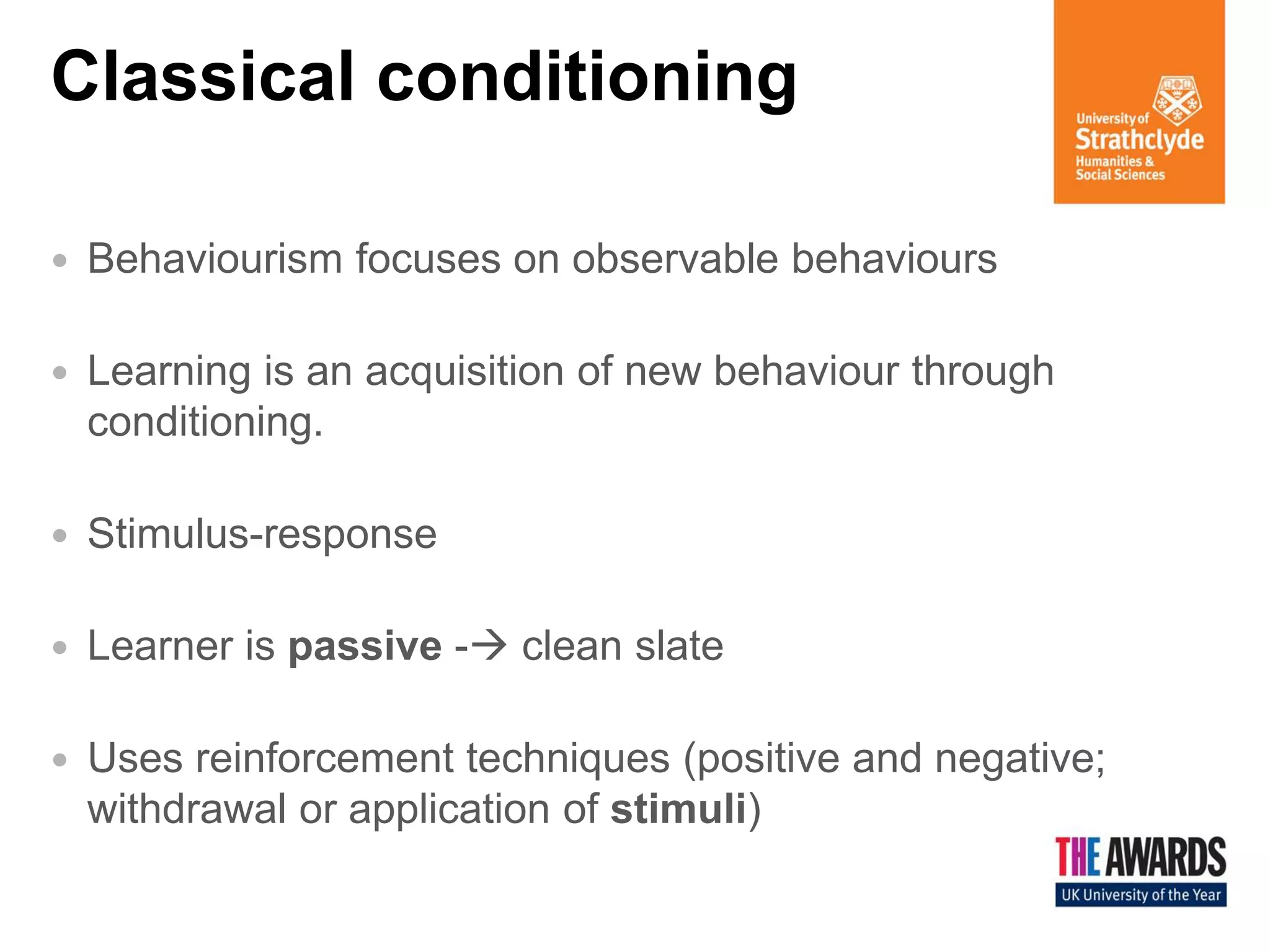
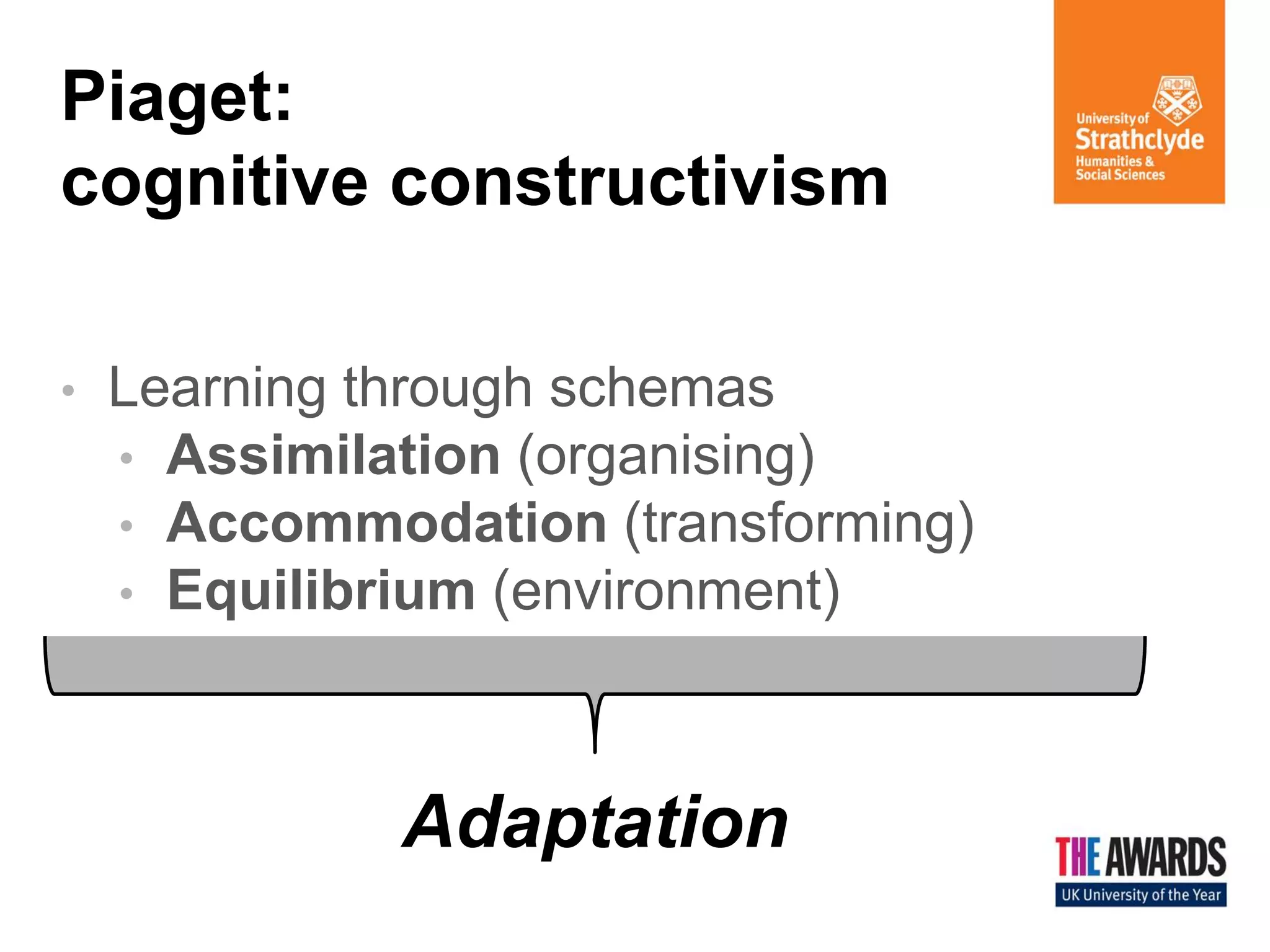
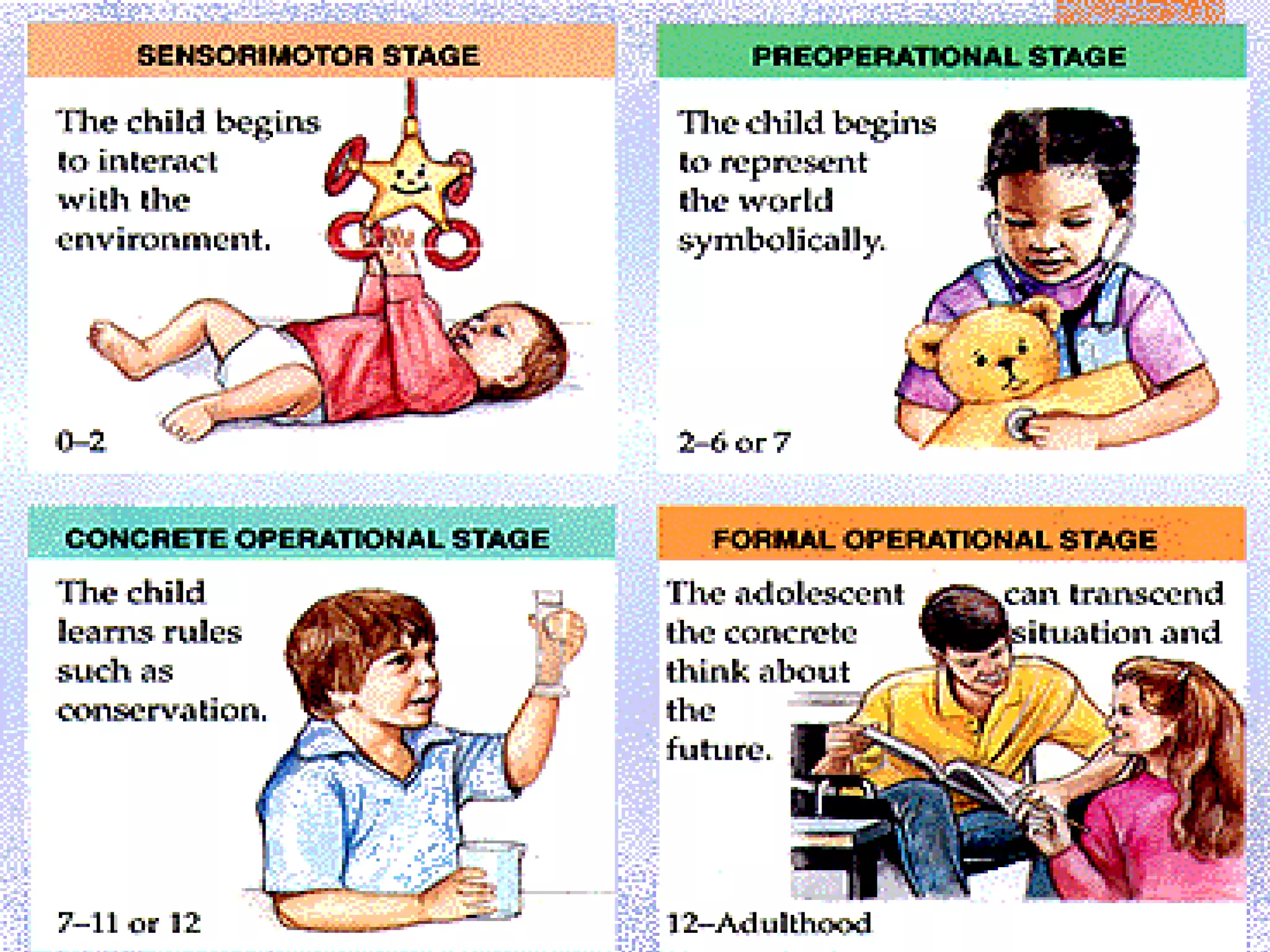
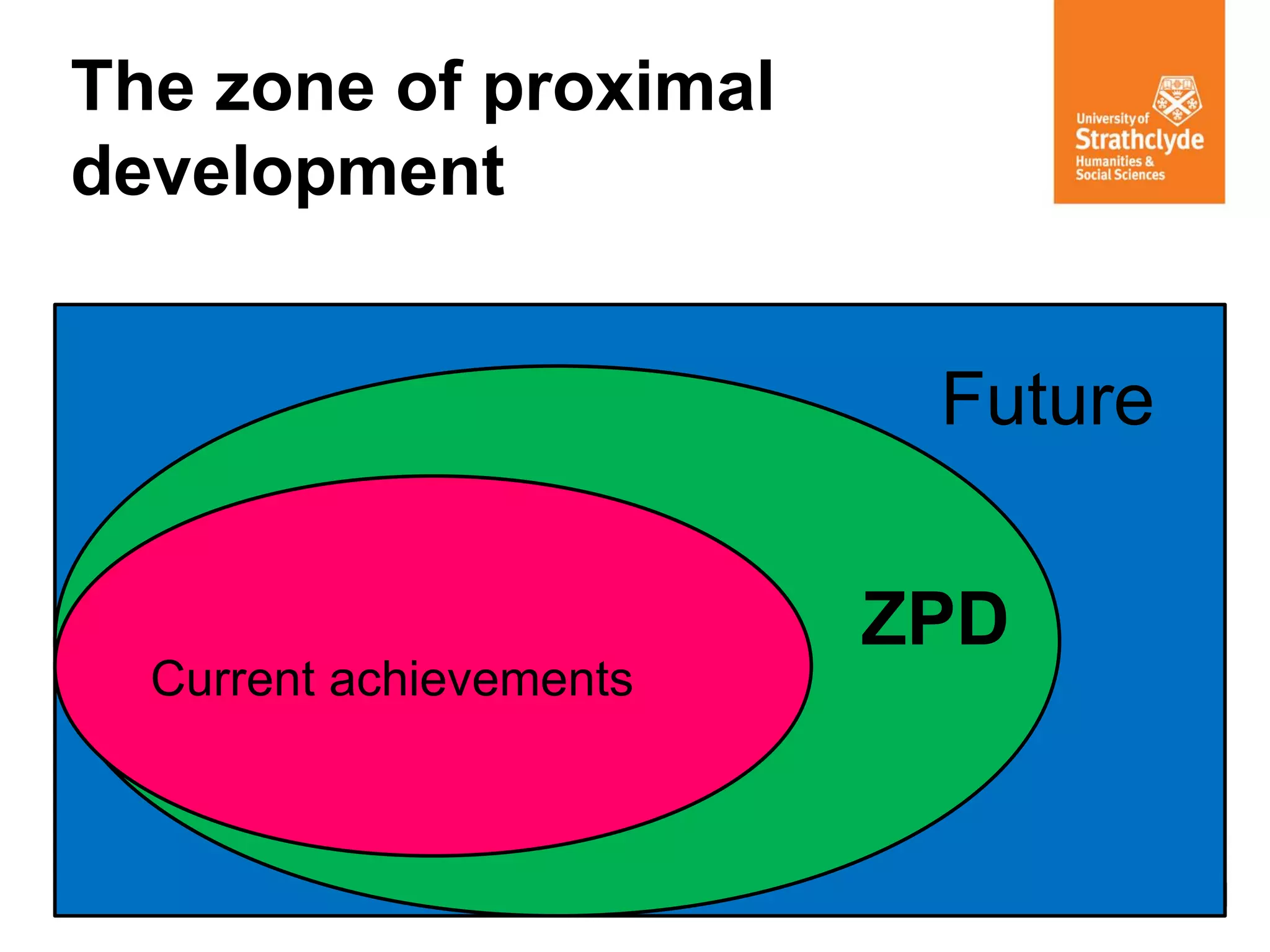
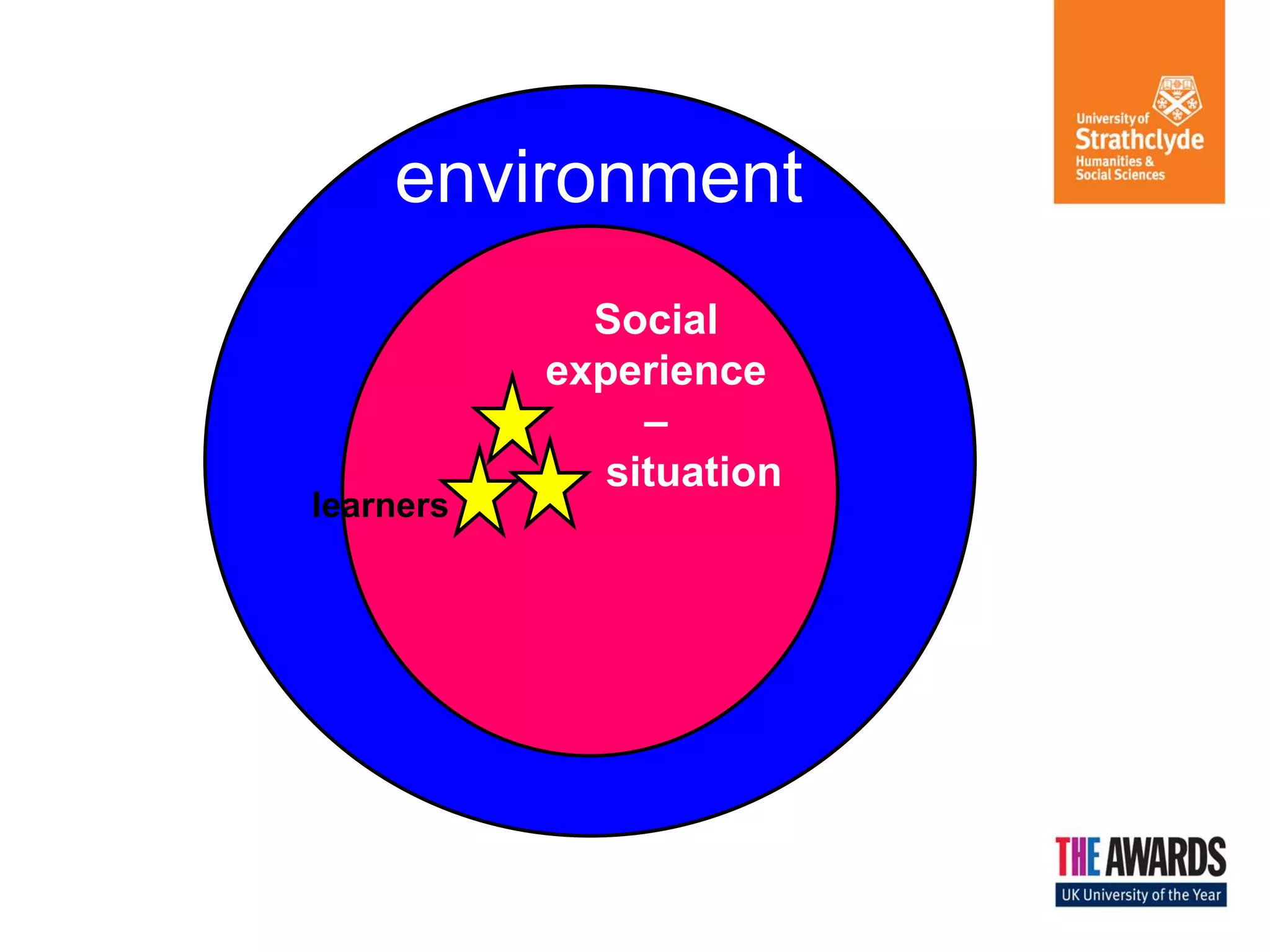
The document discusses various theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitive constructivism, and social constructivism. Behaviorism views learning as the acquisition of behaviors through conditioning and reinforcement, while cognitive constructivism sees learning as an active process of constructing knowledge based on experiences. Social constructivism, influenced by Vygotsky, emphasizes that social and cultural contexts are essential for learning and cognitive development, and that learning occurs through social interactions. The zone of proximal development and communities of practice are also discussed as frameworks for understanding learning.